Question
You collect unadjusted, quarterly data on nominal wages, unemployment, and prices in the United States from 1940 through 2011 from the United States Bureau of
You collect unadjusted, quarterly data on nominal wages, unemployment, and prices in the United States from 1940 through 2011 from the United States Bureau of Labor and Statistics. Wages are the median wage in the United States in each quarter, the unemployment rate is reported for each quarter, and the price is an index based on the Consumer Price Index in each quarter.
1. Can we use the data as is to run a reliable regression of the unemployment rate on wages? Why or why not, and is there any way we could transform the data into something more reliable?
2. You next decide to further examine the relationship between wages and prices over this time period. You run a regression of In(wage) on price and lagged price and obtain the following results (standard errors in parentheses):
ln(wage) it = 0.576 + 0.041*price it – 0.0224*price it-1 + 0.016*price it-2 – 0.029*price it-3 + µit
(0.013) (0.01) (0.008) (0.019) (0.01)
N = 284, R2 = 0.958
What is the temporary and permanent impact of an increase in prices on wages based on these results? How would we test if the permanent impact of a price change is statistically significant?3. j Can we say that this model has a strong goodness-of-fit using the information from part 8? Why or why not?
4. Do you believe that prices and wages in your model are covariance stationery? Why or why not, and how could you adjust your model accordingly?
5. Suppose you are concerned about Ma) serial correlation in your model. How would AR(2) serial correlation affect your estimates from part B?
6. After examining your model, you believe that you have no endogeneity problem with your independent variables. How can you test for the possibility of AR(2) serial correlation? What changes can you make to your estimation to correct for any potential serial correlation?
7. You now decide to run another model with the goal of examining how wages have fluctuated during this period.
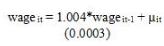 How would you characterize this model given what we have learned about time series)
How would you characterize this model given what we have learned about time series)
8. Why might we be concerned about the possibility of serial correlation given the model as specified In parts G and H?
9. You believe that your model from part H has an endogeneity problem. What changes can you make to your estimation to correct for any potential serial correlation?
10. Suppose that you are worried that your model from part H might have a heteroskedasticity problem. What are the two forms of heteroskedasticity we might be worried about in a time series regression, and how can we test for their presence in our model above?
wage it = 1.004*wageit-1 + Hit (0.0003)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 a The data provided can be used to run a reliable regression b The reason being that the data have been taken from the quarterly data that can be sa...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
609831d938d9b_28601.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
609831d938d9b_28601.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


