Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
11. Inferences about the difference between two population proportions Most major survey research organizations do not include wireless telephone numbers when conducting random-digit-dial telephone

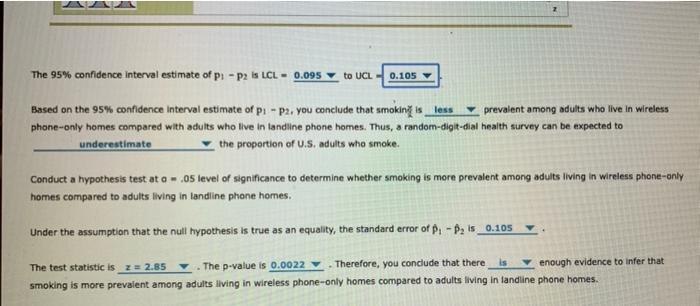
11. Inferences about the difference between two population proportions Most major survey research organizations do not include wireless telephone numbers when conducting random-digit-dial telephone surveys. If there are differences between persons with and without landline phones, using a random-digit-dial telephone survey may introduce bias into the survey results. Data on a broad range of health topics are collected through personal household interviews of a representative sample of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population in the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). Since respondents are also asked about their telephones, the NHIS data allow you to compare the health status of persons with and without landline phones. Let pi denote the proportion of adults living in wireless phone-only homes who are smokers and p2 denote the proportion of adults living in landline phone homes who are smokers. Independent random samples are selected from the two populations. Sample 1, with sample size ni 120, provides a sample proportion ; -0.31. Sample 2, with sample size n2 265, provides a sample proportion ; 0.18. (The sample results are representative of the data collected in the NHIS, but the sample sizes are much smaller.) Use the Distributions tool to help you answer the questions that follow. Standard Normal Distribution Mean-00 Standard Deviation-1.0 The 95% confidence interval estimate of p: -p2 is LCL 0.095 to UCL 0.105 prevalent among adults who live in wireless Based on the 95% confidence interval estimate of p: -p2, you conclude that smoking is less phone-only homes compared with adults who live in landline phone homes. Thus, a random-digit-dial health survey can be expected to underestimate the proportion of U.S. adults who smoke. Conduct a hypothesis test at a .05 level of significance to determine whether smoking is more prevalent among adults living in wireless phone-only homes compared to adults living in landline phone homes. Under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true as an equality, the standard error of p-p is 0.105 is enough evidence to infer that The test statistic is z=2.85 The p-value is 0.0022 Therefore, you conclude that there smoking is more prevalent among adults living in wireless phone-only homes compared to adults living in landline phone homes.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


