Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Suppose you're an investor who is very flexible in terms of the amount (principal, P) and the time (t) you will be willing

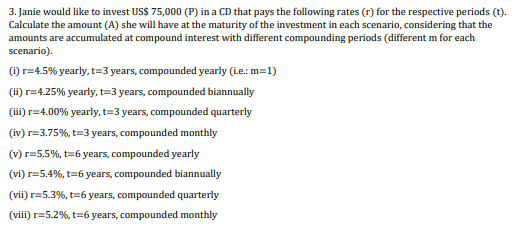
1. Suppose you're an investor who is very flexible in terms of the amount (principal, P) and the time (t) you will be willing to keep your money in the Bank A, located in the USA. Bank A's rates are always at simple interest. How much would be the amount (A) you would have at the end of the period in each of the situations below? Also, calculate the total interest (1) the bank would have paid you when the investment matures: (i) US$ 1,000,000 invested (principal, P) for 3 years (t), at 8% p.a. (r) (ii) US$ 1,250,000 invested (principal, P) for 4 years (t), at 9.5% p.a. (r) (iii) US$ 50,000 invested (principal, P) for 7 years (t), at 6.5% p.a. (r) (iv) US$ 850,000 invested (principal, P) for 3 years (t), at 7.5% p.a. (r) (v) US$ 500,000 invested (principal, P) for 5 years (t), at 5% p.a. (r) *p.a. = per annum, yearly interest rate 2. Now that you have the Bank A's proposal in hands, and you know how much in US Dollars (US$) you would have at the end of the periods in each of the 5 scenarios, you're ready to negotiate with other banks. One bank located in Brazil sends you rate (r) offers for the same amounts and periods above described if you were to invest in Bank A. Investing in Brazil is a little more risk than investing in the USA. Therefore, the Brazilian bank offer will have better interest rates than the bank in the USA, but to invest in Brazil, you would have to convert your dollars to Brazilian Reais (R$) in the first day of the investment, and to send back this money to the USA at the end of the period, you would have to convert the amounts in R$ to US$. Consider that at the first day (t=0) of the investment in Brazil, you would be able to buy R$ 5.50 with US$ 1.00. For example, US$ 1,000,000 dollars would correspond to an investment of R$ 5,500,000 in Brazil at t=0, the value considered as principal for your investment. The offers of Bank B are: (i) US$ 1,000,000 invested (principal, P) for 3 years (t), at 12% p.a. (r) (ii) US$ 1,250,000 invested (principal, P) for 4 years (t), at 13.5% p.a. (r) (iii) US$ 50,000 invested (principal, P) for 7 years (t), at 10.5% p.a. (r) (iv) US$ 850,000 invested (principal, P) for 3 years (t), at 11.5% p.a. (r) (v) US$ 500,000 invested (principal, P) for 5 years (t), at 9% p.a. (r) Supposing that you know for sure the exchange rates when your investments mature (US$ appreciates against the R$, the longer the maturity): in 3 years, each R$ 1.00 can be converted to US$ 0.1681, in 4 years, each R$ 1.00 can be converted to US$ 0.1600, in 5 years each R$ 1.00 can be converted to US$ 0.1582, and in 7 years, each R$ 1.00 can be converted to US$ 0.1488, calculate the amount you would have in US Dollars (US$) if you made the investment in each of the scenarios that the Bank B in Brazil offered you. Explain what you would do in this case: would you invest in Brazil or in the USA? Why? (Hint: convert each principal in American Dollars to Brazilian Reais, simulate the investment in Brazil as you did for USA, get amounts in Brazilian Reais, convert the amounts in Brazilian Reais to American Dollars using the exchange rate given for the end of each period), and compare in which country you would be better of investing. 3. Janie would like to invest US$ 75,000 (P) in a CD that pays the following rates (r) for the respective periods (t). Calculate the amount (A) she will have at the maturity of the investment in each scenario, considering that the amounts are accumulated at compound interest with different compounding periods (different m for each scenario). (i) r=4.5% yearly, t=3 years, compounded yearly (Le.: m=1) (ii) r=4.25% yearly, t=3 years, compounded biannually (iii) r=4.00% yearly, t=3 years, compounded quarterly (iv) r=3.75%, t=3 years, compounded monthly (v) r=5.5%, t=6 years, compounded yearly (vi) r=5.4%, t=6 years, compounded biannually (vii) r=5.3%, t=6 years, compounded quarterly (viii) r=5.2%, t=6 years, compounded monthly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Bank A Investments i P 1000000 t 3 years r 8 pa A P1 r100t 10000001083 1240000 Interest 240000 ii P 1250000 t 4 years r 95 pa A P1 r100t 12500001095...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


