1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
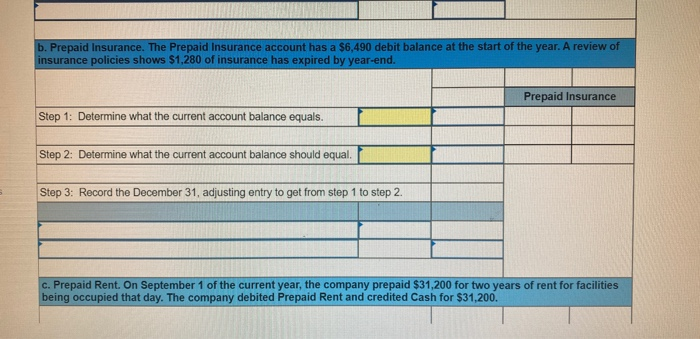
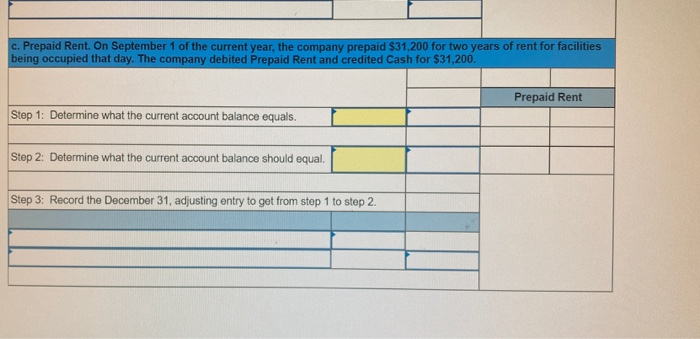
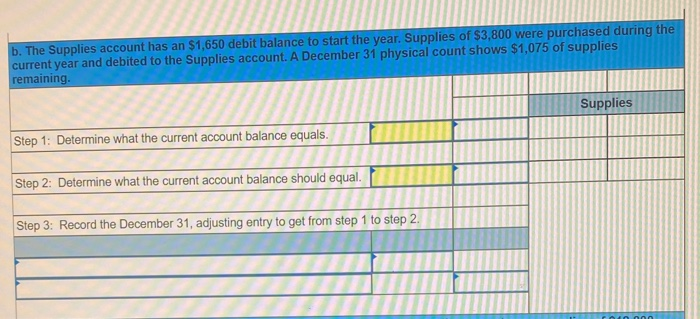
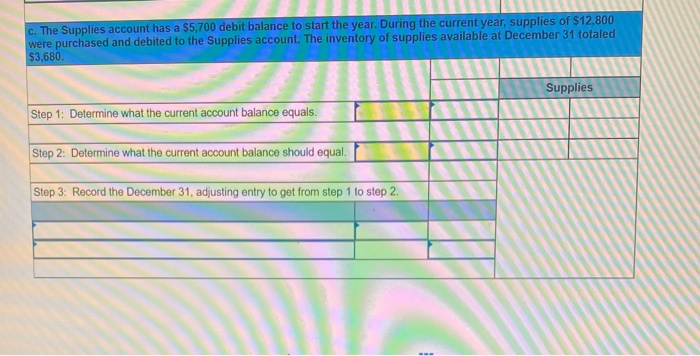
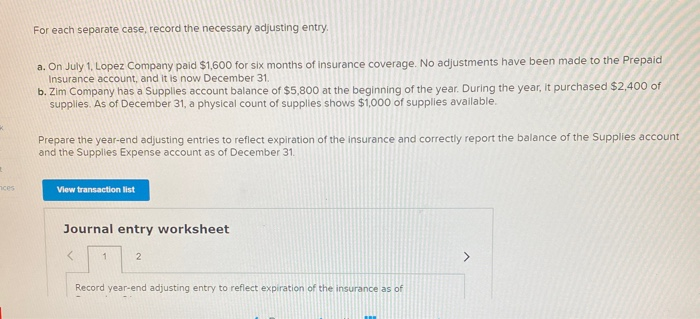
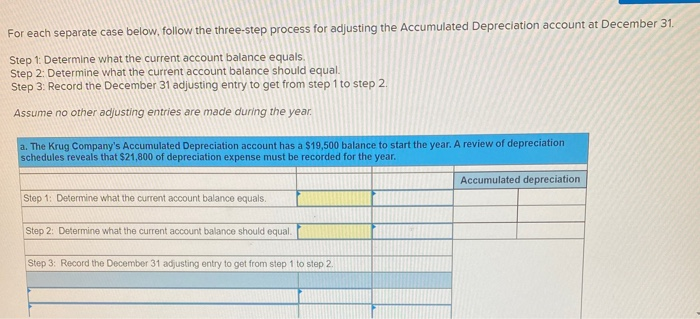
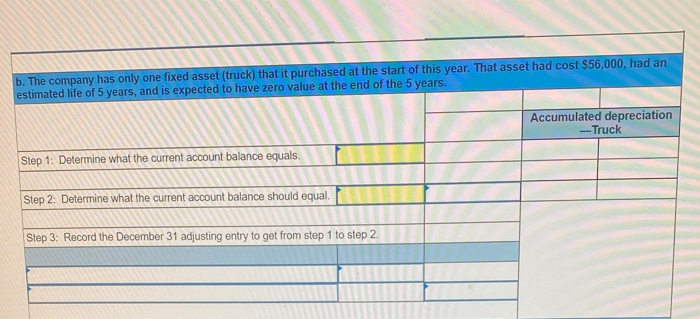
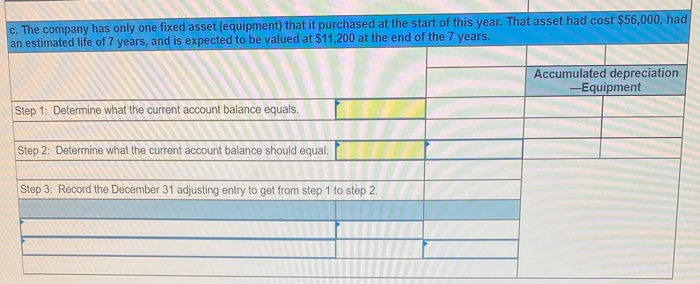
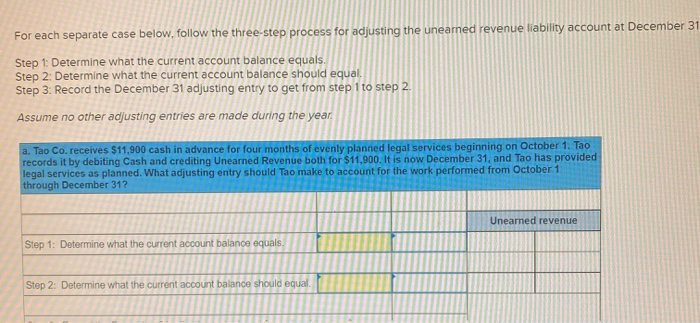
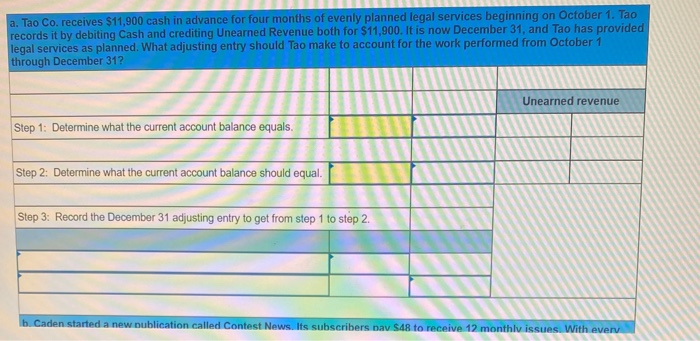
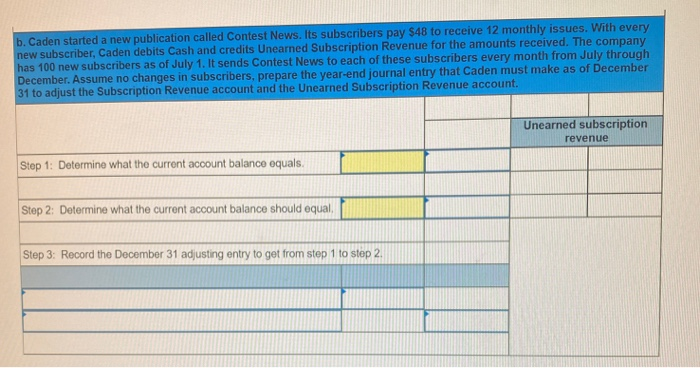
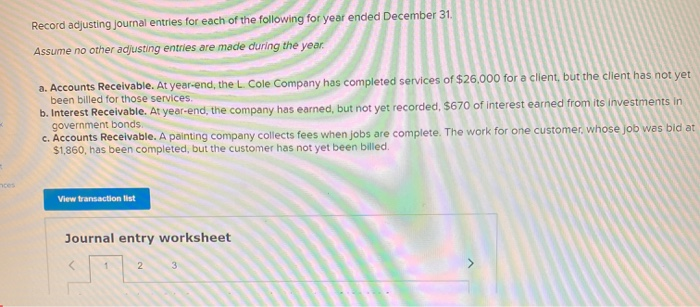
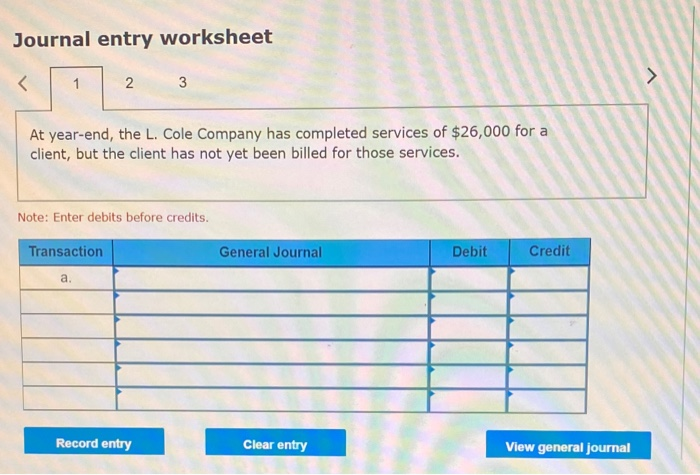
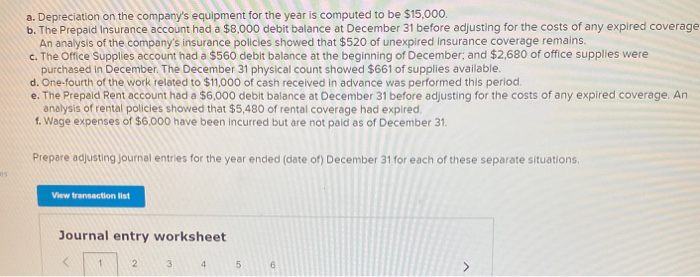
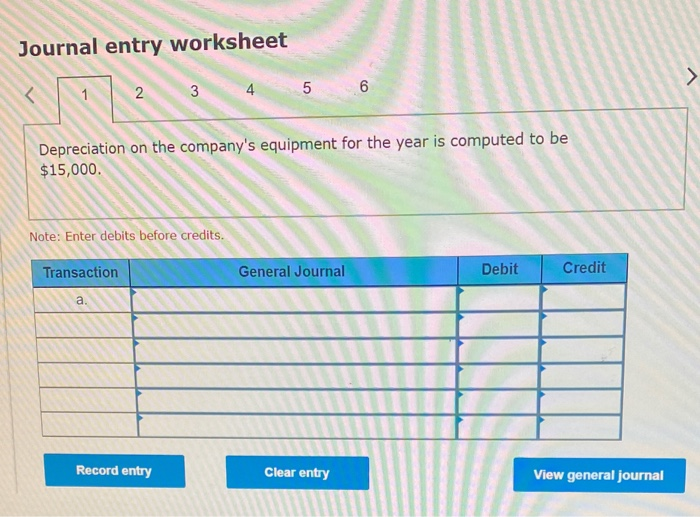
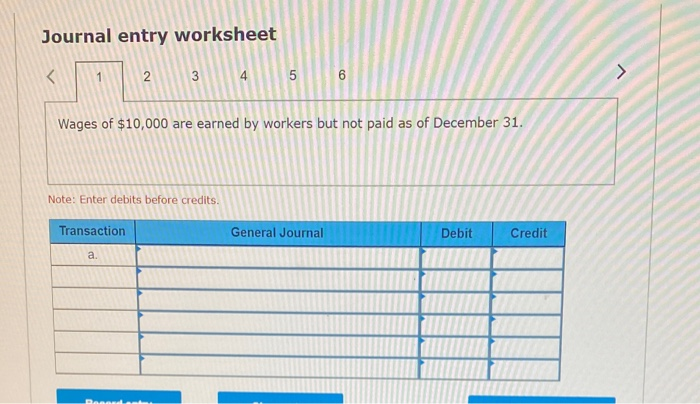
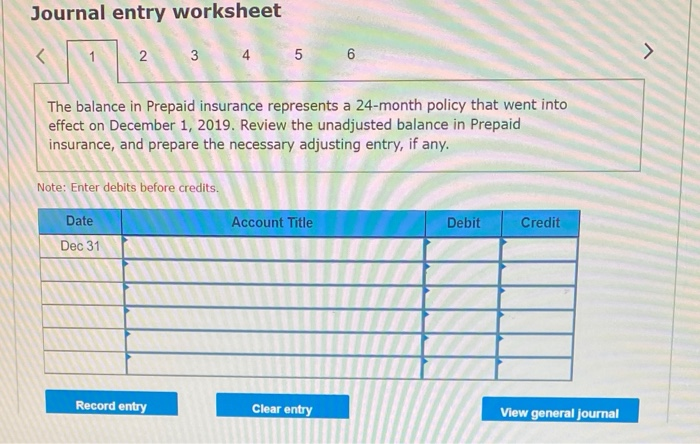
In its first year of operations, Roma Company reports the following Earned revenues of $51,000 ($43,000 cash received from customers). Incurred expenses of $28,500 ($22,350 cash paid toward them). Prepaid $8,250 cash for costs that will not be expensed until next year. Compute the company's first-year net income under both the cash basis and the accrual basis of accounting Cash Basis Accrual Basis Revenues Expenses Net income For each separate case below, follow the three-step process for adjusting the prepaid asset account at December 31. Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2 Assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year a. Prepaid Insurance. The Prepaid Insurance account has a $5,300 debit balance to start the year. A review of insurance policies shows that $1.200 of unexpired insurance remains at year-end. Prepaid Insurance Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31, adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. b. Prepaid Insurance. The Prepaid Insurance account has a $6,490 debit balance at the start of the year. A review of insurance policies shows $1,280 of insurance has expired by year-end. Prepaid Insurance Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31, adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. c. Prepaid Rent. On September 1 of the current year, the company prepaid $31,200 for two years of rent for facilities being occupied that day. The company debited Prepaid Rent and credited Cash for $31,200. c. Prepaid Rent. On September 1 of the current year, the company prepaid $31,200 for two years of rent for facilities being occupied that day. The company debited Prepaid Rent and credited Cash for $31,200. Prepaid Rent Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31, adjusting entry to get from stop 1 to step 2. Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. Assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year. a. The Supplies account has a $640 debit balance to start the year. No supplies were purchased during the current year. A December 31 physical count shows $280 of supplies remaining, Supplies Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal Step 3: Record the December 31, adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2 b. The Supplies account has an $1,650 debit balance to start the year. Supplies of $3,800 were purchased during the current year and debited to the Supplies account. A December 31 physical count shows $1,075 of supplies remaining Supplies Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal Step 3: Record the December 31, adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. c. The Supplies account has a $5,700 debit balance to start the year. During the current year, supplies of $12,800 were purchased and debited to the Supplies account. The inventory of supplies available at December 31 totaled $3,680. Wm S upplies Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31, adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. For each separate case, record the necessary adjusting entry a. On July 1, Lopez Company paid $1,600 for six months of insurance coverage. No adjustments have been made to the Prepaid Insurance account, and it is now December 31. b. Zim Company has a Supplies account balance of $5,800 at the beginning of the year. During the year, it purchased $2,400 of supplies. As of December 31, a physical count of supplies shows $1,000 of supplies available Prepare the year-end adjusting entries to reflect expiration of the insurance and correctly report the balance of the Supplies account and the Supplies Expense account as of December 31. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Record year-end adjusting entry to reflect expiration of the insurance as of Journal entry worksheet Record year-end adjusting entry to reflect expiration of the insurance as of December 31. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit For each separate case below, follow the three-step process for adjusting the Accumulated Depreciation account at December 31. Step t Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3. Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2 Assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year a. The Krug Company's Accumulated Depreciation account has a $19,500 balance to start the year. A review of depreciation schedules reveals that $21,800 of depreciation expense must be recorded for the year. Accumulated depreciation Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from stop 1 to step 2 b. The company has only one fixed asset (truck) that it purchased at the start of this year. That asset had cost $56,000, had an estimated life of 5 years, and is expected to have zero value at the end of the 5 years. Accumulated depreciation -Truck Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2 c. The company has only one fixed asset (equipment) that it purchased at the start of this year. That asset had cost $56,000, had an estimated life of 7 years, and is expected to be valued at $11,200 at the end of the 7 years Accumulated depreciation -Equipment Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. Record adjusting journal entries for each of the following for year ended December 31. Assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year a. Unearned Rent Revenue. The Krug Company collected $9,000 rent in advance on November 1, debiting Cash and crediting Unearned Rent Revenue. The tenant was paying 12 months' rent in advance and occupancy began November 1 b. Unearned Services Revenue. The company charges $100 per insect treatment. A customer paid $400 on October 1 in advance for four treatments, which was recorded with a debit to Cash and a credit to Unearned Services Revenue. At year-end, the company has applied three treatments for the customer c. Unearned Rent Revenue. On September 1, a client paid the company $30,000 cash for six months of rent in advance (the client leased a building and took occupancy Immediately). The company recorded the cash as Unearned Rent Revenue. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet THIC Ruy Lumpany LUCULLU 9,000 ICI Cash and crediting Unearned Rent Revenue. The tenant was paying 12 months' rent in advance and occupancy began November 1. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal D ebit Credit NAM Record entry Clear entry View general journal For each separate case below, follow the three-step process for adjusting the unearned revenue liability account at December 31 Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal Step 3. Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step Assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year a. Tao Co. receives $11,000 cash in advance for four months of evenly planned legal services beginning on October 1. Tao records it by debiting Cash and crediting Unearned Revenue both for $11.900. It is now December 31, and Tao has provided legal services as planned. What adjusting entry should Tao make to account for the work performed from October 1 through December 31? Uneamed revenue Step 1: Determine what the current account ba Step 2: Determine what the current account bala a. Tao Co. receives $11,900 cash in advance for four months of evenly planned legal services beginning on October 1. Tao records it by debiting Cash and crediting Unearned Revenue both for $11.900. It is now December 31, and Tao has provided legal services as planned. What adjusting entry should Tao make to account for the work performed from October 1 through December 31? Unearned revenue Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal. Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. b. Caden started a new Dublication called Contest News. Its subscribers nav 548 to receive 12 monthly issues with every b. Caden started a new publication called Contest News. Its subscribers pay $48 to receive 12 monthly issues. With every new subscriber, Caden debits Cash and credits Unearned Subscription Revenue for the amounts received. The company has 100 new subscribers as of July 1. It sends Contest News to each of these subscribers every month from July through December. Assume no changes in subscribers, prepare the year-end journal entry that Caden must make as of December 31 to adjust the Subscription Revenue account and the Unearned Subscription Revenue account. Unearned subscription revenue Step 1: Determine what the current account balance equals. Step 2: Determine what the current account balance should equal Step 3: Record the December 31 adjusting entry to get from step 1 to step 2. Record adjusting journal entries for each of the following for year ended December 31 Assume no other adjusting entries are made during the year. a. Accounts Receivable. At year-end, the L. Cole Company has completed services of $26,000 for a client, but the client has not yet been billed for those services b. Interest Receivable. At year-end, the company has earned, but not yet recorded, $670 of interest earned from its investments in government bonds c. Accounts Receivable. A painting company collects fees when jobs are complete. The work for one customer, whose job was bid at $1,860, has been completed, but the customer has not yet been billed. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Journal entry worksheet 2 3 At year-end, the L. Cole Company has completed services of $26,000 for a client, but the client has not yet been billed for those services. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit Record entry Clear entry View general journal a. Depreciation on the company's equipment for the year is computed to be $15,000. b. The Prepaid Insurance account had a $8,000 debit balance at December 31 before adjusting for the costs of any expired coverage An analysis of the company's insurance policies showed that $520 of unexpired insurance coverage remains. c. The Office Supplies account had a $560 debit balance at the beginning of December, and $2,680 of office supplies were purchased in December. The December 31 physical count showed $661 of supplies available. d. One-fourth of the work related to $11,000 of cash received in advance was performed this period e. The Prepaid Rent account had a $6,000 debit balance at December 31 before adjusting for the costs of any expired coverage. An analysis of rental policies showed that $5,480 of rental coverage had expired. f. Wage expenses of $6,000 have been incurred but are not paid as of December 31 Prepare adjusting journal entries for the year ended (date of) December 31 for each of these separate situations, View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Journal entry worksheet 5 Depreciation on the company's equipment for the year is computed to be $15,000. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit Record entry Clear entry View general journal a. Wages of $10,000 are earned by workers but not paid as of December 31. b. Depreciation on the company's equipment for the year is $11,680. C. The Office Supplies account had a $380 debit balance at the beginning of December. During December, $5,705 of office supplies are purchased. A physical count of supplies at December 31 shows $621 of supplies available. d. The Prepaid Insurance account had a $5,000 balance at the beginning of December. An analysis of insurance policies shows that $2,500 of unexpired insurance benefits remain at December 31 e. The company has earned (but not recorded) $750 of interest revenue for the year ended December 31. The interest payment will be received on 10 days after the year-end January 10. f. The company has a bank loan and has incurred (but not recorded) interest expense of $2,500 for the year ended December 31. The company will pay the interest five days after the year-end on January 5. For each of the above separate cases, prepare adjusting entries required of financial statements for the year ended (date of) December 31 Journal entry worksheet Wages of $10,000 are earned by workers but not paid as of December 31. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit The unadjusted trial balance of the Green Initiatives Company as of December 31, 2019 is found on the trial balance tab. The following information is required to prepare the necessary adjusting entries for the Green Initiatives Company 1) The balance in Prepaid insurance represents a 24-month policy that went into effect on December 1, 2019. Review the unadjusted balance in Prepaid insurance, and prepare the necessary adjusting entry, if any. 2) Based on a physical count, supplies on hand total $4,350. Review the unadjusted balance in Supplies, and prepare the necessary adjusting entry, if any. 3) The equipment is expected to have a 5-year useful life, and be worth about $12,000 at the end of five years. Review the unadjusted balance in Accumulated depreciation, and prepare the necessary adjusting entry to record the monthly depreciation, if any, 4) On December 26, the client paid a $7,800 60-day fee in advance, covering December 27 to February 24. Review the unadjusted balance in Unearned Consulting Revenue, and prepare the necessary adjusting entry, if any. 5) Green Initiatives's employee earns $100 per day for a five-day workweek beginning on Monday and ending on Friday. The employee was last paid on Friday, December 26. Review the unadjusted balance in Salaries expense, and prepare the necessary adjusting entry, if any. 6) In the second week of December, Green Initiatives agreed to provide 30 days of consulting services to a local fitness club for a fixed fee of $4,620. The terms of the initial agreement call for Green Initiatives to provide services from December 12, 2019, through January 10, 2020, or 30 days of service. The club agrees to pay Green Initiatives $4,620 on January 10, 2020, when the service period is complete. Review the unadjusted balance in Consulting revenue, and prepare the necessary adjusting entry, if any Journal entry worksheet