Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. This exercise is designed to cement your understanding of basic work and energy concepts. A block with a mass of 12.0 kg is
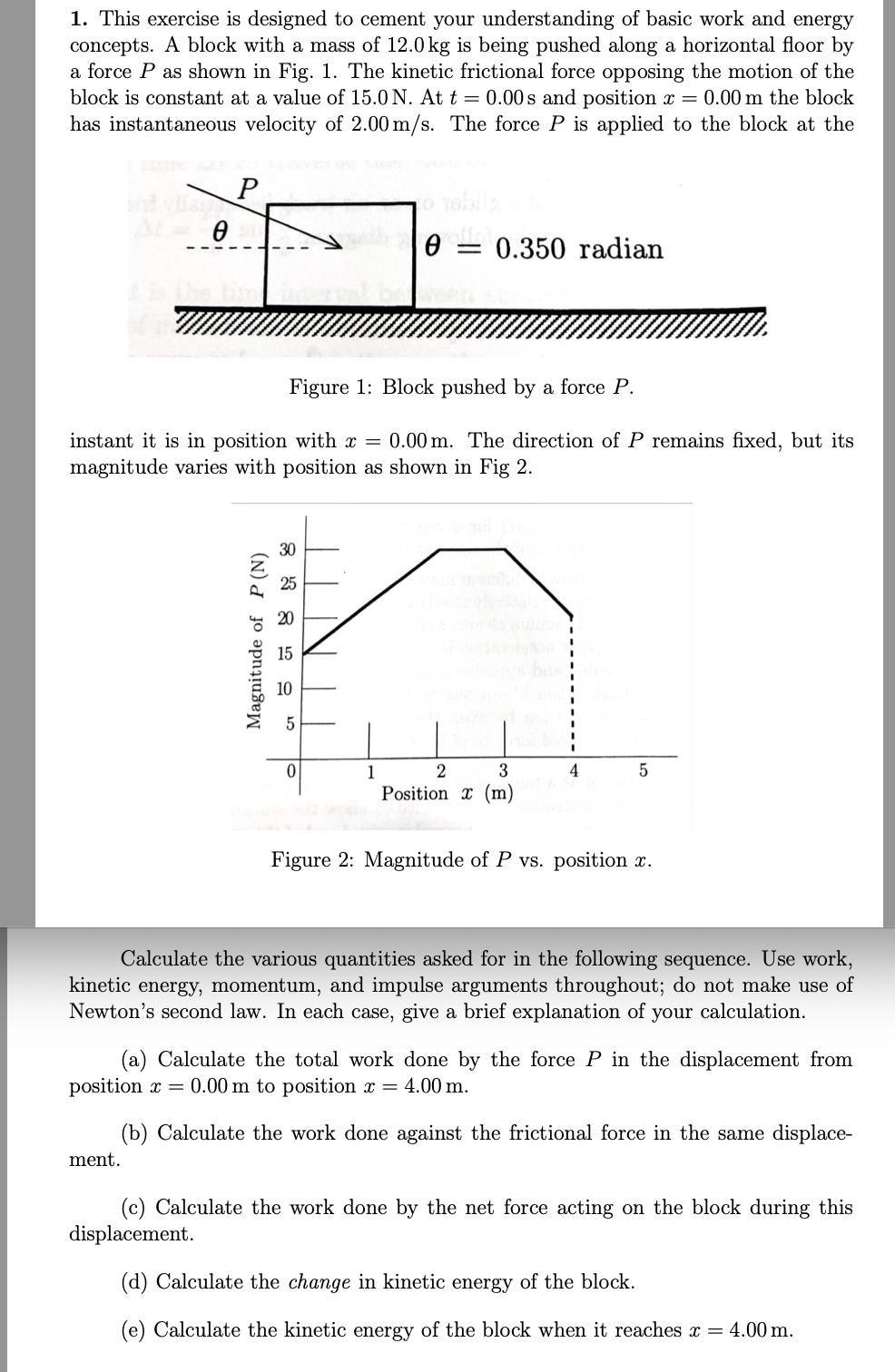
1. This exercise is designed to cement your understanding of basic work and energy concepts. A block with a mass of 12.0 kg is being pushed along a horizontal floor by a force P as shown in Fig. 1. The kinetic frictional force opposing the motion of the block is constant at a value of 15.0 N. At t = 0.00s and position x = 0.00 m the block has instantaneous velocity of 2.00 m/s. The force P is applied to the block at the P = 0.350 radian the t Figure 1: Block pushed by a force P. instant it is in position with x = 0.00 m. The direction of P remains fixed, but its magnitude varies with position as shown in Fig 2. Magnitude of P(N) 158 10 15 30 25 1 2 bus 3 4 5 Position x (m) Figure 2: Magnitude of P vs. position x. Calculate the various quantities asked for in the following sequence. Use work, kinetic energy, momentum, and impulse arguments throughout; do not make use of Newton's second law. In each case, give a brief explanation of your calculation. (a) Calculate the total work done by the force P in the displacement from position x = 0.00 m to position x = 4.00 m. ment. (b) Calculate the work done against the frictional force in the same displace- (c) Calculate the work done by the net force acting on the block during this displacement. (d) Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the block. (e) Calculate the kinetic energy of the block when it reaches x = 4.00 m.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


