Question
1) Why is there a strong negative correlation between Swiss francs exchange rate and SNB foreign reserves? Apply the demand and supply model to explain.
1) Why is there a strong negative correlation between Swiss francs exchange rate and SNB foreign reserves? Apply the demand and supply model to explain. 2) What is an exchange rate floor policy? Was it effective? Why could the policy trigger a rebound in Swiss franc exchange rate around September of 2011? 3) How could the SNB achieve the exchange rate floor via its monetary policy? What does this policy imply about Swiss monetary policy, interest rate, and foreign reserves? 4) Why has the interest rate been negative? Apply the money demand and supply model. 5) Apply the money-supply-reserve-adjustment model to analyze the domestic money and credit conditions in Switzerland for the period examined. 6) Based on the SNB policy interest rate graph, was FX sterilization pursued by the SNB when it engaged in exchange rate floor policy? Explain. 7) How would the SNB exchange rate and interest rate policies affect Swiss internal and external balances? Explain with the DD-AA-XX model. 8) What and how can the macroeconomic and financial data be used to verify the prediction in (7)?
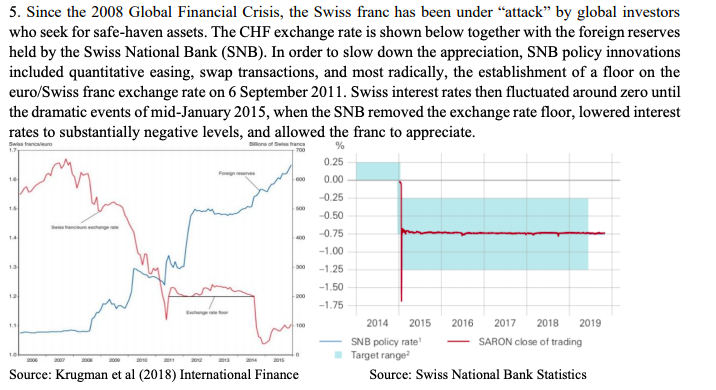
5. Since the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, the Swiss franc has been under "attack by global investors who seek for safe haven assets. The CHF exchange rate is shown below together with the foreign reserves held by the Swiss National Bank (SNB). In order to slow down the appreciation, SNB policy innovations included quantitative easing, swap transactions, and most radically, the establishment of a floor on the euro/Swiss franc exchange rate on 6 September 2011. Swiss interest rates then fluctuated around zero until the dramatic events of mid-January 2015, when the SNB removed the exchange rate floor, lowered interest rates to substantially negative levels, and allowed the franc to appreciate. % 0.25 0.00 -0.25 -0.50 -0.75 -1.00 13 -1.25 -1.50 -1.75 100 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 SNB policy rate SARON close of trading Target range? Source: Swiss National Bank Statistics 0 Source: Krugman et al (2018) International Finance 5. Since the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, the Swiss franc has been under "attack by global investors who seek for safe haven assets. The CHF exchange rate is shown below together with the foreign reserves held by the Swiss National Bank (SNB). In order to slow down the appreciation, SNB policy innovations included quantitative easing, swap transactions, and most radically, the establishment of a floor on the euro/Swiss franc exchange rate on 6 September 2011. Swiss interest rates then fluctuated around zero until the dramatic events of mid-January 2015, when the SNB removed the exchange rate floor, lowered interest rates to substantially negative levels, and allowed the franc to appreciate. % 0.25 0.00 -0.25 -0.50 -0.75 -1.00 13 -1.25 -1.50 -1.75 100 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 SNB policy rate SARON close of trading Target range? Source: Swiss National Bank Statistics 0 Source: Krugman et al (2018) International FinanceStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


