Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
11. The rotating solid shaft is simply supported by bearings at points B1 and B2 and it's made of a heat-treated steel (yield strength
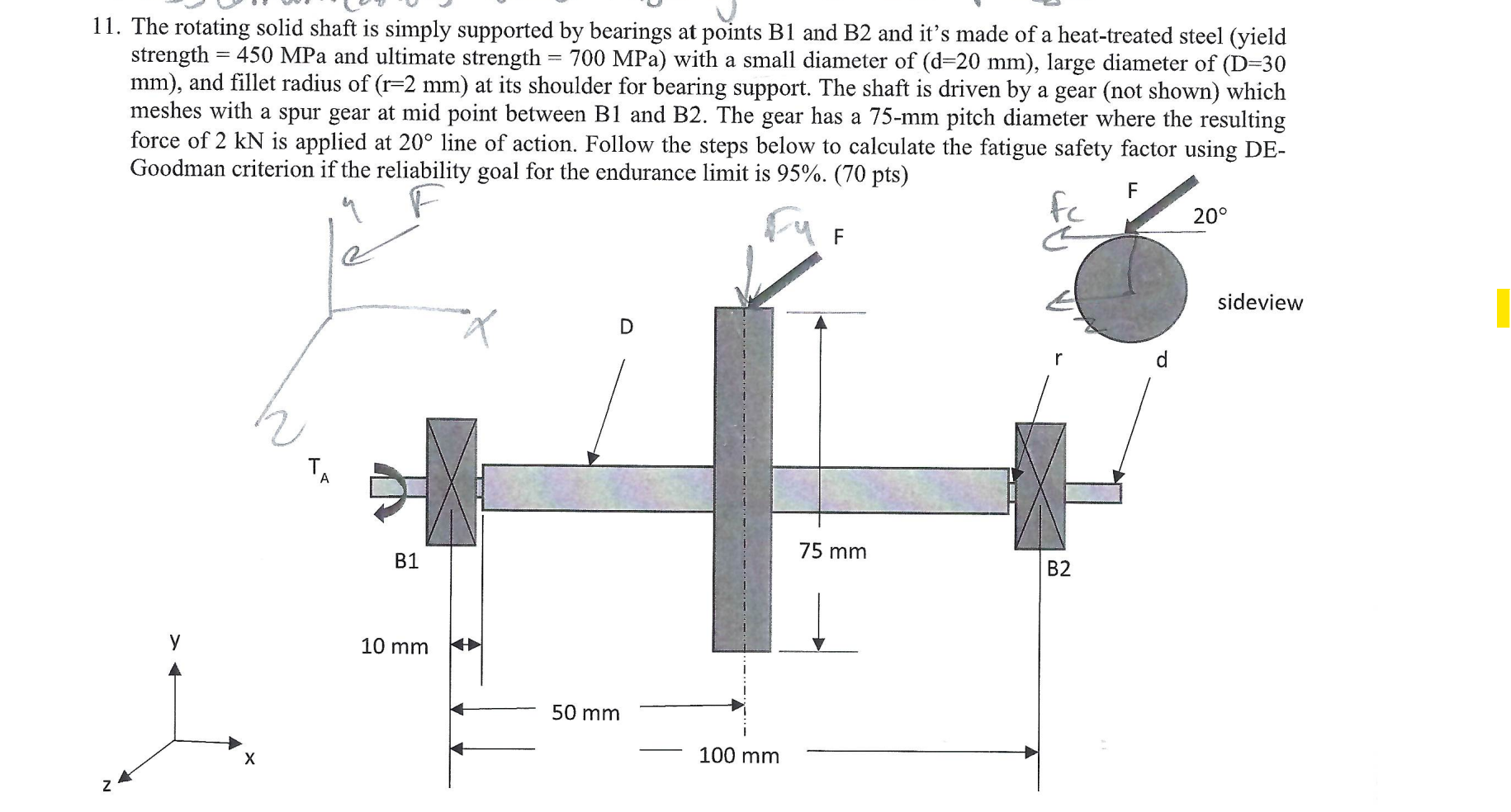


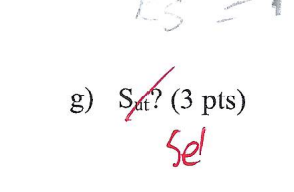

11. The rotating solid shaft is simply supported by bearings at points B1 and B2 and it's made of a heat-treated steel (yield strength = 450 MPa and ultimate strength = 700 MPa) with a small diameter of (d=20 mm), large diameter of (D=30 mm), and fillet radius of (r-2 mm) at its shoulder for bearing support. The shaft is driven by a gear (not shown) which meshes with a spur gear at mid point between B1 and B2. The gear has a 75-mm pitch diameter where the resulting force of 2 kN is applied at 20 line of action. Follow the steps below to calculate the fatigue safety factor using DE- Goodman criterion if the reliability goal for the endurance limit is 95%. (70 pts) F F fc Z X B1 10 mm X H 50 mm D 100 mm F 75 mm r B2 d 20 sideview b) Draw resultant moment and torque diagrams from point B1 to B2. (8 pts) c) What are the values of Ma. Mm. Ta. Tm at the shoulder? (4 pts) n) Extra credit (10 points): Continuing from Problem 11, a customer wants to use the device for about 10 years during working days (for 5 hours per day) at 1256 rpm. Do you recommend using an 02-series single-row deep-groove ball bearing with a 55-mm bore for B2? Why? g) Sat? (3 pts) Sel h) Se? (8 pts) i) a'? (5 pts) j) om'? (5 pts) k) Omax'? (6 pts) 1) Fatigue factor of safety ne? m) Static factor of safety ns? (5 pts)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


