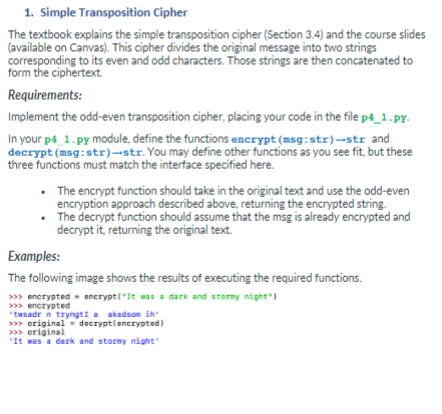


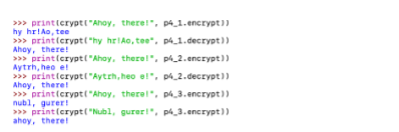
1. Simple Transposition Cipher The textbook explains the simple transposition cipher (Section 3.4) and the course slides (available on Canvas). This cipher divides the original message into two strings corresponding to its even and odd characters. Those strings are then concatenated to form the ciphertext. Requirements: Implement the odd-even transposition cipher, placing your code in the file p4_1.py. In your p4 1.py module, define the functions encrypt(msg:str)-str and decrypt (msg str)-str. You may define other functions as you see fit, but these three functions must match the interface specified here. The encrypt function should take in the original text and use the odd-even encryption approach described above, returning the encrypted string. The decrypt function should assume that the msg is already encrypted and decrypt it returning the original text. Examples: The following image shows the results of executing the required functions. >>> encrypted encrypt("It was a dark and story night") >>> encrypted wsadr trygt! akadson in >>> original - decrypt(encrypted) It was a dark and storny night >>> original 2. Three-rail Cipher Problem In this problem, you will implement a transposition cipher that instead of dividing the original text into odd and even characters, separates it into three sets of characters. As an example, we will use this 1977 quote by Digital Equipment Corp. president Ken Olson -- "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." (Spaces are represented with the square u-like character.) There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home. Rail 1: T Tsuy du Fitih Rail 2: a una orn Rail 3: Example three-rail transposition The resulting encrypted text is produced by reading the text horizontally, i.e., adding the three rails: Rail 1 + Rail 2 + Rail 3 = "Trinrs yeoda cpeitihehesoeoao u naournhro.e annnwlwt mt e m" (without the quotes) Requirements Implement the three-rail transposition cipher above, placing your code in the file p4 2-py. Define the functions encrypt (msg:str)-strand decrypt (msg=str)-str. You may define other functions, but these functions must match the interface specified here. The encrypt function should take in the original text and use the three-rail encryption approach described above, returning the encrypted string. The decrypt function should assume that the msg is already encrypted as described above and decrypt it, returning the original text. Examples The following image shows the results of executing the required functions. >>> encrypted anerypt("There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home.") 'Trinra yeoda cpeitihehescono unaournhroe annulut mt em >>> original - decrypt Concrypted) >>> original There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home. >>> encrypted 3. ROT-13 Cipher Problem Implement a ROT13 simple replacement cipher as described in Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ROT13). Limit your transformation to the lowercase letters, and enforce it by converting the input string to lower case. Also, you do not have to transform punctuation or spaces. Requirements Implement the ROT13 cipher above, placing your code in the file p4_3-py. Define the functions encrypt (msg-str)-str and decrypt (msg:str)-str. You may define other functions, but these functions must match the interface specified here. Examples The following image shows the results of executing the required functions. >>> encrypted = encrypt("To driven jocks help fax my big quiz") >>> encrypted "gjb gevira wboxt urye snk al ovt dhun >>> original = encrypt(encrypted) >>> original two driven jacks help fax my big quiz Use the tests provided in CodingRooms to verify your solution. You can also use https://rot13.com/to check the correctness of your encryption results. 4. Cipher Chooser [50] Problem In this final problem, you will create a cipher chooser function crypt, which takes as an argument a specific cipher to use and applies it to the input string This problem requires that you use the solutions from parts 1.2 and 3, so before you start, import the p4_1-py. P4_2-py, and p4_3-py files. crypt is a straightforward function; your code should not extend beyond a couple of lines Examples The following image shows the results of executing the required functions. >>> print (cryptiahoy, there!".04.1. encrypt) hy hr! A, tee >>>print(crypt'hy hrl, tee 4_1.decrypt)) Ahoy, there! >>> print (crypt("Ahoy, there!". Pl_2.encrypt)) Aytr, heo el >>>print(crypt("Aytrh, heee!", p4_2.decrypt)) Ahoy, there! >>> print (crypt("Ahoy, therel, 4_3.encrypt)) nubl, gurer! >>>print(crypt("Nubl, gurer!", p4_3.encrypt)) ahoy, there










