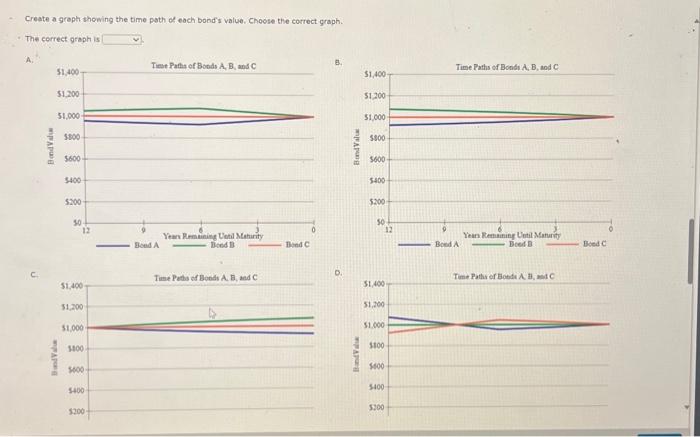
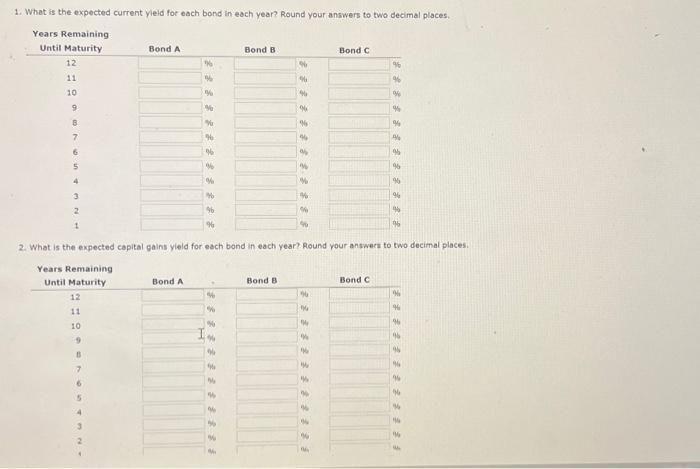
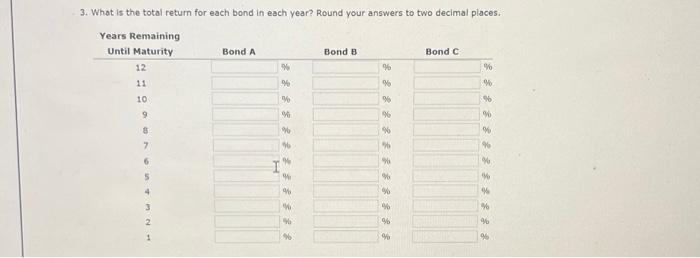
1. What is the expected current yleid for each bond in each year? Round your answers to two decimal places. 2. What is the expected capital gains yield for each bond in each year? Round vour answern to two decimal places: - 1. Explain briefiy the difference between price risk and reinvestment risk. This riak of a decline in bond values due to an increase in interest rates is called The risk of an income decline due to a drop in interest rates is calied Which of the following bonds has the mont price risko which has the most reinvestment risk? - A 1-year bond with an Bs annual coupon - A 5 veear bood with an 6 wh annual coupon - A s-year bond with a zero coupon - A 10 -year bond with an aw annual coupon - A 10-vear bond with a zero coupon A has the most price risk. A has the most reinvestment risk. 9. Calculate the price of each bend ( A,0, and C) at the end of esch year until maturity, assuming interest rates remain constant. llound your ansmert to the oearest cent. Clifford Clark is o recent cetiree who is interested in investing some of his savings in corperate bonds. His financial planner has suggested the following bonds: - Bond A has a 706 annual coupon, matures in 12 years, and has a $1,000 face value. - Bond B has a 9% annual coupon, matures in 12 years, and has a $1,000 face value. - Bond C has an 84t annual coupon, motures in 12 years, and has a $1,000 face value. Each bend has a vield to maturity of ast. The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel file below. Downioad the speeadaheet and perform the requiced analysis to answer the questiens below, Do not round intermedsate calculabons. Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any, If an anawer is zero, enter " 0 ". a. Before calculatiog the prices of the bends, indicate whether each bend is trading at a premium, at a dinceunt, of at pac- Bond A is welling at because its coupon rate is the going internt rete. Bond B is selling at because its coupon rate is the going interest rete. Bond C is selling at becouse iss coupon rate is the going interest rote. b. Calculate the price of each of the three bonds. Rgund your anwwers to the nesrest cent. Frice (Bond A) s s Price (bond B) : 1 Price (Band C) is C. Caleulate the current yield fer esch of the three bends. (Hint: The expected current vield is calcviated as the annuel interest divided by the price of the bend.) Reund vour answers to the decimal places. Current vield (Bond A): c. Calculate the current yield for each of the three bonds. (Hint: The expected current yield is caiculated as the annual interest divided by the price of the bond.) Round your answers to two decimal places. Current yieid (Bond A ): Current yield (Bond B): Current yield (Bond C ): d. If the yeld to maturity for esch bend remains at as, what will be the price of each bond 1 year from now? Round your answers to the neareat cent. Price (Bond A): 5 Price ( Bond B): 5 Price (Bond C): 5 What is the expected capital gains yield for esch bond? What is the expected total return for each bond? Round your answers to two decimal places. C. Mr. Clark a considering another bend, Eond D, It has an 0% semiannual coupon and a $1,000 foce value (1.e, it pays a 540 coupon every 6 months). Bond D is scheduled to mature in 6 vears and has a price of $1,160. It is also callable in 4 yesrs at a call price of $1,070. 1. What is the fonds nominal veld to maturity? Round your answer to two decimal places. 2. What is the bond's nominal vield to call? Round your answer to two decinal places. 3. If Me Cark were to purchate this bond, would he be more likely to recelve the vieid to maturity or yield to call? Euplein your answer. Becruis the vTM is the vTC, Mr. Clark expect the bond to be called. Consequentiy, he would earm f. Copiain briefly the ofference beteeth price riak and reinyestment risk: Create a grept thewing the time path of each bond's value. Choose the correct graph. - The correct graph is 3. What is the total return for each bond in each year? Round your answers to two decimal places












