Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. A portfolio has a total value of $160,000,000. The portfolio consists of $100,000,000 in US equity and $60,000,000 in European equity. The volatility
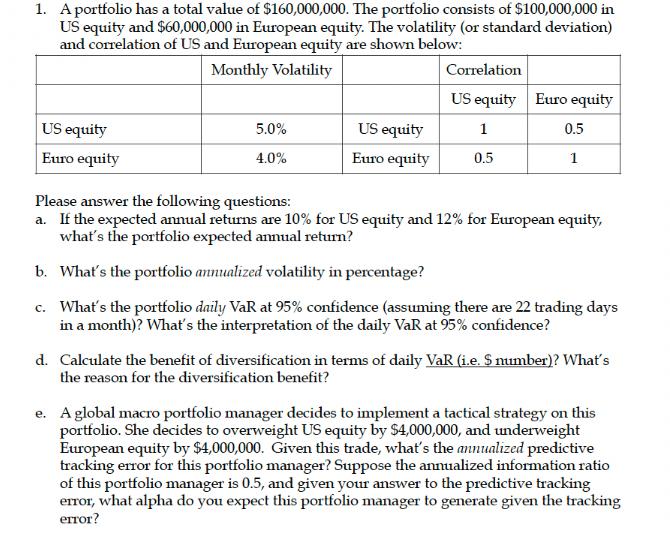


1. A portfolio has a total value of $160,000,000. The portfolio consists of $100,000,000 in US equity and $60,000,000 in European equity. The volatility (or standard deviation) and correlation of US and European equity are shown below: Monthly Volatility US equity Euro equity 5.0% 4.0% US equity Euro equity Correlation US equity 1 0.5 Euro equity 0.5 1 Please answer the following questions: a. If the expected annual returns are 10% for US equity and 12% for European equity, what's the portfolio expected annual return? b. What's the portfolio annualized volatility in percentage? c. What's the portfolio daily VaR at 95% confidence (assuming there are 22 trading days in a month)? What's the interpretation of the daily VaR at 95% confidence? d. Calculate the benefit of diversification in terms of daily VaR (i.e. S number)? What's the reason for the diversification benefit? e. A global macro portfolio manager decides to implement a tactical strategy on this portfolio. She decides to overweight US equity by $4,000,000, and underweight European equity by $4,000,000. Given this trade, what's the annualized predictive tracking error for this portfolio manager? Suppose the annualized information ratio of this portfolio manager is 0.5, and given your answer to the predictive tracking error, what alpha do you expect this portfolio manager to generate given the tracking error? 2. Suppose the geometric mean for Japanese Government Bond monthly return in a year is 1.75% and arithmetic mean is 2%. Suppose the Emerging market equity is twice as volatile as the Japanese bond in the same period. a. If the geometric mean for emerging market equity monthly return is 2% in a year, what's the arithmetic mean of the Emerging market equity monthly return in a year? 3. For the pension plan of a company XYZ, the strategic asset allocation is 60% in global equity and 35% in global fixed income and 5% in US cash. a. If the global equity market generates negative return and bond yield declines in the coming year, what will happen to the PBO funded ratio? Why? b. The pension plan sponsor of company XYZ wants to reduce the risk of the portfolio. His suggestion is to increase the cash allocation from 5% to 20% since cash is the "risk-free" asset. Considering cash as an asset and as an investment in a pension portfolio, do you agree with his suggestion? Why? c. The pension plan sponsor expects the asset return to be low and bond yield remains low in the future. Suppose the pension plan has a PBO funded ratio of 85% currently. In order to minimize the amount of corporate contribution to the pension plan and increase funded ratio, the pension plan sponsor is very interested in applying the Alpha Beta framework to his pension fund. Please provide your recommendation using Alpha/Beta investment framework. What should be the new asset allocation strategy? How much active risk should the pension plan take? Be specific and provide the rationale for your recommendation. d. In particular, the pension plan sponsor is considering investing in hedge fund. Do you think hedge fund is a good investment vehicle for the pension plan? Give a detailed discussion of hedge funds as an investment in pension plans. Be thorough in your answers. 4. An endowment Chief Investment Officer is considering investment ($100 million) with an active global equity manager. One candidate manager is a fundament driven stock picker (very similar to the China Fund manager that we have talked about in the class). The fundamental manager runs a strategy that has an alpha target of 5% and a track error target of 10%. The other candidate manager is a quantitatively driven active equity manager (very similar to GSAM case as we have discussed in the class). The quantitative manager has an alpha target of 2.5% and a tracking error target of 3.5%. The two managers' alpha streams historically have a correlation of 0.1. a. Please comment on the pros and cons of these two investment styles (fundamental vs. quantitative) for active equity management. b. How would you recommend the endowment CIO to structure her active global equity allocation ($100 million)? Specifically, should she hire one manager vs. another? Should she split her allocation between the two managers? If so, what's the split? Please provide detailed rationale for your recommendation. 1. A portfolio has a total value of $160,000,000. The portfolio consists of $100,000,000 in US equity and $60,000,000 in European equity. The volatility (or standard deviation) and correlation of US and European equity are shown below: Monthly Volatility US equity Euro equity 5.0% 4.0% US equity Euro equity Correlation US equity 1 0.5 Euro equity 0.5 1 Please answer the following questions: a. If the expected annual returns are 10% for US equity and 12% for European equity, what's the portfolio expected annual return? b. What's the portfolio annualized volatility in percentage? c. What's the portfolio daily VaR at 95% confidence (assuming there are 22 trading days in a month)? What's the interpretation of the daily VaR at 95% confidence? d. Calculate the benefit of diversification in terms of daily VaR (i.e. S number)? What's the reason for the diversification benefit? e. A global macro portfolio manager decides to implement a tactical strategy on this portfolio. She decides to overweight US equity by $4,000,000, and underweight European equity by $4,000,000. Given this trade, what's the annualized predictive tracking error for this portfolio manager? Suppose the annualized information ratio of this portfolio manager is 0.5, and given your answer to the predictive tracking error, what alpha do you expect this portfolio manager to generate given the tracking error? 2. Suppose the geometric mean for Japanese Government Bond monthly return in a year is 1.75% and arithmetic mean is 2%. Suppose the Emerging market equity is twice as volatile as the Japanese bond in the same period. a. If the geometric mean for emerging market equity monthly return is 2% in a year, what's the arithmetic mean of the Emerging market equity monthly return in a year? 3. For the pension plan of a company XYZ, the strategic asset allocation is 60% in global equity and 35% in global fixed income and 5% in US cash. a. If the global equity market generates negative return and bond yield declines in the coming year, what will happen to the PBO funded ratio? Why? b. The pension plan sponsor of company XYZ wants to reduce the risk of the portfolio. His suggestion is to increase the cash allocation from 5% to 20% since cash is the "risk-free" asset. Considering cash as an asset and as an investment in a pension portfolio, do you agree with his suggestion? Why? c. The pension plan sponsor expects the asset return to be low and bond yield remains low in the future. Suppose the pension plan has a PBO funded ratio of 85% currently. In order to minimize the amount of corporate contribution to the pension plan and increase funded ratio, the pension plan sponsor is very interested in applying the Alpha Beta framework to his pension fund. Please provide your recommendation using Alpha/Beta investment framework. What should be the new asset allocation strategy? How much active risk should the pension plan take? Be specific and provide the rationale for your recommendation. d. In particular, the pension plan sponsor is considering investing in hedge fund. Do you think hedge fund is a good investment vehicle for the pension plan? Give a detailed discussion of hedge funds as an investment in pension plans. Be thorough in your answers. 4. An endowment Chief Investment Officer is considering investment ($100 million) with an active global equity manager. One candidate manager is a fundament driven stock picker (very similar to the China Fund manager that we have talked about in the class). The fundamental manager runs a strategy that has an alpha target of 5% and a track error target of 10%. The other candidate manager is a quantitatively driven active equity manager (very similar to GSAM case as we have discussed in the class). The quantitative manager has an alpha target of 2.5% and a tracking error target of 3.5%. The two managers' alpha streams historically have a correlation of 0.1. a. Please comment on the pros and cons of these two investment styles (fundamental vs. quantitative) for active equity management. b. How would you recommend the endowment CIO to structure her active global equity allocation ($100 million)? Specifically, should she hire one manager vs. another? Should she split her allocation between the two managers? If so, what's the split? Please provide detailed rationale for your recommendation.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.34 Rating (148 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Lets address each question one by one Portfolio Analysis a To find the portfolios expected annual return you can use a weighted average of the expected returns for US and European equity Portfolio Exp...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


