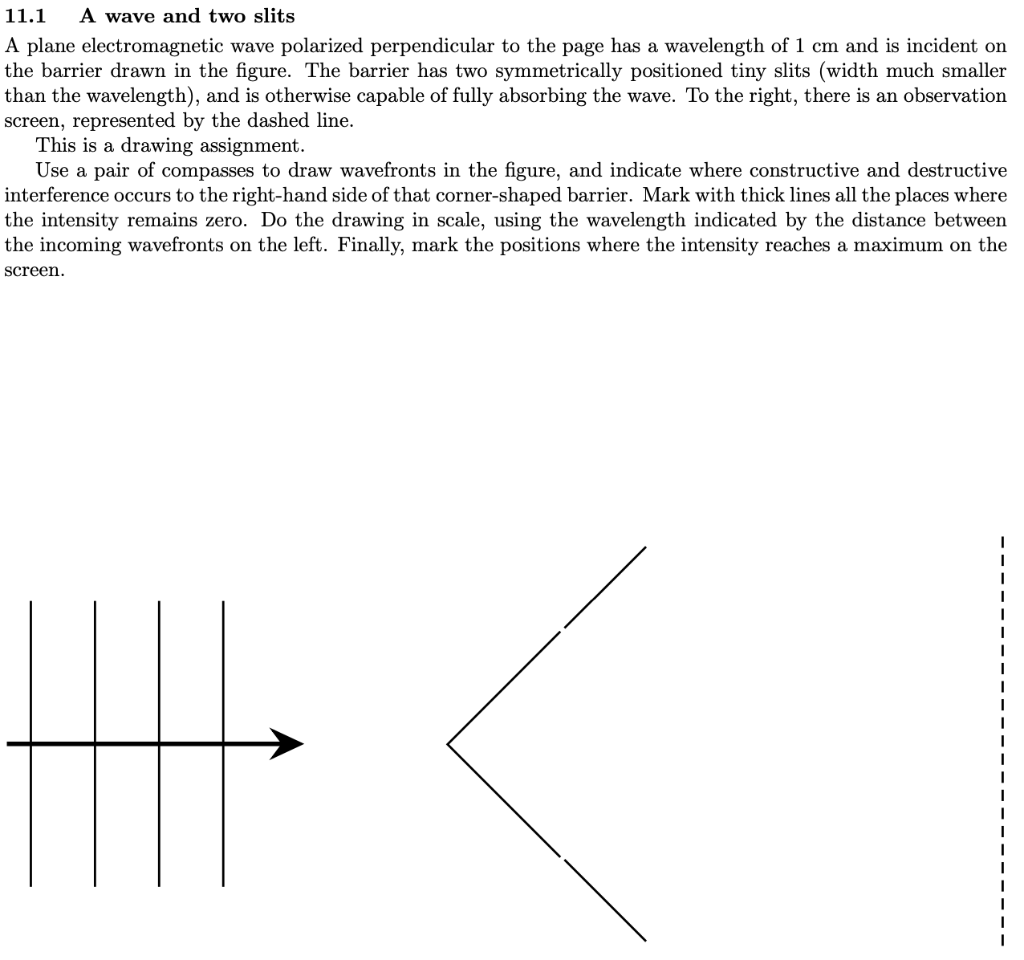

11.1 A wave and two slits A plane electromagnetic wave polarized perpendicular to the page has a wavelength of 1 cm and is incident on the barrier drawn in the figure. The barrier has two symmetrically positioned tiny slits (width much smaller than the wavelength), and is otherwise capable of fully absorbing the wave. To the right, there is an observation screen, represented by the dashed line. This is a drawing assignment. Use a pair of compasses to draw wavefronts in the figure, and indicate where constructive and destructive interference occurs to the right-hand side of that corner-shaped barrier. Mark with thick lines all the places where the intensity remains zero. Do the drawing in scale, using the wavelength indicated by the distance between the incoming wavefronts on the left. Finally, mark the positions where the intensity reaches a maximum on the screen. I 1 1 1 I 1 1 1 1 I 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 I 1 1 I screen x=0 11.2 Two plane waves Two plane electromagnetic waves have the same wavelength, the same polarization (their electric field points out of the page), the same intensity Io, and two different wavevectors, ki and k2, as given in the figure. We are measuring the total intensity in a region of space where the two waves cross cross. This problem is about finding out how the pattern of intensity (or of electric energy density) looks like in the region where the two waves cross. First, draw the wavefronts like in the previous problem (you know their direction, just pick a wavelength the distance be- k2 tween the wavefronts that gives you a beautiful drawing). Then, use the wavefronts to get a picture of the intensity pat- tern. In a next step use the algebraic expressions that describe these two waves to find the intensity pattern mathematically. Do as much as you can. This assignment is graded for effort, not for doing everything and getting everything right. One good way to start is to consider a screen that is illuminated at the same time by both waves. The intensity that falls on the screen is measured as a function of the position on the r-axis, as shown in the figure. The wavevectors of the two waves are at an angle +8 and -B with respect to the plane (indicated by a dashed line in the figure) that is perpendicular to the x-axis. In the figure, B = +30. The crests of both waves arrive at the same time at the point with coordinate x = 0 on the screen, but in general they will arrive at different times at other points. The following list gives a few hints about ways to approach these questions, which can serve as a step-by-step guide towards answering them. But those are only suggestions. You can also follow other paths. One good alternative to the list below is to calculate the intensity at any given point by just calculating the energy density and then time-averaging it, based on the time dependence of the electric fields of the two waves, that can in general be written as functions of the time and their wavevectors ki and k2. As an example, the electric field of one wave can be written as Et,r) = E. cos(wt-kir). From this, find the total electric field, square it for the energy density, and determine how it depends on space. Will there be places where the energy density becomes zero? 1. Assume that the wave with wavevector k2 oscillates as sin(wt) at the coordinate I = 0. It will oscillate as sin(wt+) at a coordinate . Calculate the phase-shift o as a function of c. 2. The wave with wavevector ki also oscillates as sin(wt) at the coordinate r = 0. But what is its phase shift as a function of r? 3. We have seen that both waves oscillate as sin(wt) at x = 0. What is the total light intensity at








