Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Consider the following set of one-dimensional points: {0.1,0.25,0.45,0.55,0.8,0.9}. All the points are located in the range between [0,1]. (a) Suppose we apply kmeans clustering
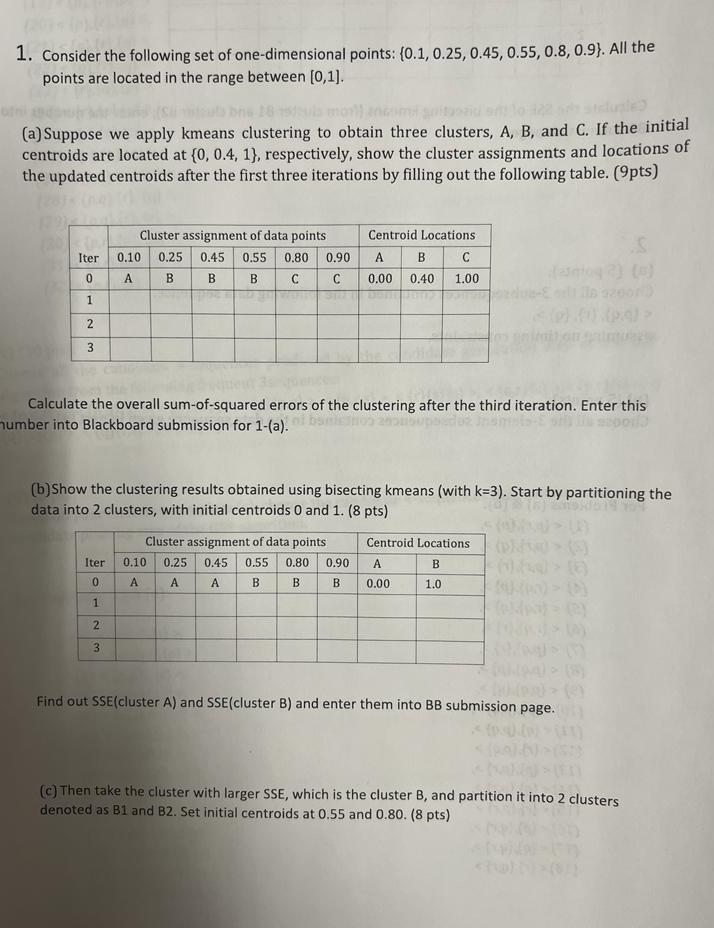





1. Consider the following set of one-dimensional points: {0.1,0.25,0.45,0.55,0.8,0.9}. All the points are located in the range between [0,1]. (a) Suppose we apply kmeans clustering to obtain three clusters, A, B, and C. If the initial centroids are located at {0,0.4,1}, respectively, show the cluster assignments and locations of the updated centroids after the first three iterations by filling out the following table. (9pts) Calculate the overall sum-of-squared errors of the clustering after the third iteration. Enter this umber into Blackboard submission for 1-(a). (b)Show the clustering results obtained using bisecting kmeans (with k=3 ). Start by partitioning the data into 2 clusters, with initial centroids 0 and 1 . (8 pts) Find out SSE(cluster A) and SSE(cluster B) and enter them into BB submission page. (c) Then take the cluster with larger SSE, which is the cluster B, and partition it into 2 clusters denoted as B1 and B2. Set initial centroids at 0.55 and 0.80. ( 8 pts) 4. Consider the following training set, which contains 3 binary attributes X1,X2, and X3. There are 50 examples in the training set, with equal number of positive and negative examples. (a, weu pis) compute tne class conditional probabilities P(X1=1+),P(X1=1),P(X2=1+),P(X2 =11,P(X3=1+), and P(X3=1). (b) (10 pts) Use the class conditional probabilities given in the previous question to predict the class label of each example with the feature set given in the training set above. You need to find out whether the given X vectors in the table is predicted as + or . For example, X=(1,1,1) is predicted as + or ; etc. (c) (5pts) What is the error rate from the predictions you got from (b)? (19),(30), (4) {p,q,r},{s} (5) (10) (12), assuming no timing constraints. (b) (5 points): Choose all the 3 -element subsequences contained in the data sequence given in part (a). For Problems (a) \& (b): (1) (4), (7) , (9), (10), (12) (13), (15) (16) (b) (7 pts) Suppose all the candidate 3-itemsets above are frequent. List all candidate 4itemsets that can be generated from the frequent 3itemsets using the candidate generation procedure for Apriori. (c) ( 7 pts) List all candidate 4-itemsets that survive the candidate pruning step of the Apriori algorithm. (d) (4 pts) Based on the list of frequent 3-itemsets given above, is it possible to generate a frequent 5 -itemset? (15)(16)(17)(18)(19)(20) 3. Consider the following set of candidate 3 -itemsets: {p,q,r},{p,q,s},{p,q,t},{p,r,s},{p,r,t},{q,r,s},{q,r,t},{q,s,t},{r,s,t}. (a) (7pts) Construct a binary hash tree for storing the above 3-itemsets. Assume the hash tree uses a hash function where items p,r,t are hashed to the left child of a node, while items q,s,u are hashed to the right child. A candidate k-itemset is inserted into the tree by hashing on each successive item in the candidate and then following the appropriate branch of the tree according to the hash value. Once a leaf node is reached, the candidate is inserted based on one of the following conditions: Condition 1: If the depth of the leaf node is equal to k (the root node is assumed to be at depth 0 ), then the candidate is added to the leaf node irrespective of the number of itemsets already stored at the node. Condition 2: If the depth of the leaf node is less than k, then the candidate is added to the leaf node as long as the number of itemesets already stored at the leaf node is less than maxsize =2. Otherwise, change the leaf node into an internal node and distribute the candidates (including the new candidate to be added) to its children based on their respective hash values. Note: It is possible that a node will become non-existent (should be removed) if its parent node become a leaf (where some itemsets are stored). For example, If node 7 becomes a leaf node by having one itemset, then its children nodes, 14 and 15 , will be removed from the tree
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


