Question
1. Professor Bunyan thinks he has discovered a remarkable property of binary search trees. Suppose that the search for key k in a binary search
1. Professor Bunyan thinks he has discovered a remarkable property of binary search trees. Suppose that the search for key k in a binary search tree ends up in a leaf. Consider three sets: A, the keys to the left of the search path; B, the keys on the search path; and C, the keys to the right of the search path. Professor Bunyan claims that any three keys a in A, b in B, and c in C must satisfy a
2. Let T be a binary search tree whose keys are distinct, let x be a leaf node, and let y be its parent. Show that key[y] is the smallest key in T larger than key[x].
3. Expression tree is a binary tree in which leaf nodes are numbers and internal nodes are operators (+,-,*). The following figure is an example of an expression tree which evaluates to (12-3)*2=18.
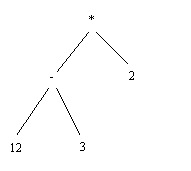
You are given a program that generates a random expression tree of any size given as an input. The code for preorder traversal is given. Please read the code and comments carefully. Complete the following program by implementing the following incomplete functions:
void binary_tree::postorder_traverse(node *p)
void binary_tree::inorder_traverse(node *p)
int binary_tree::size(node *p)
int binary_tree::height(node *p)
int binary_tree::max_value(node *p)
int binary_tree::evaluate(node *p)
The requirements of these functions are described in the program. The following is the program that you need to complete:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
char alloperators[] = "+-*";
enum nodetype { OPERATOR, NUMBER };
class node {
public:
nodetype ntype; // OPERATOR for internal nodes, NUMBER for leaves
int value; // when ntype is NUMBER, value represents the values of the node
char op; // when ntype is OPERATOR, value represents the operator of current node
node *left, *right;
node(int v,node *l,node *r) { // constructor for NUMBER nodes
value = v;
left = l;
right = r;
ntype = NUMBER;
}
node(char s,node *l,node *r) { // constructor for OPERATOR nodes
op = s;
left = l;
right = r;
ntype = OPERATOR;
}
};
class binary_tree {
private:
node *root;
node* create_random_tree(int n); // creates a random binary tree of n internal nodes recursively, and returns the tree
void preorder_traverse(node *p); // prints nodes in preorder from tree p
void postorder_traverse(node *p); // prints nodes in postorder from tree p
void inorder_traverse(node *p); // prints nodes in inorder from tree p
int size(node *p); // return the number of nodes in a tree from tree p
int height(node *p); // return the height from tree from tree p
int max_value(node *p); // returns the maximum node value from tree p
int evaluate(node *p); // returns the value of tree p
public:
binary_tree(int n) { // creates a random binary tree of n nodes
root = create_random_tree(n);
}
void preorder_traverse() {
preorder_traverse(root);
cout
};
void postorder_traverse() {
postorder_traverse(root);
cout
};
void inorder_traverse() {
inorder_traverse(root);
cout
};
int size() {
return size(root);
}
int height() {
return height(root);
}
int max_value() {
return max_value(root);
}
int evaluate() {
return evaluate(root);
}
};
node* binary_tree::create_random_tree(int n) { // creates a random binary tree with n internal nodes
if (n==0) { // creates a randomly valued NUMBER node as a leaf
return new node(rand()%100,NULL,NULL);
}
else { // creates an OPERATOR node with a random operation
int num_left = rand() % n; // left child has 0 to (n-1) internal nodes
node *p = new node(alloperators[rand()%3],create_random_tree(num_left),create_random_tree(n-1-num_left));
return p;
}
}
void binary_tree::preorder_traverse(node *p) {
// preorder traversal from tree p
if (p == NULL) return;
if (p->ntype == NUMBER) cout value
else cout op
preorder_traverse(p->left);
preorder_traverse(p->right);
}
void binary_tree::postorder_traverse(node *p) {
// postorder traversal from tree p
// ************ FILL IN YOUR CODE HERE ********************
}
void binary_tree::inorder_traverse(node *p) {
// inorder traversal from tree p
// ************ FILL IN YOUR CODE HERE ********************
}
int binary_tree::size(node *p) {
// returns the number of nodes (both NUMBER and OPERATOR nodes) for tree p
// ************ FILL IN YOUR CODE HERE ********************
}
int binary_tree::height(node *p) {
// returns the height of tree p
// Note: Single node tree's height is 0
// ************ FILL IN YOUR CODE HERE ********************
}
int binary_tree::max_value(node *p) {
// returns the maximum value of a NUMBER node
// ************ FILL IN YOUR CODE HERE ********************
}
int binary_tree::evaluate(node *p) {
// returns the value of expression tree p
// ************ FILL IN YOUR CODE HERE ********************
}
int main()
{
int n;
srand(time(NULL));
cout
cin >> n;
assert(n>=2);
binary_tree mytree(n-1); // creates a tree of size n leaves (n-1 internal nodes)
cout
cout
cout
cout
mytree.preorder_traverse();
cout
mytree.postorder_traverse();
cout
mytree.inorder_traverse();
cout
return 0;
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


