
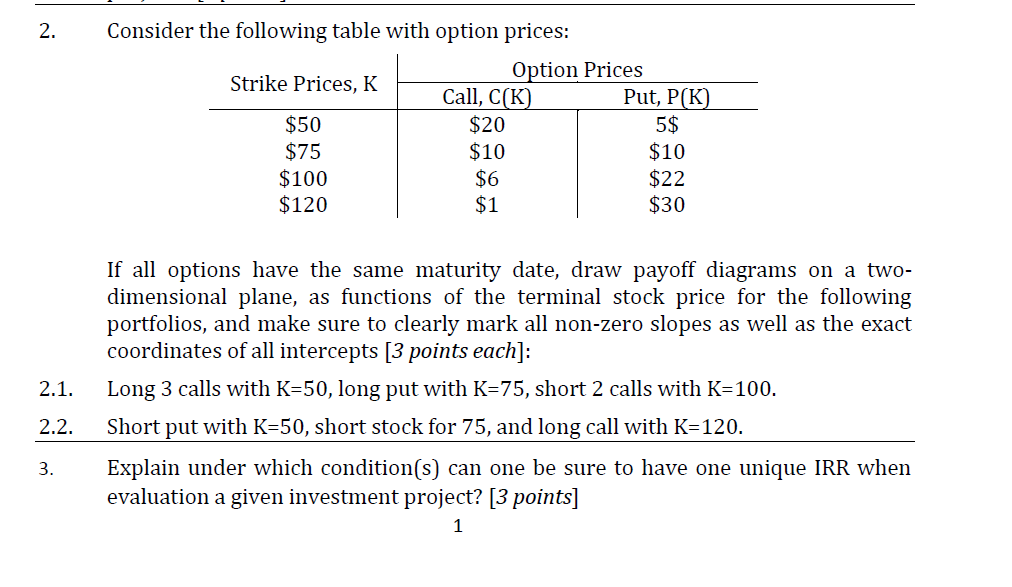
1. Consider an economy which is to go into a booming development or enter a recession in the near future. You are interested in buying a European put option written on a firm's non-dividend-paying common stock, with a strike price of $96 and six months until expiration. Currently, the firm's stock price is $90 per share. In three months, you expect this stock to be trading at either $108 per share or $81 per share, depending on whether the economy booms or falls into recession respectively. 1.1. 1.2. If you are able to borrow and lend at the risk-free EAR of 4 percent, how can you create a portfolio today that will exhibit no risk in 3 months? [2 points] What should be the fair value of the put option's price today? [2 points] If presently the market is not offering the put options that you want to buy (described in the problem), is there a way to create a synthetic one with identical payoffs to the option described above? If there is, how should one do it? If not, explain why. [2 points] 1.3. 1.4. 1.5. How much would it cost to create the synthetic put option? Is this greater than, less than, or equal to what the actual put option costs? Does this make sense? Explain. [2 points] Assume that you observe that a European call option written on the same underlying asset with a strike price of $96 and three months until expiration is currently selling for $4.051. Is there a way for John to make riskless profit? If there is, how should he do it? [2 points] 1.6. Assume, in the same economy, the market is offering a non-divisible investment project which generates $200K, of cash flows, if the economy booms or $90K if otherwise in three months. How much should you be willing to invest in this project? [3 points) 2. Consider the following table with option prices: Strike Prices, K $50 $75 $100 $120 Option Prices Call, C(K) Put, P(K) $20 5$ $10 $10 $6 $22 $1 $30 If all options have the same maturity date, draw payoff diagrams on a two- dimensional plane, as functions of the terminal stock price for the following portfolios, and make sure to clearly mark all non-zero slopes as well as the exact coordinates of all intercepts [3 points each]: Long 3 calls with K=50, long put with K=75, short 2 calls with K=100. Short put with K=50, short stock for 75, and long call with K=120. 2.1. 2.2. 3. Explain under which condition(s) can one be sure to have one unique IRR when evaluation a given investment project? [3 points] 1 1. Consider an economy which is to go into a booming development or enter a recession in the near future. You are interested in buying a European put option written on a firm's non-dividend-paying common stock, with a strike price of $96 and six months until expiration. Currently, the firm's stock price is $90 per share. In three months, you expect this stock to be trading at either $108 per share or $81 per share, depending on whether the economy booms or falls into recession respectively. 1.1. 1.2. If you are able to borrow and lend at the risk-free EAR of 4 percent, how can you create a portfolio today that will exhibit no risk in 3 months? [2 points] What should be the fair value of the put option's price today? [2 points] If presently the market is not offering the put options that you want to buy (described in the problem), is there a way to create a synthetic one with identical payoffs to the option described above? If there is, how should one do it? If not, explain why. [2 points] 1.3. 1.4. 1.5. How much would it cost to create the synthetic put option? Is this greater than, less than, or equal to what the actual put option costs? Does this make sense? Explain. [2 points] Assume that you observe that a European call option written on the same underlying asset with a strike price of $96 and three months until expiration is currently selling for $4.051. Is there a way for John to make riskless profit? If there is, how should he do it? [2 points] 1.6. Assume, in the same economy, the market is offering a non-divisible investment project which generates $200K, of cash flows, if the economy booms or $90K if otherwise in three months. How much should you be willing to invest in this project? [3 points) 2. Consider the following table with option prices: Strike Prices, K $50 $75 $100 $120 Option Prices Call, C(K) Put, P(K) $20 5$ $10 $10 $6 $22 $1 $30 If all options have the same maturity date, draw payoff diagrams on a two- dimensional plane, as functions of the terminal stock price for the following portfolios, and make sure to clearly mark all non-zero slopes as well as the exact coordinates of all intercepts [3 points each]: Long 3 calls with K=50, long put with K=75, short 2 calls with K=100. Short put with K=50, short stock for 75, and long call with K=120. 2.1. 2.2. 3. Explain under which condition(s) can one be sure to have one unique IRR when evaluation a given investment project? [3 points] 1








