Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. (25 points) You have the opportunity to purchase a triplex rental property. You expect this property to generate $108,000 in rent one year

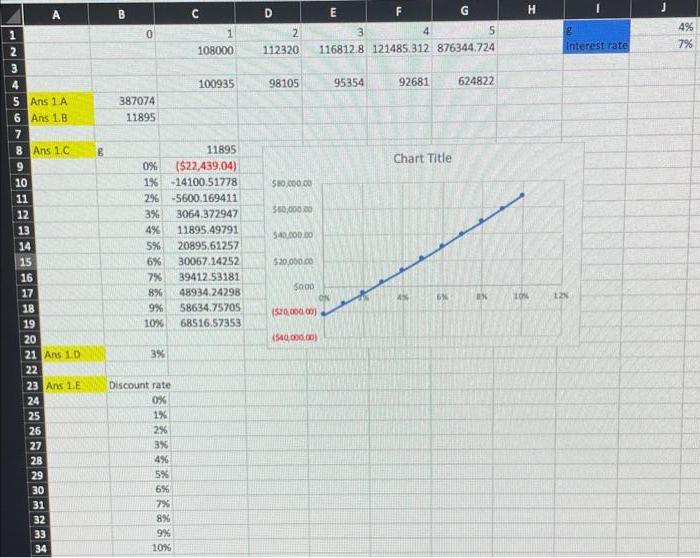
1. (25 points) You have the opportunity to purchase a triplex rental property. You expect this property to generate $108,000 in rent one year from now and for rent to increase at 4% per year for the following four years. Five years from now, you believe you will be able to sell the property for $750,000. Assume the interest rate is 7% per year. a. How much should you be willing to pay today for this property? b. If you can buy the property for $1,000,000 what is the NPV of this opportunity? c. Acknowledging that the dollar values above are in the future (and therefore are estimates) explore what the NPV would be if your assumptions about growth are wrong. Using a Data Table ("Data tab -> What-if analysis -> Data Table"), calculate the NPV for values of g between 0% and 10% (NPV @g=0%, NPV @ g=1% etc.) Plot your results in a connected (the dots are connected) scatter plot. d. At what value of g is the NPV = 0? (Hint: use Goal Seek, found in "Data tab -> What-if analysis -> Goal Seek"). Logic check your value against the scatter plot you just created. Record your answer as a hard-coded value and reset g to 4% before moving on. e. Repeat your analysis from the last two questions, but now change the interest rate (discount rate). Evaluate the NPV for all values of r between 0% and 10%. Plot the results in a connected scatter plot. This is called an NPV profile. f. At what value of r is the NPV = 0? This is called the Internal Rate of Return (IRR). Logic check your value against the scatter plot you created. g. Now use a two-way Data Table to simultaneously evaluate NPV at all values of g between 0% and 10% AND all values of r between 0% and 10%. (you should have a 10x10 matrix). Highlight cells where NPV is negative (hint: try using conditional formatting on the Home tab). 223 1 4 5 Ans 1 A 6 Ans 1.B 7 8 Ans 1.C 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 A 20 21 Ans 1.0 22 23 Ans 1.E 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 B B 0 387074 11895 3% 11895 0% ($22,439.04) 1% -14100.51778 2% -5600.169411 Discount rate 0% 1% C 3% 3064.372947 4% 11895.49791 5% 20895.61257 6% 30067.14252 7% 39412.53181 8% 48934.24298 58634.75705 9% 10% 68516.57353 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 1 108000 7% 8% 9% 10% 100935 D 2 112320 98105 $80,000.00 550,000.00 540,000.00 $20,000.00 5000 (520,000,00) (540,000,00) E F 95354 3 116812.8 121485.312 876344.724 92681 Chart Title 45 G 6% 5 624822 IN H 10% Interest rate 12% 4% 7%
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.52 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


