Question
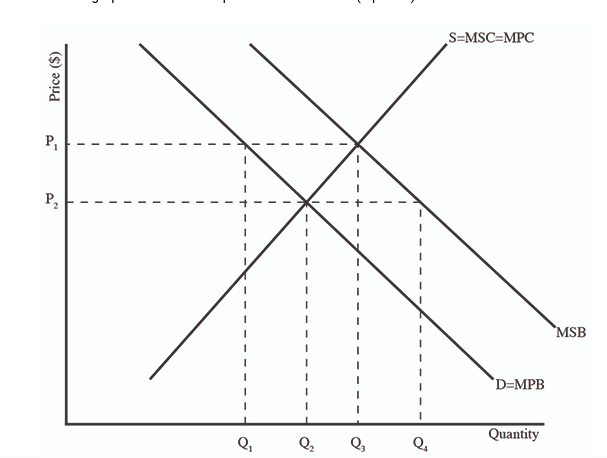
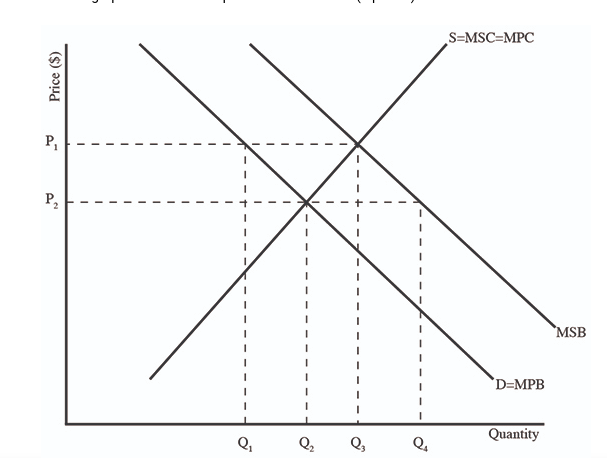
1. (06.01 MC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) Which of the following identifies the socially optimal output and price
1.
(06.01 MC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) Which of the following identifies the socially optimal output and price level?
| P1and Q1 | |
| P1and Q3 | |
| P2and Q2 | |
| P2and Q3 | |
| P2and Q4 |
2.
(06.01 MC) Which of the following scenarios could describe a market experiencing a negative production externality? (3 points)
| Optimal social quantity will be less than the private unregulated quantity, and the optimal social price will be greater than the private price. | |
| Optimal social quantity will equal private quantity, and social price will equal private price. | |
| Optimal social quantity will be less than the private unregulated quantity, and social price will be less than private price. | |
| Optimal social quantity will be greater than the private unregulated quantity, and social price will be less than private price. | |
| Optimal social quantity will be greater than the private unregulated quantity, and social price will be greater than private price. |
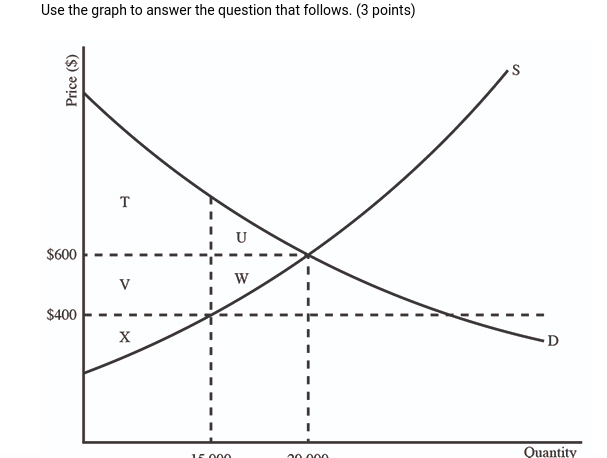
3.
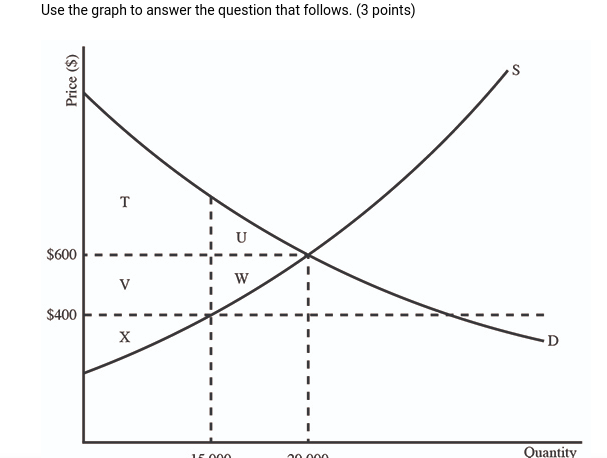
(06.01 MC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) Assume that the market shown is perfectly competitive with no externalities. If the production output is 15,000 units, then the market is
| inefficient, with a total economic surplus of T + X | |
| inefficient, and producer surplus is X | |
| efficient, and deadweight loss is being maximized | |
| efficient, with a consumer surplus of T V | |
| efficient, and consumer and producer surplus are maximized |
4.
(06.02 MC) Which of the following could lead to an externality? (3 points)
| Increased competition | |
| Regulation of production or consumption | |
| Minimal or zero transaction costs | |
| Perfectly symmetric information | |
| Unclear property rights |
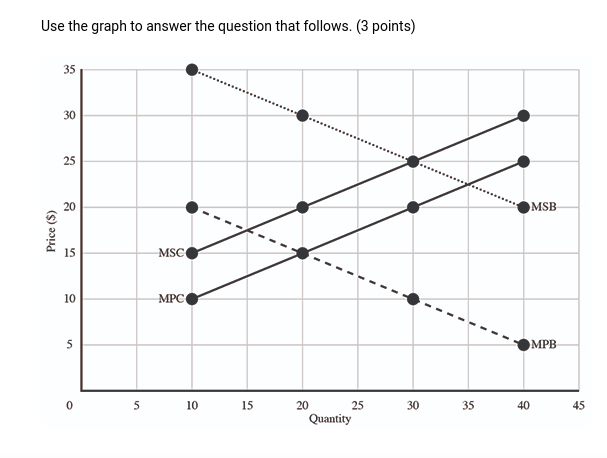
5.
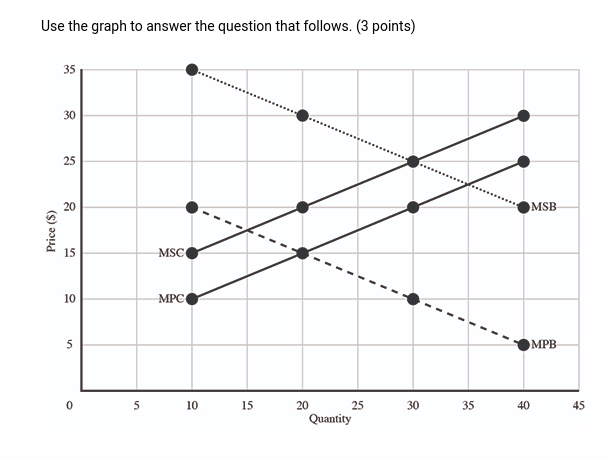
(06.02 HC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) Assuming there is no government regulation, which of the following makes a true statement about this market?
| The market output and price levels are higher than the allocatively efficient output and price levels. | |
| The market output and price levels are lower than the allocatively efficient output and price levels. | |
| The market output is higher than the allocatively efficient output, while the market price is lower than the allocatively efficient price. | |
| The market output is lower than the allocatively efficient output, while the market price level is higher than the allocatively efficient price level. | |
| There is insufficient data to make any evaluation of price and output levels in this market. |
6.
(06.02 MC) Advanced research is considered under-produced by the private market. This is thought to be due to the lack of incentives for such research. Which of the following could most practically correct for this? (3 points)
| Private provision | |
| Environmental deregulation | |
| Lump-sum tax | |
| Per-unit subsidy | |
| Ensure property rights are not transferable |
7.
(06.03 MC) Which of the following scenarios best exemplifies an excludable and rivalrous good? (3 points)
| An uncongested river in a state where people can fish | |
| A wireless internet service without a password | |
| A public radio broadcast | |
| An online newspaper requiring a subscription | |
| A pair of shoes made by a popular name brand |
8.
(06.03 MC) A bicycle taxi in the historic district of a city has room for one seat, available for anyone to rent. What type of good best describes this taxi seat? (3 points)
| Public good | |
| Private good | |
| Survival good | |
| Artificially scarce good | |
| Common pool resource |
9.
(06.03 MC) Why do private businesses underproduce public goods? (3 points)
| They are non-excludable, and so it is difficult to earn profits by producing the good. | |
| They are rivalrous, and so only one producer can supply the good. | |
| They are excludable, and so there are too few consumers available to buy the good. | |
| They are non-rivalrous, and so market power will limit output of the good. | |
| They are non-affordable, and so there are no consumers willing to purchase the good. |
10.
(06.04 MC) A per-unit tax on a good with relatively elastic supply will result in (3 points)
| more deadweight loss than if demand were elastic | |
| a higher tax burden on consumers than on producers | |
| less tax revenue than if demand were elastic | |
| a lower tax burden on consumers than on producers | |
| a tax burden that is equally distributed between consumers and producers |
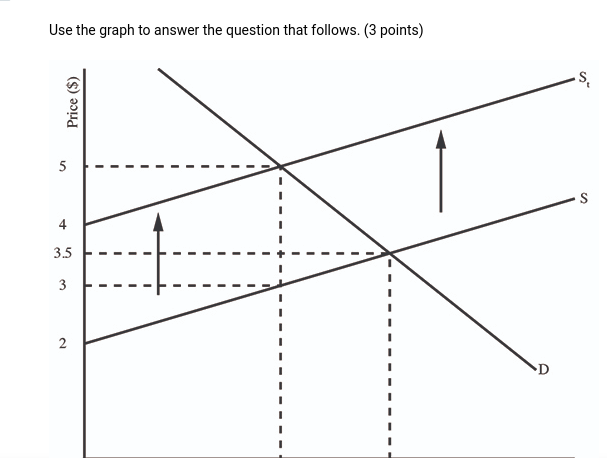
11.
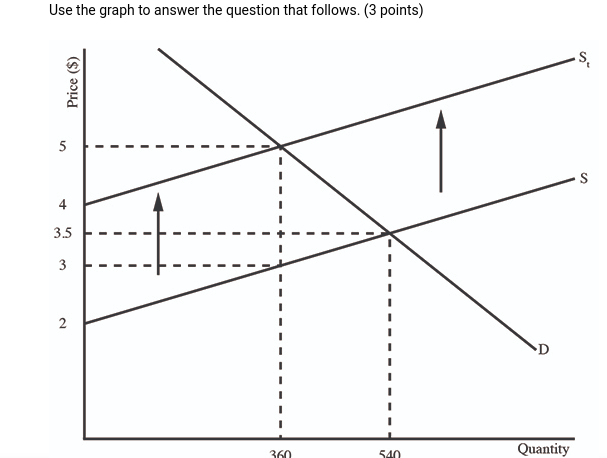
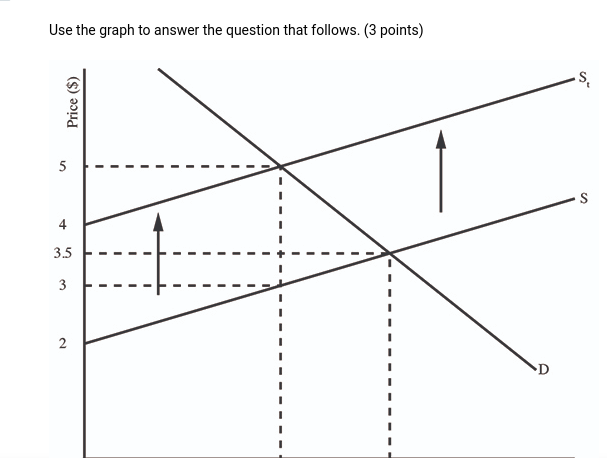
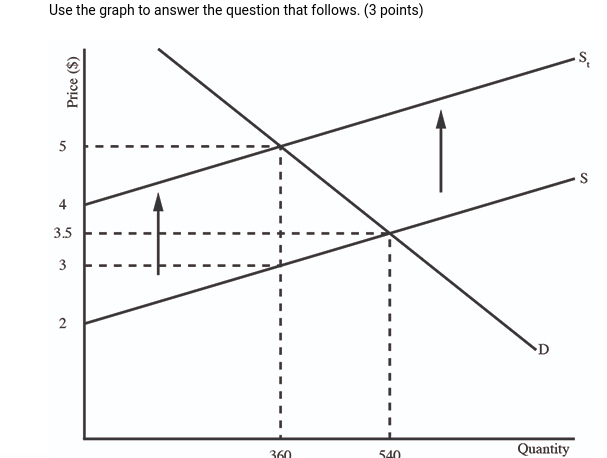
(06.04 MC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) What is the producers' total revenue after the tax in this market?
| $180 | |
| $720 | |
| $1080 | |
| $1620 | |
| $1890 |
12.
(06.04 MC) Which of the following is the most common government response to a classic monopoly's tendency to produce less output at a higher cost than the socially optimal quantity? (3 points)
| A per-unit subsidy | |
| A patent | |
| A price floor | |
| Antitrust legislation | |
| A per-unit tax |
13.
(06.04 MC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) What is the value of the producer surplus after the tax in this market?
| $90 | |
| $180 | |
| $360 | |
| $540 | |
| $720 |
14.
(06.05 MC) If Country M has greater income inequality than Country H, which of the following must be true? (3 points)
| Country M will have a higher population than Country H. | |
| Country M will have a lower population than Country H. | |
| Country M will have a higher Gini coefficient than Country H. | |
| Country M will have a lower Gini coefficient than Country H. | |
| Country M will have more people in poverty than Country H. |
15.
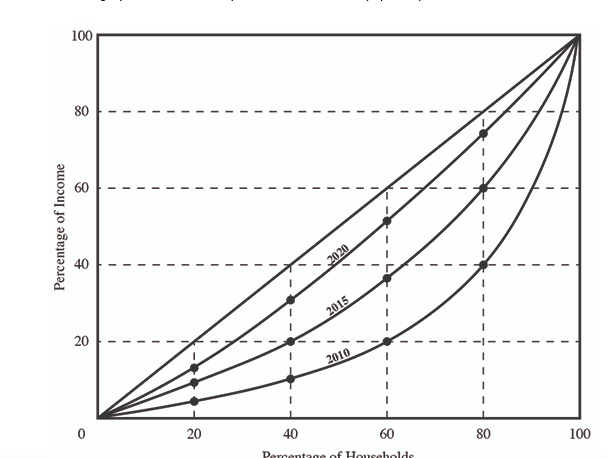
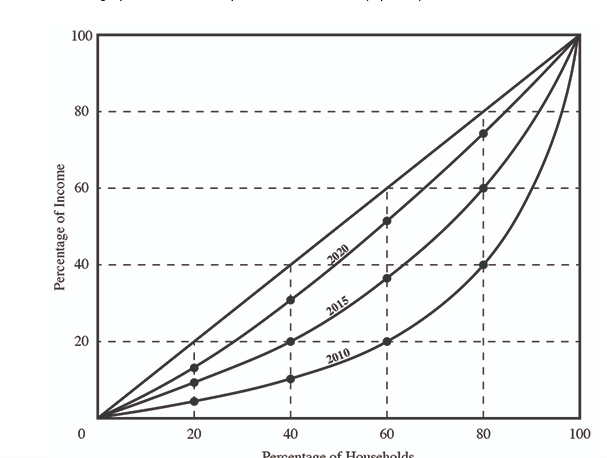
(06.05 MC) Use the graph to answer the question that follows. (3 points) In 2020, ________ of the households earned ________ of the income in this economy.
| 20 percent; 40 percent | |
| 40 percent; 80 percent | |
| 40 percent; 30 percent | |
| 60 percent; 80 percent | |
| 80 percent; 40 percent |
16.
(06.05 MC) Which of the following is a reason for increased income inequality? (3 points)
| There is a decrease in the productive capacity of capital so that wages and salaries are instead paid to an improving labor force. | |
| Taxes on earnings are collected each year, and the amount per worker is based on a progressive calculation. | |
| Market wages are rising, and so the unemployed are incentivized to find a job. | |
| The structure of the labor union is reorganized such that their bargaining power is increased significantly. | |
| Incentives for providing higher education and passing on family wealth are high enough to limit access. |
PREVIOUS
Graphs
1.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


