Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Given the information in Table 14.1, please calculate the free energy generated by the net electron transfers of each electron transport complex (I -

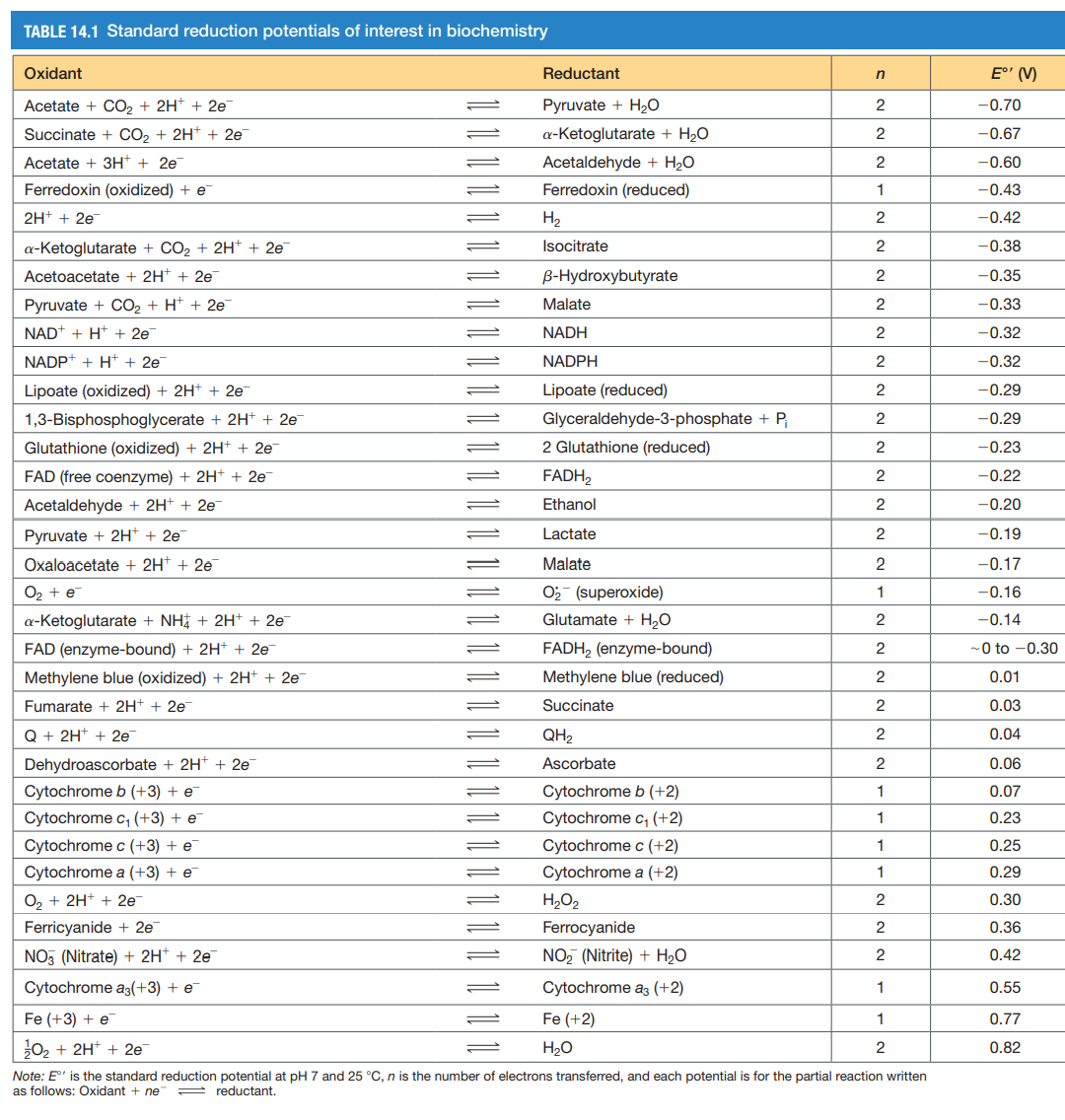
1. Given the information in Table 14.1, please calculate the free energy generated by the net electron transfers of each electron transport complex (I - IV). Just use the beginning and end electron carrying molecules. Remember that the number of electrons donated and accepted needs to be the same. 2. Cyanide (CN) binds very strongly to the oxidized form of cytochrome a3 and prevents its reduction. A. What effect do you think this has on electron transport? B. The effects of cyanide can be reduced by immediate administration of sodium nitrite (NaNO2). Why does this counteract the effects of cyanide? TABLE 14.1 Standard reduction potentials of interest in biochemistry Oxidant Reductant n E' (V) -0.70 -0.67 -0.60 -0.43 -0.42 -0.38 -0.35 -0.33 -0.32 -0.32 -0.29 -0.29 -0.23 -0.22 -0.20 -0.19 -0.17 Acetate + CO2 + 2H+ + 2e Pyruvate + H2O 2 Succinate + CO2 + 2H+ + 2e a-ketoglutarate + H2O 2 Acetate + 3H+ + 2e Acetaldehyde + H2O 2 Ferredoxin (oxidized) + e Ferredoxin (reduced) 1 2H+ + 2e H2 2 a-ketoglutarate + CO2 + 2H+ + 2e Isocitrate 2 Acetoacetate + 2H+ + 2e B-Hydroxybutyrate 2 Pyruvate + CO2 + H+ + 2e Malate 2 NAD + H+ + 2e NADH 2 NADP+ + H+ + 2e NADPH 2 Lipoate (oxidized) + 2H+ + 2e Lipoate (reduced) 2 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + 2H+ + 2e Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + P 2 Glutathione (oxidized) + 2H+ + 2e 2 Glutathione (reduced) 2 FAD (free coenzyme) + 2H+ + 2e FADH2 2 Acetaldehyde + 2H+ + 2e Ethanol 2 Pyruvate + 2H+ + 2e Lactate 2 Oxaloacetate + 2H+ + 2e Malate 2 O2 + e 02 (superoxide) 1 a-ketoglutarate + NH4 + 2H+ + 2e Glutamate + H2O 2 FAD (enzyme-bound) + 2H+ + 2e FADH2 (enzyme-bound) 2 Methylene blue (oxidized) + 2H+ + 2e Methylene blue (reduced) 2 Fumarate + 2H+ + 2e Succinate 2 Q + 2H+ + 2e QH2 2 Dehydroascorbate + 2H+ + 2e Ascorbate 2 Cytochrome b (+3) + e Cytochrome b (+2) 1 Cytochrome C1 (+3) + e Cytochrome (+2) 1 Cytochrome c (+3) + e Cytochrome c (+2) 1 Cytochrome a (+3) + e Cytochrome a (+2) 1 O + 2H+ + 2e H2O2 2 Ferricyanide + 2e Ferrocyanide 2 NO3 (Nitrate) + 2H+ + 2e NO2 (Nitrite) + H2O 2 Cytochrome az(+3) + e Cytochrome az (+2) 1 Fe (+3) + e Fe (+2) 1 202 + 2H+ + 2e H2O 2 Note: E' is the standard reduction potential at pH 7 and 25 C, n is the number of electrons transferred, and each potential is for the partial reaction written as follows: Oxidant + ne - reductant. -0.16 -0.14 - to -0.30 0.01 0.03 0.04 0.06 0.07 0.23 0.25 0.29 0.30 0.36 0.42 0.55 0.77 0.82
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


