Question
1. Compare and contrast the 3 basic types of derivatives used to hedge systematic riskthe advantages and disadvantages of each and the markets on which
1. Compare and contrast the 3 basic types of derivatives used to hedge systematic riskthe advantages and disadvantages of each and the markets on which they trade.
2. Suppose you have determined that your business has a long exposure to the price of oilwhen oil prices fall, so do your earnings (and vice versa). Under what circumstances might you hedge this risk? Why might you decide not to hedge this risk?
3. What is a real option? Where do they come from? From what sources do they derive their value? What do they tell you about a project that a simple discounted cash flow analysis does not? And what do real options have to do with risk management, anyway?
4. Suppose you work for Oil-Can, an independent oil exploration and development company. Oil-Can has just discovered an oil field with commercial potential. Given current crude oil prices, developing this field should be marginally profitable. If oil price volatility increases, would you delay or accelerate the project? Why?
5. What is the ART market? What are some of the factors that led to its rise?
6. Apart from self-insuring, what are the 3 most commonly used techniques in todays ART market? Briefly explain why each is so popular.
7. Consider the current hot concept in risk management, enterprise risk management (ERM). How are the concepts weve considered this semester used in an ERM program? What does ERM add to them?
Questions from a previous final
1. (32 points) The Chinese symbol for risk combines danger with opportunity. Modern corporate risk management seeks to manage both of these risks with the goal of maximizing firm value. What role does each of the following tools or concepts play in achieving this goal? (Please answer in broad terms only. For most tools or concepts, 2-3 sentences should be sufficient.)
i. Insurance
ii. Statistics / heat maps / Monte Carlo simulation
iii. Discounted cash flow method of firm valuation
iv. Derivatives
v. Alternative risk transfer (ART) techniques
vi. Real options
vii. Strategic risk management
viii. Enterprise risk management
2. (8 points) The core challenges to any ERM program are identifying strategic and operational risks, defining risk appetite, and integrating ERM into decision making. Briefly explain how Hydro Ones ERM program did or did not meet two of these challenges.
? Identifying strategic and operational risks
? Defining risk appetite
? Integrating ERM into decision making
3. (8 points) Captive insurers
? What is a captive insurer? How does a simple captive work?
? What is one of the benefits realized by forming a captive insurer? What is one of the drawbacks to forming a captive insurer?
4. (8 points) Suppose you are the risk manager for Tims Tin Can Company (Tims). Tims has, of course, a short exposure to tin. When tin prices rise, Tims net income falls. Tims previous Chief Risk Officer hedged this exposure using call options. Her goal was to ensure that Tims net income would not fall below C if tins price rose above P (see graph below).
? The chart below depicts the relationship between the price of tin and Tims net income. Show how the call options hedged Tims net income by sketching in 1) the option payoff, and 2) the net effect on Tims income.
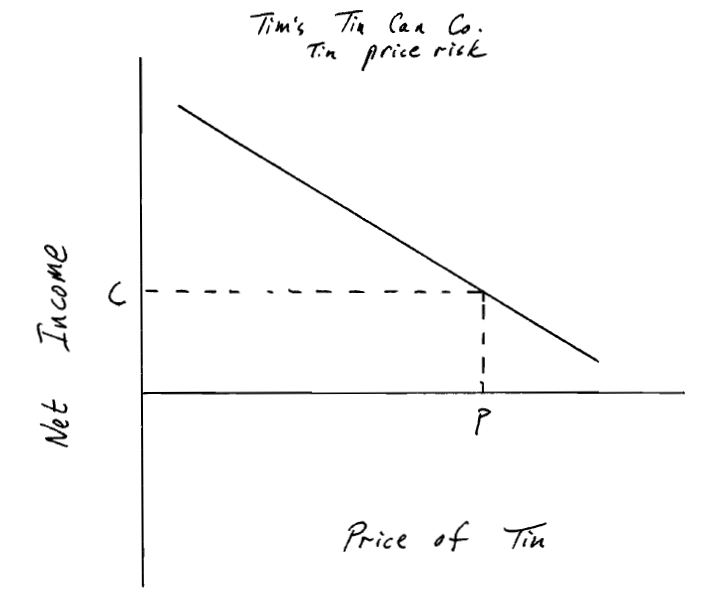
? Hedging using simple call options is expensive. Suggest a lower cost alternative derivative strategy that mitigates Tims tin price risk exposure (several alternative strategies were used by American Barrick at one time or another). What would Tims give up with this alternative strategy?
lim's 7, n price ri rice of inStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


