1. Air flows through the venturi shown in the figure. At the neck of the venturi the air flow accelerates and reaches its maximum
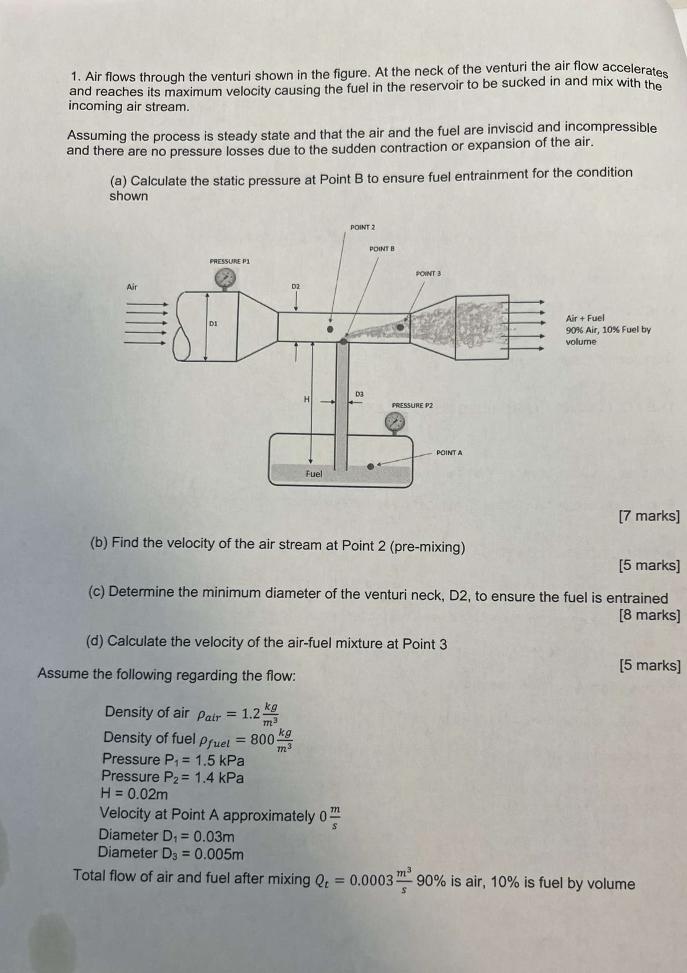
1. Air flows through the venturi shown in the figure. At the neck of the venturi the air flow accelerates and reaches its maximum velocity causing the fuel in the reservoir to be sucked in and mix with the incoming air stream. Assuming the process is steady state and that the air and the fuel are inviscid and incompressible and there are no pressure losses due to the sudden contraction or expansion of the air. (a) Calculate the static pressure at Point B to ensure fuel entrainment for the condition shown Air PRESSURE P Fuel Assume the following regarding the flow: POINT 2 Density of air Pair = 1.2 Density of fuel Pfuel = 800 Pressure P = 1.5 kPa Pressure P = 1.4 kPa m3 POINT B PICKS 03 POINT 3 (b) Find the velocity of the air stream at Point 2 (pre-mixing) PRESSURE P2 POINT A (d) Calculate the velocity of the air-fuel mixture at Point 3 [5 marks] (c) Determine the minimum diameter of the venturi neck, D2, to ensure the fuel is entrained [8 marks] Air + Fuel 90% Air, 10% Fuel by volume [7 marks] [5 marks] H = 0.02m Velocity at Point A approximately 0 Diameter D = 0.03m Diameter D3 = 0.005m Total flow of air and fuel after mixing Q = 0.0003 90% is air, 10% is fuel by volume
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


