Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. For quasi-static pure shear (a.k.a. planar tension) testing, a thin rectangular sheet is mounted in a wide-grip uniaxial tension fixture and pulled along
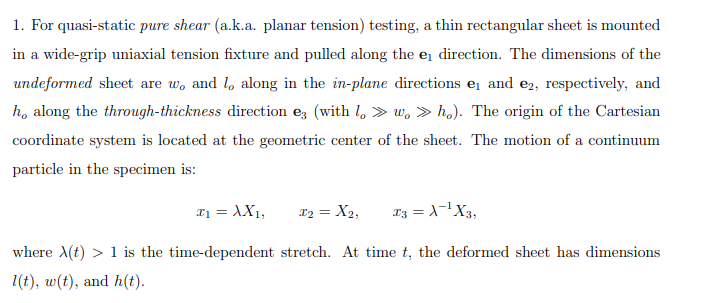
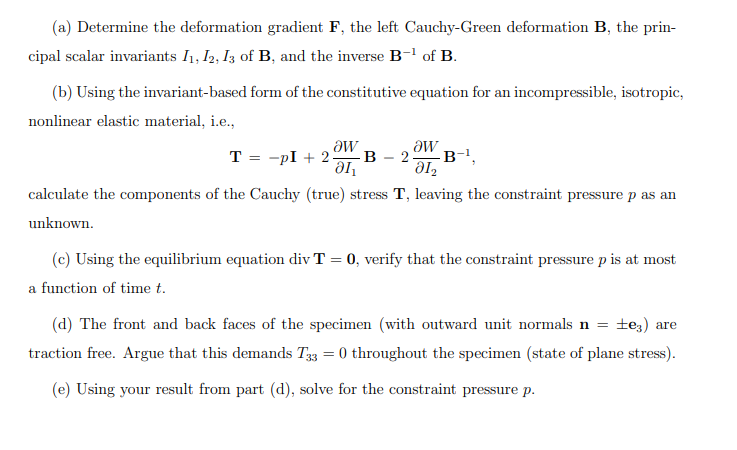

1. For quasi-static pure shear (a.k.a. planar tension) testing, a thin rectangular sheet is mounted in a wide-grip uniaxial tension fixture and pulled along the e direction. The dimensions of the undeformed sheet are w, and 1, along in the in-plane directions e and e2, respectively, and h, along the through-thickness direction 3 (with low, ho). The origin of the Cartesian coordinate system is located at the geometric center of the sheet. The motion of a continuum particle in the specimen is: x = XX1, x2 = X2, x3 = X3, where (t) 1 is the time-dependent stretch. At time t, the deformed sheet has dimensions 1(t), w(t), and h(t). (a) Determine the deformation gradient F, the left Cauchy-Green deformation B, the prin- cipal scalar invariants 11, 12, 13 of B, and the inverse B-1 of B. (b) Using the invariant-based form of the constitutive equation for an incompressible, isotropic, nonlinear elastic material, i.e., aw aw = T = -pI +2. B 2. -B-, 12 calculate the components of the Cauchy (true) stress T, leaving the constraint pressure p as an unknown. (c) Using the equilibrium equation div T = 0, verify that the constraint pressure p is at most a function of time t. (d) The front and back faces of the specimen (with outward unit normals n = e) are traction free. Argue that this demands T33 = 0 throughout the specimen (state of plane stress). (e) Using your result from part (d), solve for the constraint pressure p. (f) Using your result from part (e), determine the Cauchy (true) stress-stretch relationship (T11 vs. X) and the first Piola-Kirchhoff (engineering) stress-stretch relationship ((T)11 vs. A). (g) Using your result from part (f), compute the resultant force exerted on the top/bottom surfaces of the specimen.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Solutions Step 1 Calculation 1 Convert units Height h43 mm0043 m Diameter d143 mm00143 m Crosssectional area Ad240014324161104 m2 2 Potential energy P...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


