1. Using the RK4 method, give the numerical approximation for the IVP: y' y(0)=e; with a step size of h = 0.5 for the
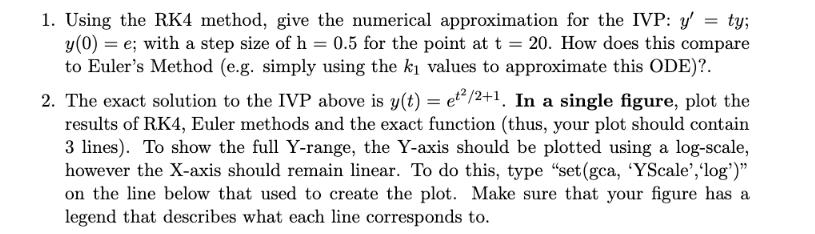
1. Using the RK4 method, give the numerical approximation for the IVP: y' y(0)=e; with a step size of h = 0.5 for the point at t = 20. How does this compare to Euler's Method (e.g. simply using the k values to approximate this ODE)?. 2. The exact solution to the IVP above is y(t) = et/2+1. In a single figure, plot the results of RK4, Euler methods and the exact function (thus, your plot should contain 3 lines). To show the full Y-range, the Y-axis should be plotted using a log-scale, however the X-axis should remain linear. To do this, type "set(gca, 'YScale', 'log')" on the line below that used to create the plot. Make sure that your figure has a legend that describes what each line corresponds to.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Solutions Step 1 To approximate the solution of the initial value problem IVPIVP using the fourthord... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed-or Get a Refund!
Step: 2Unlock detailed examples and clear explanations to master concepts

Step: 3Unlock to practice, ask and learn with real-world examples

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
-
 Access 30 Million+ textbook solutions.
Access 30 Million+ textbook solutions.
-
 Ask unlimited questions from AI Tutors.
Ask unlimited questions from AI Tutors.
-
 Order free textbooks.
Order free textbooks.
-
 100% Satisfaction Guaranteed-or Get a Refund!
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed-or Get a Refund!
Claim Your Hoodie Now!

Study Smart with AI Flashcards
Access a vast library of flashcards, create your own, and experience a game-changing transformation in how you learn and retain knowledge
Explore Flashcards