Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1,2,3,4,5 Q 1 of 5 + View as Text Download Q1. Kitchen Appliances has two divisions --- Southern division and a Northern division. The following
1,2,3,4,5 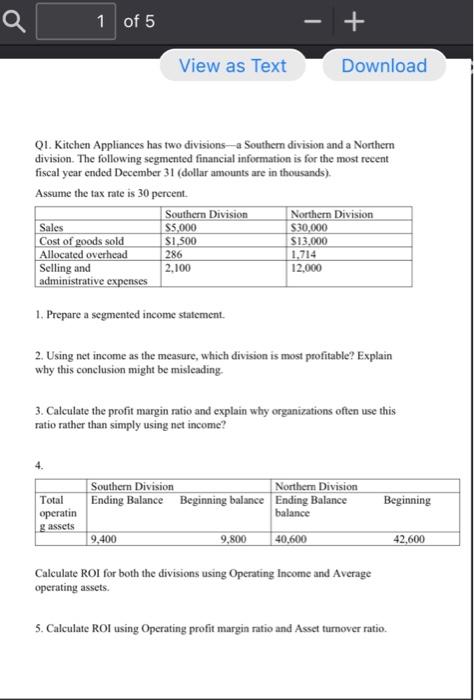
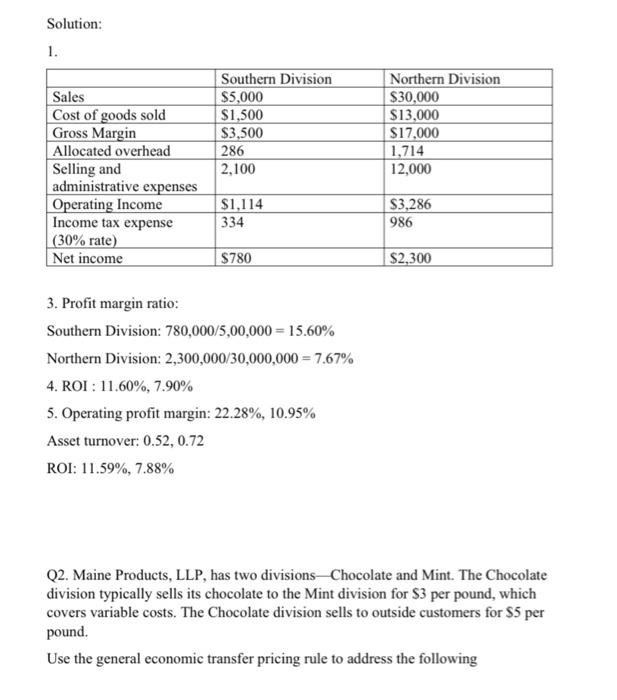

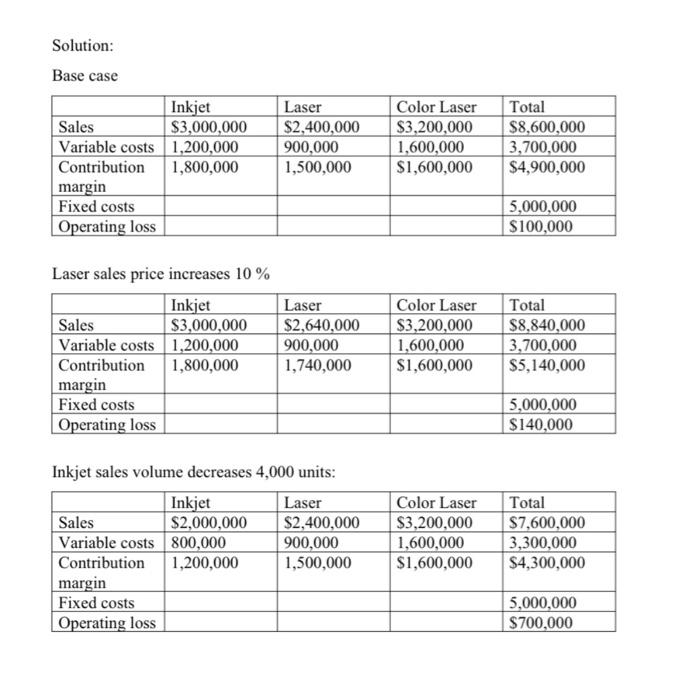
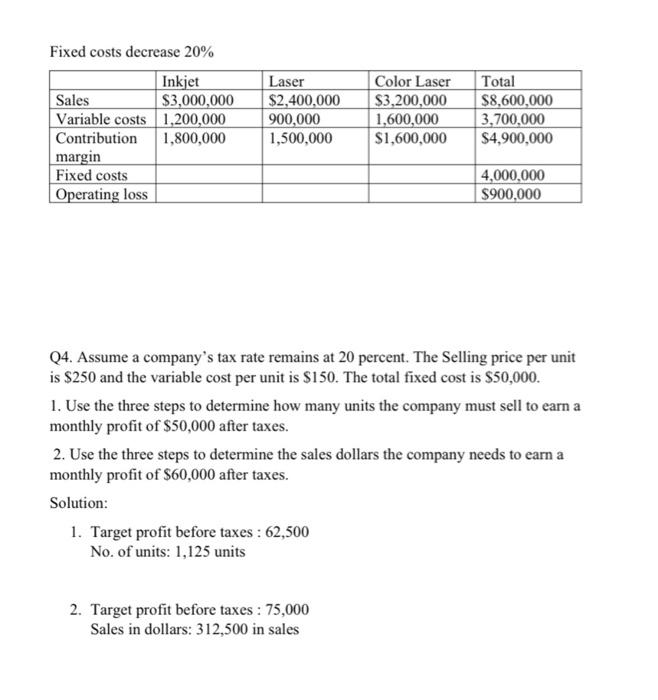
Q 1 of 5 + View as Text Download Q1. Kitchen Appliances has two divisions --- Southern division and a Northern division. The following segmented financial information is for the most recent fiscal year ended December 31 (dollar amounts are in thousands) Assume the tax rate is 30 percent. Southern Division Northern Division Sales $5,000 $30,000 Cost of goods sold $1.500 $13,000 Allocated overhead 286 1.714 Selling and 2,100 12.000 administrative expenses 1. Prepare a segmented income statement. 2. Using net income as the measure, which division is most profitable? Explain why this conclusion might be misleading 3. Calculate the profit margin ratio and explain why organizations often use this ratio rather than simply using net income? 4. Total Beginning operatin g assets Southern Division Northern Division Ending Balance Beginning balance Ending Balance balance 9,400 9,800 40.600 42,600 Calculate ROI for both the divisions using Operating Income and Average operating assets. 5. Calculate ROI using Operating profit margin ratio and Asset turnover ratio. Solution: 1. Southern Division $5,000 $1,500 $3,500 286 2.100 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross Margin Allocated overhead Selling and administrative expenses Operating Income Income tax expense (30% rate) Net income Northern Division $30,000 $13,000 $17,000 1,714 12,000 $1,114 334 $3,286 986 $780 $2,300 3. Profit margin ratio: Southern Division: 780,000/5,00,000 = 15.60% Northern Division: 2,300,000/30,000,000 = 7.67% 4. ROI : 11.60%, 7.90% 5. Operating profit margin: 22.28%, 10.95% Asset turnover: 0.52, 0.72 ROI: 11.59%, 7.88% Q2. Maine Products, LLP, has two divisions-Chocolate and Mint. The Chocolate division typically sells its chocolate to the Mint division for $3 per pound, which covers variable costs. The Chocolate division sells to outside customers for $5 per pound. Use the general economic transfer pricing rule to address the following 1. Calculate the optimal transfer price assuming the Chocolate division is below capacity. Ans is $3 2. Calculate the optimal transfer price assuming the Chocolate division is at capacity. Ans is $5 Q3. Sensitivity analysis IPM builds three computer printer models: Inkjet, Laser, and color Laser. Base case information for these three products is as follows: Inkjet Laser Color laser Total Selling price $250 $400 $1,600 per unit Variable cost $100 $150 $800 per unit Expected unit 12,000 6,000 2,000 20,000 sales(annual) Sales mix 60% 30% 10% 100% Total annual fixed costs are $5,000,000. Assume that each scenario that follows is independent of the others. Unless stated otherwise, the variables are the same as in the base case. 1. Prepare a contribution margin income statement for the base case. 2. How will total profit change if the Laser sales price increases by 10 percent? 3. How will total profit change if the Inkjet sales volume decreases by 4,000 units and the sales volume of other products remains the same? 4. How will total profit change if fixed costs decrease by 20 percent? Solution: Base case Inkjet Sales $3,000,000 Variable costs 1,200,000 Contribution 1,800,000 margin Fixed costs Operating loss Laser $2,400,000 900,000 1,500,000 Color Laser $3,200,000 1,600,000 $1,600,000 Total $8,600,000 3,700,000 $4,900,000 5,000,000 $100,000 Laser sales price increases 10% Inkjet Laser Sales $3,000,000 $2,640,000 Variable costs 1,200,000 900,000 Contribution 1,800,000 1,740,000 margin Fixed costs Operating loss Color Laser $3,200,000 1,600,000 $1,600,000 Total $8,840,000 3,700,000 $5,140,000 5,000,000 $140,000 Inkjet sales volume decreases 4,000 units: Inkjet Laser Sales $2,000,000 $2,400,000 Variable costs 800,000 900,000 Contribution 1,200,000 1,500,000 margin Fixed costs Operating loss Color Laser $3,200,000 1,600,000 $1,600,000 Total $7,600,000 3,300,000 $4,300,000 5,000,000 $700,000 Fixed costs decrease 20% Inkjet Sales $3,000,000 Variable costs 1,200,000 Contribution 1,800,000 margin Fixed costs Operating loss Laser $2,400,000 900,000 1,500,000 Color Laser $3,200,000 1,600,000 $1,600,000 Total $8,600,000 3,700,000 $4,900,000 4,000,000 $900,000 Q4. Assume a company's tax rate remains at 20 percent. The Selling price per unit is $250 and the variable cost per unit is $150. The total fixed cost is $50,000. 1. Use the three steps to determine how many units the company must sell to earn a monthly profit of $50,000 after taxes. 2. Use the three steps to determine the sales dollars the company needs to earn a monthly profit of $60,000 after taxes. Solution: 1. Target profit before taxes : 62,500 No. of units: 1,125 units 2. Target profit before taxes : 75,000 Sales in dollars: 312,500 in sales 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


