Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Equilibrium Review (10 pts) (10 pts) An airplane with a gross weight of 14,000 lbf is flying in steady level flight as shown.


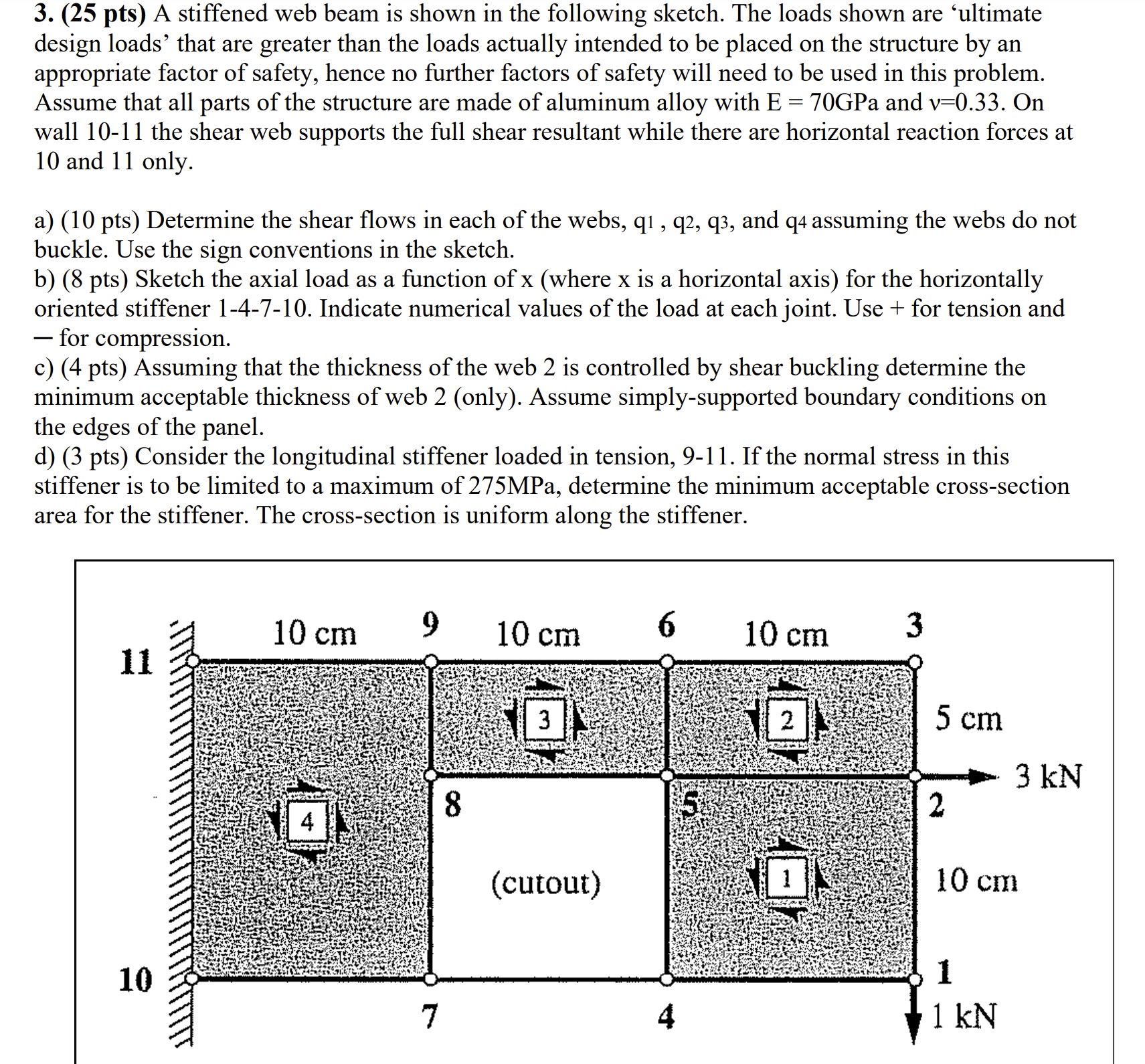
1. Equilibrium Review (10 pts) (10 pts) An airplane with a gross weight of 14,000 lbf is flying in steady level flight as shown. Locations of the center of gravity of the complete aircraft and the centers of pressure of the main wing and the tail are illustrated in the figure. Because the tail is a symmetric airfoil, assume that it generates no aerodynamic moment. The main wing, however, does produce an aerodynamic moment about the aerodynamic center (with this reference point, CM is independent of angle of attack) according to: M=pV = 1 pV SCCM. where p is the density of the air, V is the velocity of the plane, S is the wing area, c is the chord length and Co is the coefficient of moment (note that by definition the aerodynamic moment is positive when it produces a nose up pitching moment). Given: p = 2.3769x10- slug/ft, S = 300 ft, c = 10 ft and Co = -0.008 a) Neglecting all horizontal forces (thrust and drag), Determine the total lift on the main wing and the total lift that must be produced by the tail (obviously, the sum of these two must be 14,000 lbf) for each of the following cases: V = 500 mph, V = 350 mph and V = 200 mph. 8in 210 in c.g a.ca -a.c. b) Answer qualitatively: In part a we neglected thrust and drag forces. Do you think that including thrust and drag could significantly affect the computed lift in the wing and the tail? Explain. Also, under what circumstances is neglecting these things a good approximation? What might make it not such a good approximation? 2. V-M Diagram Review (15 pts) A simplified representation of loads on an airplane wing are shown in the sketch below. The distributed loading shown includes aerodynamic lift and the weight of the wing and its contents. Point loads corresponding to the weight of the engines are shown at point(s) a and the two 6,990 lb point loads at points b represent the interaction of the fuselage with the wing box. Note that "WS" means "Wing Station," and is a designation of the location of a given position on the wing, in inches from a reference zero position which is in this case at the center of the fuselage. a) Confirm that the wing is in equilibrium under the given loads (show calculations) b) Determine the internal resultants V and M at WS 0, WS61.5 and at WS135 based on equilibrium of appropriate free body diagrams. c) Sketch V-M diagrams for the entire wing. Required: All FBDs must be shown in standard form, with the FBD, the V diagram and the M diagram stacked vertically on a single page as in the example at http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shear Moment Diagram.svg. Numerical values at key points must also be provided. Note: you are not required to obtain equations for V(x) and M(x), only the V-M diagram is required. It is PERMITTED to use a web-based shear-moment diagram tool to obtain the diagrams, but each individual student must operate the tool and you must explain what tool you used and how you applied it in this case. WS -175 500 lb WS -95 WS 95 70 lb/in 70 lb/in a WS 6990 lb 6990 lb 500 lb 175 WS WS -28 28 3. (25 pts) A stiffened web beam is shown in the following sketch. The loads shown are ultimate design loads' that are greater than the loads actually intended to be placed on the structure by an appropriate factor of safety, hence no further factors of safety will need to be used in this problem. Assume that all parts of the structure are made of aluminum alloy with E = 70GPa and v=0.33. On wall 10-11 the shear web supports the full shear resultant while there are horizontal reaction forces at 10 and 11 only. a) (10 pts) Determine the shear flows in each of the webs, q1,q2, q3, and q4 assuming the webs do not buckle. Use the sign conventions in the sketch. b) (8 pts) Sketch the axial load as a function of x (where x is a horizontal axis) for the horizontally oriented stiffener 1-4-7-10. Indicate numerical values of the load at each joint. Use + for tension and - for compression. c) (4 pts) Assuming that the thickness of the web 2 is controlled by shear buckling determine the minimum acceptable thickness of web 2 (only). Assume simply-supported boundary conditions on the edges of the panel. d) (3 pts) Consider the longitudinal stiffener loaded in tension, 9-11. If the normal stress in this stiffener is to be limited to a maximum of 275MPa, determine the minimum acceptable cross-section area for the stiffener. The cross-section is uniform along the stiffener. 10 cm 9 6 3 10 cm 10 cm 11 4 10 7 8 3 (cutout) 5 cm 3 kN 2 10 cm 1 1 kN
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Problem 1a Determine the Total Lift on the Main Wing and the Tail Given Weight of the aircraft W 14000 lbf Density of air 23769 1 0 3 slugft 3 23769 times 103 textslugft3 23769103slugft3 Wing area S 3...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


