Question
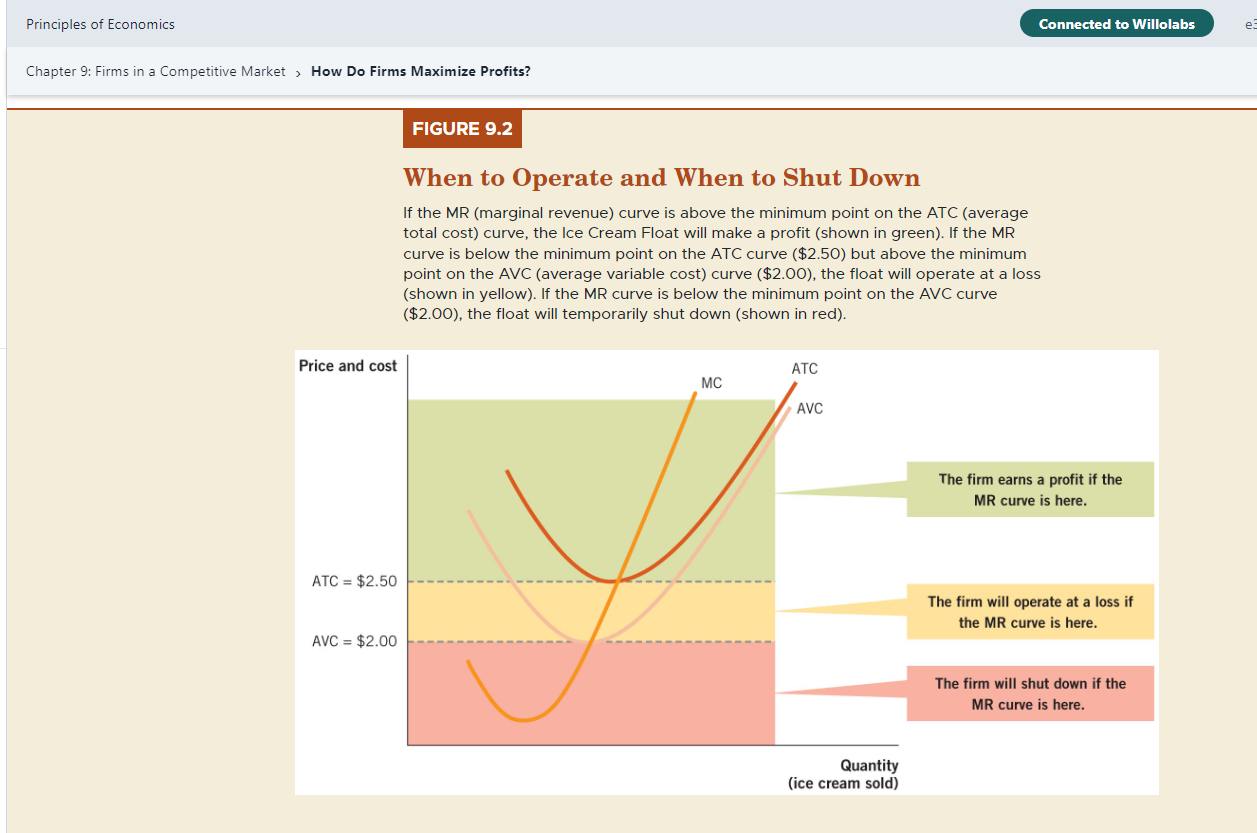
1. Locate the chart in Chapter 9, Study Problems question 2. Change the price to $5. Provide the chart in your answer to the following.
1. Locate the chart in Chapter 9, Study Problems question 2. Change the price to $5. Provide the chart in your answer to the following. .
a. Calculate the total revenue for the business at each rate of output.
b. Calculate the total profit for the business at each rate of output.
c. Is the business operating in the short run or the long run? Please explain.
d. What is the MR=MC rule? Calculate the profit maximizing rate of output using the MR=MC rule.
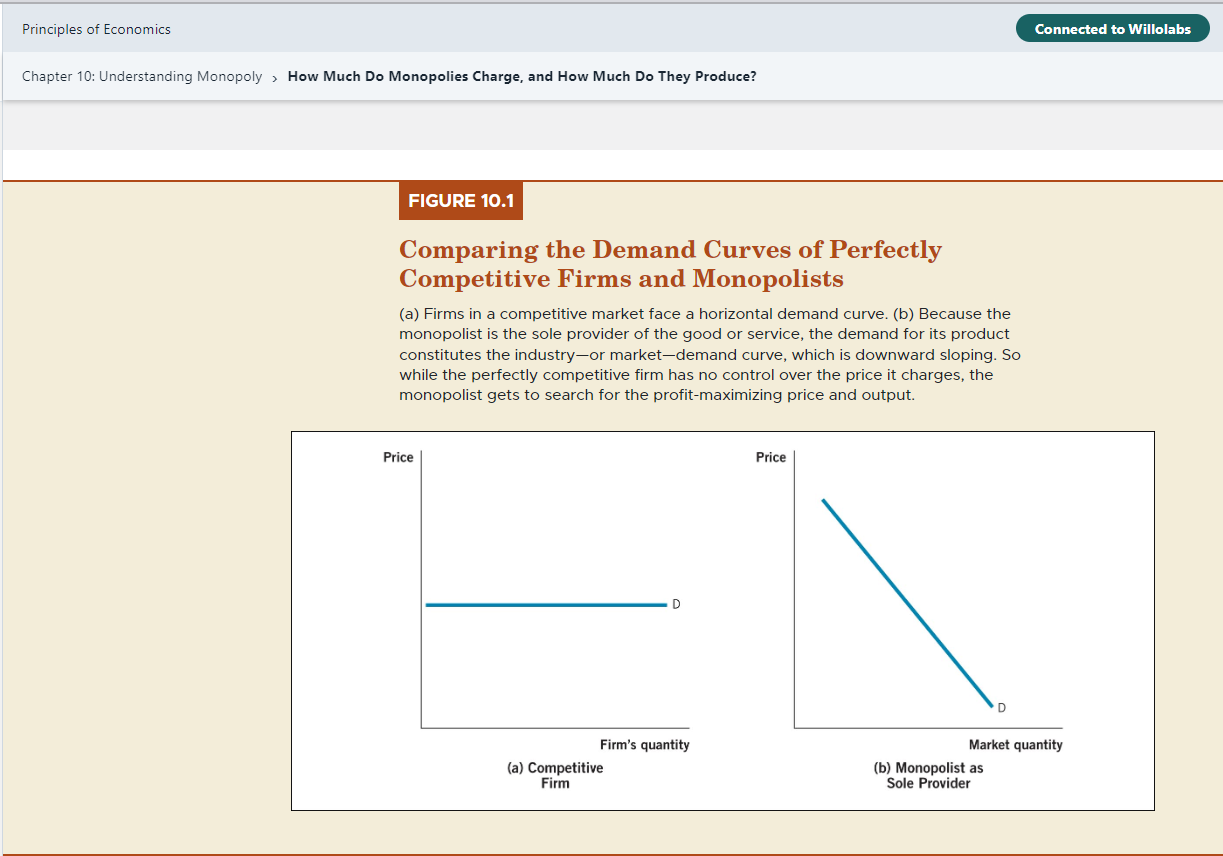
2. Locate the graph in Chapter 10, study problems question 1. Use the graph to answer the following questions.
a. Draw the graph as shown in the book.
b. Identify the price that the monopolist will charge and the output the monopolist will produce? Explain how you identify the two points.
c. On the graph, identify the consumer surplus for the monopolist.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


