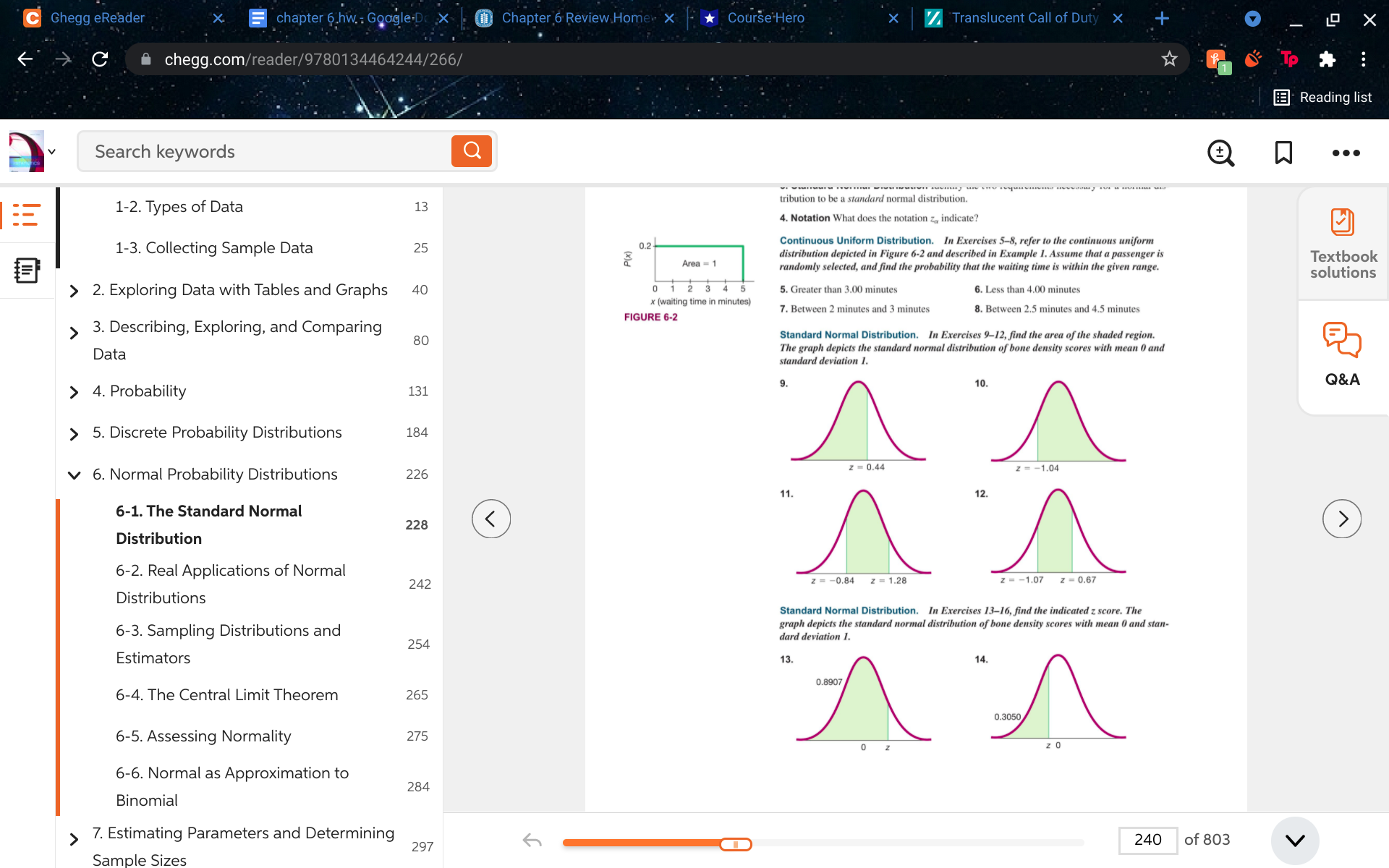
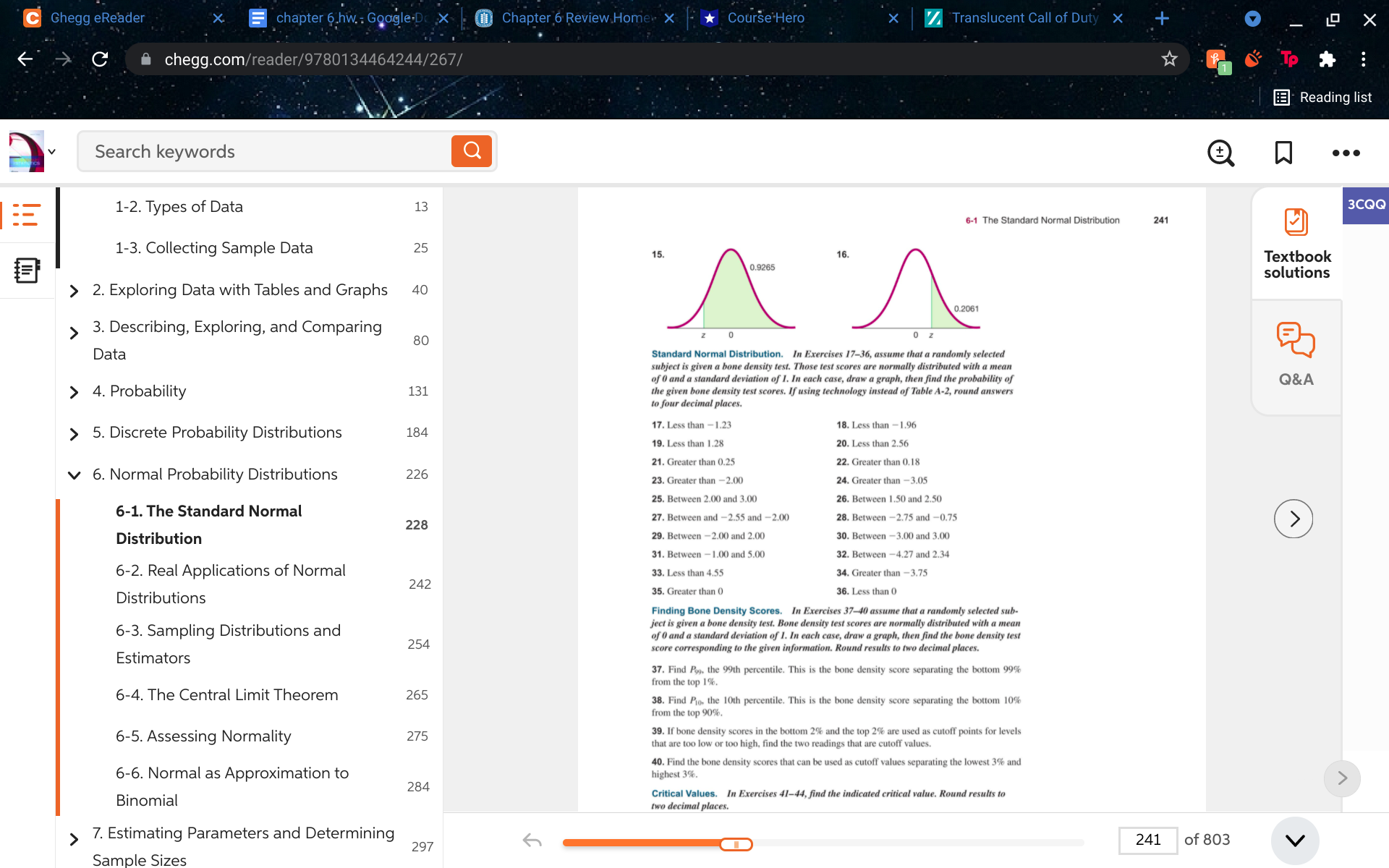
13, 14, 15, 16
C Chegg eReader chapter 6 hw. : Google.Dc X Chapter 6 Review Home X Course Hero X Translucent Call of Duty X 4 X C A chegg.com/reader/9780134464244/266/ To . .. Reading list 2 Search keywords Q . . . 1-2. Types of Data 13 tribution to be a standard normal distribution. 4. Notation What does the notation z, indicate? 1-3. Collecting Sample Data 25 0.2 Continuous Uniform Distribution. In Exercises 5-8, refer to the continuous uniform P(x ) distribution depicted in Figure 6-2 and described in Example 1. Assume that a passenger is Area = 1 Textbook randomly selected, and find the probability that the waiting time is within the given range. solutions > 2. Exploring Data with Tables and Graphs 40 0 1 2 3 4 5 5. Greater than 3.00 minutes 6. Less than 4.00 minutes x (waiting time in minutes) FIGURE 6-2 7. Between 2 minutes and 3 minutes 8. Between 2.5 minutes and 4.5 minutes 3. Describing, Exploring, and Comparing 80 Standard Normal Distribution. In Exercises 9-12, find the area of the shaded region. Data The graph depicts the standard normal distribution of bone density scores with mean 0 and standard deviation 1. Q&A > 4. Probability 131 > 5. Discrete Probability Distributions 184 6. Normal Probability Distributions 226 z = 0.44 Z = -1.04 11. 12. 6-1. The Standard Normal 228 7. Estimating Parameters and Determining 297 240 of 803 V Sample SizesC Chegg eReader chapter 6 hw. : Google.Dc X Chapter 6 Review Home X Course Hero X Translucent Call of Duty X 4 X C A chegg.com/reader/9780134464244/267/ To . .. Reading list 2 Search keywords Q .. . 1-2. Types of Data 13 3CQG 6-1 The Standard Normal Distribution 241 1-3. Collecting Sample Data 25 15. 16. Textbook 0.9265 solutions > 2. Exploring Data with Tables and Graphs 40 0.2061 3. Describing, Exploring, and Comparing 80 0 0 z Data Standard Normal Distribution. In Exercises 17-36, assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. In each case, draw a graph, then find the probability of Q& A > 4. Probability 131 the given bone density test scores. If using technology instead of Table A-2, round answers to four decimal places. > 5. Discrete Probability Distributions 184 17. Less than - 1.23 18. Less than - 1.96 19. Less than 1.28 20. Less than 2.56 21. Greater than 0.25 22. Greater than 0.18 6. Normal Probability Distributions 226 23. Greater than -2.00 24. Greater than - 3.05 25. Between 2.00 and 3.00 26. Between 1.50 and 2.50 6-1. The Standard Normal 228 27. Between and -2.55 and -2.00 28. Between -2.75 and -0.75 Distribution 29. Between - 2.00 and 2.00 30. Between -3.00 and 3.00 31. Between - 1.00 and 5.00 32. Between - 4.27 and 2.34 6-2. Real Applications of Normal 33. Less than 4.55 34. Greater than -3.75 242 Distributions 35. Greater than O 36. Less than 0 Finding Bone Density Scores. In Exercises 37-40 assume that a randomly selected sub- 6-3. Sampling Distributions and ject is given a bone density test. Bone density test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. In each case, draw a graph, then find the bone density test 254 score corresponding to the given information. Round results to two decimal places. Estimators 37. Find Poo, the 99th percentile. This is the bone density score separating the bottom 99% from the top 1%. 6-4. The Central Limit Theorem 265 38. Find Pio, the 10th percentile. This is the bone density score separating the bottom 10% from the top 90%. 6-5. Assessing Normality 275 39. If bone density scores in the bottom 2% and the top 2% are used as cutoff points for levels that are too low or too high, find the two readings that are cutoff values. 40. Find the bone density scores that can be used as cutoff values separating the lowest 3% and 6-6. Normal as Approximation to highest 3%. 284 Binomial Critical Values. In Exercises 41-44, find the indicated critical value. Round results to two decimal places. > 7. Estimating Parameters and Determining 297 241 of 803 V Sample Sizes