Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Give a minimal realization for the transfer function matrix 8 +2 S (s+1)2(s+4) (s+1)(s+5) G(s) = 2 s+1 8+1 (s+6)(s+5) You'll want to
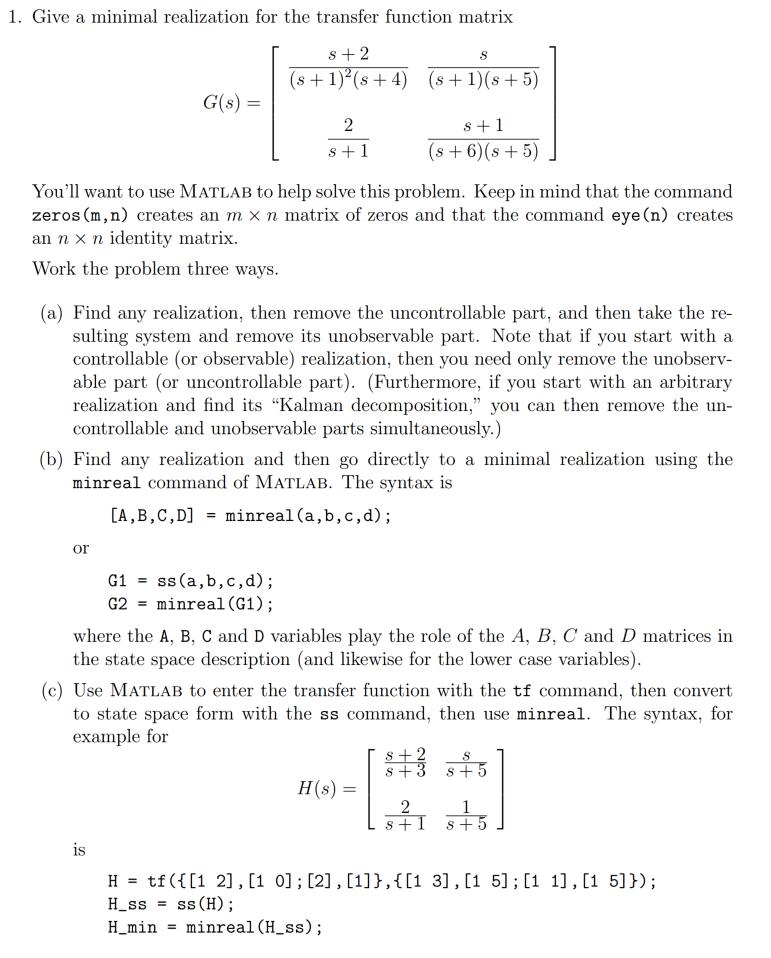
1. Give a minimal realization for the transfer function matrix 8 +2 S (s+1)2(s+4) (s+1)(s+5) G(s) = 2 s+1 8+1 (s+6)(s+5) You'll want to use MATLAB to help solve this problem. Keep in mind that the command zeros (m, n) creates an m x n matrix of zeros and that the command eye (n) creates an nxn identity matrix. Work the problem three ways. (a) Find any realization, then remove the uncontrollable part, and then take the re- sulting system and remove its unobservable part. Note that if you start with a controllable (or observable) realization, then you need only remove the unobserv- able part (or uncontrollable part). (Furthermore, if you start with an arbitrary realization and find its "Kalman decomposition," you can then remove the un- controllable and unobservable parts simultaneously.) (b) Find any realization and then go directly to a minimal realization using the minreal command of MATLAB. The syntax is [A,B,C,D] = minreal (a, b, c,d); or G1 ss (a,b,c,d); G2 minreal (G1); where the A, B, C and D variables play the role of the A, B, C and D matrices in the state space description (and likewise for the lower case variables). (c) Use MATLAB to enter the transfer function with the tf command, then convert to state space form with the ss command, then use minreal. The syntax, for example for $+2 8+3 S 8+5 H(s) = 2 1 8+1 +5 is Htf ({[12], [1 0]; [2], [1]}, {[1 3], [1 5]; [1 1], [15]}); H_ss = ss (H); H_min=minreal (H_ss);
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


