Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. For the most recent reporting period, J&J's largest resource of cash was from: a. Investing activities b. operating activites c. financing activites 2. J&J
1. For the most recent reporting period, J&J's largest resource of cash was from: 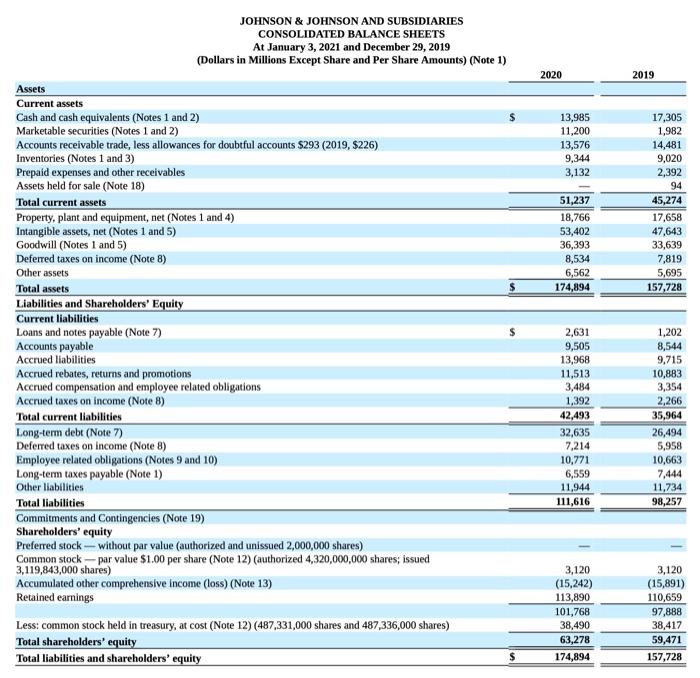
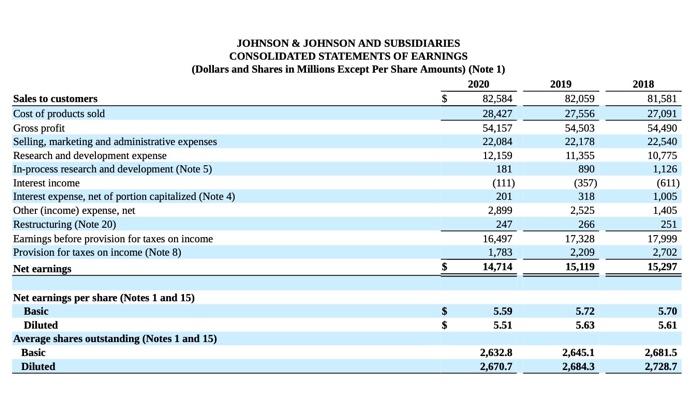
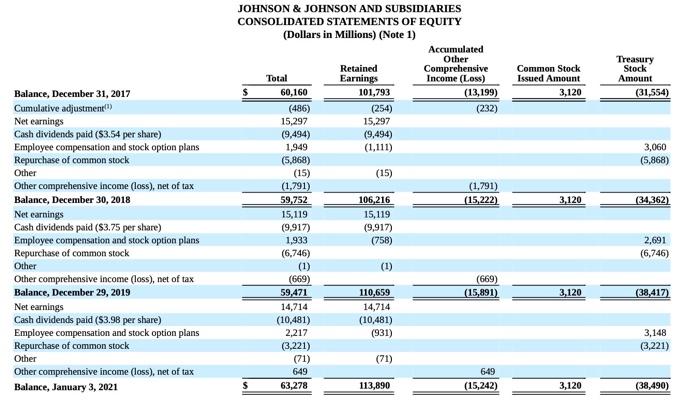
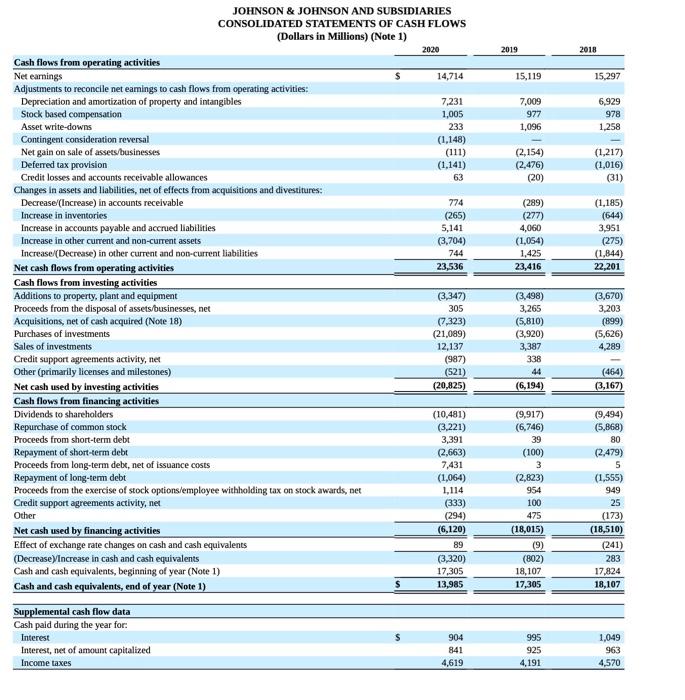
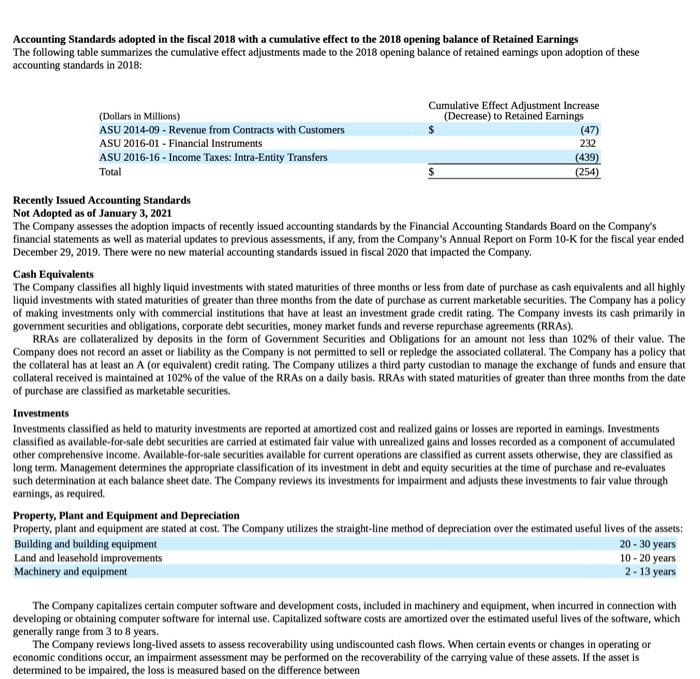

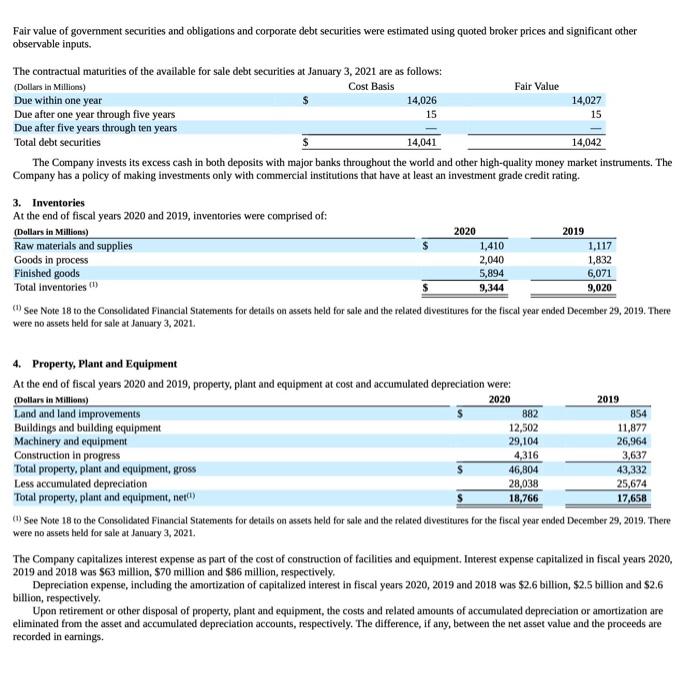
JOHNSON \& JOHNSON AND SUBSIDIARIES JOHNSON \& JOHNSON AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS (Dollars and Shares in Millions Except Per Share Amounts) (Note 1) JOHNSON \& JOHNSON AND SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY (Dollars in Millions) (Note 1) JOHNSON \& JOHNSON AND SUBSIDIARIES Accounting Standards adopted in the fiscal 2018 with a cumulative effect to the 2018 opening balance of Retained Earnings The following table summarizes the cumulative effect adjustments made to the 2018 opening balance of retained eamings upon adoption of these accounting standards in 2018: Recently Issued Accounting Standards Not Adopted as of January 3, 2021 The Company assesses the adoption impacts of recently issued accounting standards by the Financial Accounting Standards Board on the Company's financial statements as well as material updates to previous assessments, if any, from the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 29, 2019. There were no new material accounting standards issued in fiscal 2020 that impacted the Company. Cash Equivalents The Company classifies all highly liquid investments with stated maturities of three months or less from date of purchase as cash equivalents and all highly liquid investments with stated maturities of greater than three months from the date of purchase as current marketable securities. The Company has a policy of making investments only with commercial institutions that have at least an investment grade credit rating. The Company invests its cash primarily in government securities and obligations, corporate debt securities, money market funds and reverse repurchase agreements (RRAs). RRAs are collateralized by deposits in the form of Government Securities and Obligations for an amount not less than 102\% of their value. The Company does not record an asset or liability as the Company is not permitted to sell or repledge the associated collateral. The Company has a policy that the collateral has at least an A (or equivalent) credit rating. The Company utlizes a third party custodian to manage the exchange of funds and ensure that collateral received is maintained at 102% of the value of the RRAs on a daily basis. RRAs with stated maturities of greater than three months from the date of purchase are classified as marketable securities. Investments Investments classified as held to maturity investments are reported at amortized cost and realized gains or losses are reported in eamings. Investments classified as available-for-sale debt securities are carried at estimated fair value with unrealized gains and losses recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income. Available-for-sale securities available for current operations are classified as current assets otherwise, they are classified as long term. Management determines the appropriate classification of its investment in debt and equity securities at the time of purchase and re-evaluates such determination at each balance sheet date. The Company reviews its investments for impairment and adjusts these investments to fair value through earnings, as required. Property, Plant and Equipment and Depreciation Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. The Company utilizes the straight-line method of depreciation over the estimated useful lives of the assets: BuildingandbuildingequipmentLandandleaseholdimprovementsMachineryandequipment2030years1020years2=13years The Company capitalizes certain computer software and development costs, included in machinery and equipment, when incurred in connection with developing or obtaining computer software for internal use. Capitalized software costs are amortized over the estimated useful lives of the software, which generally range from 3 to 8 years. The Company reviews long-lived assets to assess recoverability using undiscounted cash flows. When certain events or changes in operating or economic conditions occur, an impairment assessment may be performed on the recoverability of the carrying value of these assets. If the asset is determined to be impaired, the loss is measured based on the difference between the asset's fair value and its carrying value. If quoted market prices are not available, the Company will estimate fair value using a discounted value of estimated future cash flows. Revenue Recognition The Company recognizes revenue from product sales when obligations under the terms of a contract with the customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the goods to customers. The Company's global payment terms are typically between 30 to 90 days. Provisions for certain rebates, sales incentives, trade promotions, coupons, product returns and discounts to customers are accounted for as variable consideration and recorded as a reduction in sales. The liability is recognized within Accrued Rebates, Returns, and Promotions on the consolidated balance sheet. Product discounts granted are based on the terms of arrangements with direct, indirect and other market participants, as well as market conditions, including consideration of competitor pricing. Rebates are estimated based on contractual terms, historical experience, patient outcomes, trend analysis and projected market conditions in the various markets served. A significant portion of the liability related to rebates is from the sale of the Company's pharmaceutical products within the U.S., primarily the Managed Care, Medicare and Medicaid programs, which amounted to S7.2 billion and $7.0 billion as of January 3, 2021 and December 29, 2019, respectively. The Company evaluates market conditions for products or groups of products primarily through the analysis of wholesaler and other third-party sell-through and market research data, as well as intemally generated information. Sales returns are estimated and recorded based on historical sales and returns information. Products that exhibit unusual sales or return pattems due to dating, competition or other marketing matters are specifically investigated and analyzed as part of the accounting for sales return accruals. Sales returns allowances represent a reserve for products that may be returned due to expiration, destruction in the field, or in specific areas, product recall. The sales returns reserve is based on historical return trends by product and by market as a percent to gross sales. In accordance with the Company's accounting policies, the Company generally issues credit to customers for returned goods. The Company's sales retums reserves are accounted for in accordance with the U.S. GAAP guidance for revenue recognition when right of return exists. Sales returns reserves are recorded at full sales value. Sales returns in the Consumer Health and Pharmaceutical segments are almost exclusively not resalable, Sales returns for certain franchises in the Medical Devices segment are typically resalable but are not material. The Company infrequently exchanges products from inventory for returned products. The sales returns reserve for the total Company has been approximately 1.0% of annual net trade sales during each of the fiscal years 2020 , 2019 and 2018. Promotional programs, such as product listing allowances and cooperative advertising arrangements, are recorded in the same period as related sales. Continuing promotional programs include coupons and volume-based sales incentive programs. The redemption cost of consumer coupons is based on historical redemption experience by product and value. Volume-based incentive programs are based on the estimated sales volumes for the incentive period and are recorded as products are sold. These arrangements are evaluated to determine the appropriate amounts to be deferred or recorded as a reduction of revenue. The Company also earns profit-share payments through collaborative arrangements for certain products, which are included in sales to customers. For all years presented, profit-share payments were less than 3.0% of the total revenues and are included in sales to customers. See Note 17 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further disaggregation of revenue. Shipping and Handling Shipping and handling costs incurred were $1.0 billion, $1.0 billion and $1.1 billion in fiscal years 2020,2019 and 2018 , respectively, and are included in selling, marketing and administrative expense. The amount of revenue recelved for shipping and handing is less than 0.5% of sales to customers for all periods presented. Inventories Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value determined by the first-in, first-out method. Intangible Assets and Goodwill The authoritative literature on U.S. GAAP requires that goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives be assessed annually for impairment. The Company completed its annual impairment test for 2020 in the fiscal fourth quarter. Future impaiment tests will be performed annually in the fiscal fourth quarter, or sooner if warranted. Purchased in-process research and development is accounted for as an indefinite lived intangible asset until the underlying project is completed, at which point the intangible asset will be accounted for as a definite lived intangible asset, or abandoned, at which point the intangible asset will be written off or partially impaired. Intangible assets that have finite useful lives continue to be amortized over their useful lives, and are reviewed for impairment when warranted by economic conditions. See Note 5 for further details on Intangible Assets and Goodwill. Fair value of government securities and obligations and corporate debt securities were estimated using quoted broker prices and significant other observable inputs. The Company invests its excess cash in both deposits with major banks throughout the world and other high-quality money market instruments. The Company has a policy of making investments only with commercial institutions that have at least an investment grade credit rating. (1) See Note 18 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for details on assets held for sale and the related divestitures for the fiscal year ended December 29 , 2019. There were no assets held for sale at January 3, 2021. 4. Property, Plant and Equipment (1) See Note 18 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for details on assets held for sale and the related divestitures for the fiscal year ended December 29, 2019. There were no assets held for sale at January 3,2021. The Company capitalizes interest expense as part of the cost of construction of facilities and equipment. Interest expense capitalized in fiscal years 2020 , 2019 and 2018 was $63 million, \$70 million and \$86 million, respectively. Depreciation expense, including the amortization of capitalized interest in fiscal years 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $2.6 billion, $2,5 billion and \$2.6 billion, respectively. Upon retirement or other disposal of property, plant and equipment, the costs and related amounts of accumulated depreciation or amortization are eliminated from the asset and accumulated depreciation accounts, respectively. The difference, if any, between the net asset value and the proceeds are recorded in earnings a. Investing activities
b. operating activites
c. financing activites
2. J&J increased which account when it orginally issued shares of its stock for cash?
a. retained earnings
b. common stock in treasury
c. common stock
d. sales to customers
3. J&J's undistributed earnings ar the most recent balance shest date was (in millions):
a. $14,714
b. $82,584
c. $113,890
d. $63,278
4. Use the following formula to calculate J&J's accounts receivable turnover ratio at the last two balance sheet dates:
Accounts receivable turnover ratio= Sales to customers / Accounts receuvable. Round your answer to two decimal places. Select the correct answer below.
a. the company collected accounts receivable slightly faster in the most recent reporting period than the prior reporting period
b. the company collected accounts receivable slightly slower in the most recent reporting period than the prior reporting period
c. the company collected accounts receivable at the same rate as in the prior reporting period
5. J&J's cash-based net income for the most recent reporting period was (in millions):
a. $14,714
b. $23,536
c. $83,584
d. $13,985
6. Calculate J&J's return on assers ratio (net earnings / total assets) for the last two reporting periods. Based on the company's return on assets ratio, the company's management:
a. used its assets more efficiently to generate earnings in 2020 than in 2019
b. used its assets less efficiently to generate earnings in 2020 than in 2019
c. used its earnings more efficiently to generate earnings in 2020 than in 2019
d. used its earnings less efficiently to generate earnings in 2020 than in 2019
7. J&J's depreciation method results in ____ book value being reported on the company's balance shest early in an asset's useful life than compared to the accelerated depreciation methods.
a. the same
b. less
c. more
8. At the most recent balance sheet date, the historical cost of J&J's property, plant and equipment was (in millions):
a. $18,766
b. $28,038
c. $63
d. $46,804
9.At the most recent balance sheet date, total depreciation expense recognized by J&J on property, plant and equipment since the assets were acquired was (in millions):
a. $28,038
b. $2,600
c. $2,364
d. $46,804
10. Which of J&J's financial statements is not accrual-based?
a. income statement
b. balance sheet
c. statement of shareholders' equity
d. statement of cash flows







Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


