Question: 16. An electron and a proton, each with a speed of 1.2 x 107 m/s enter a magnetic field of 0.0020 T at 90 to
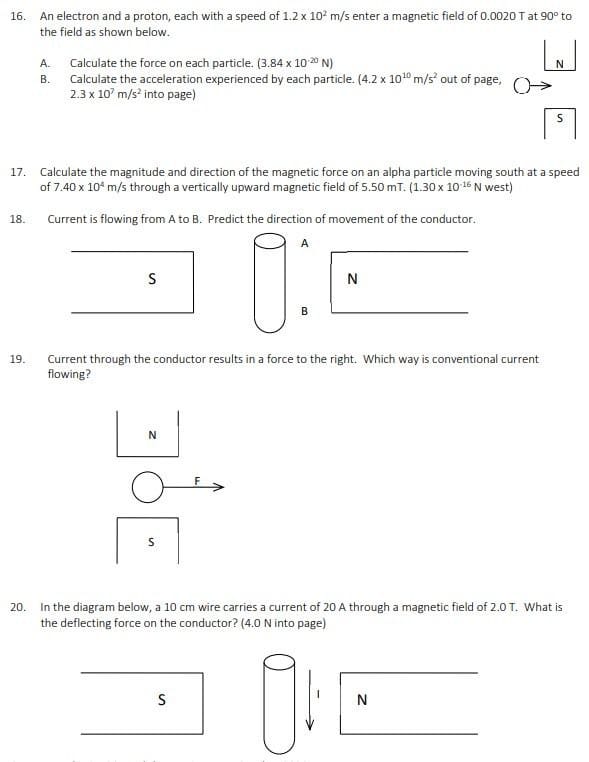
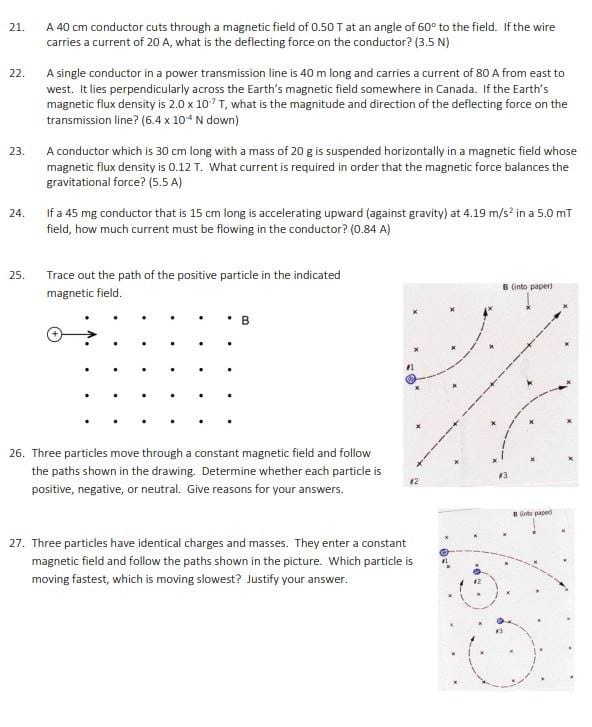
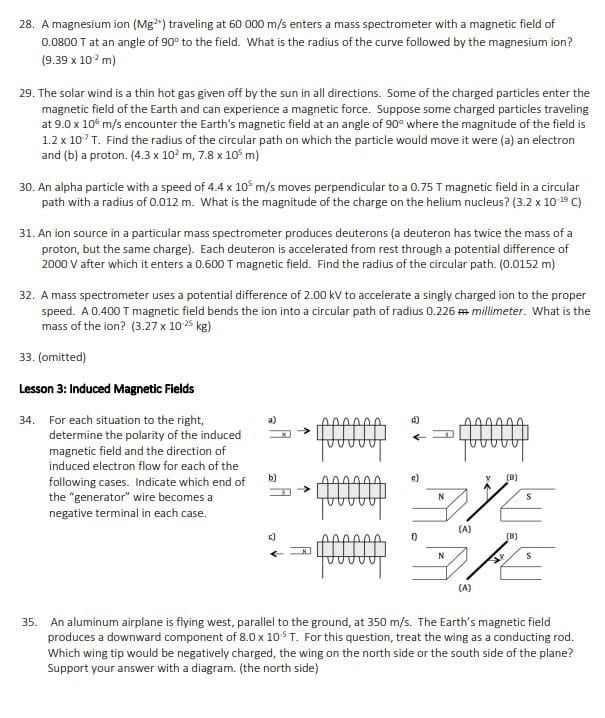
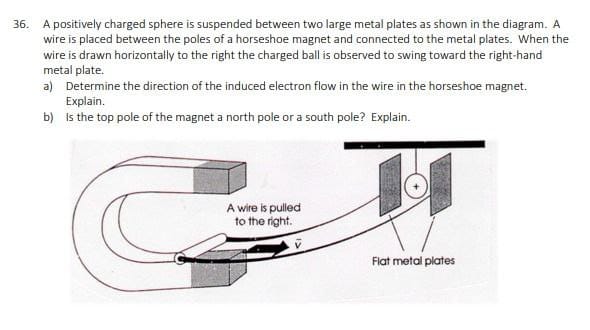
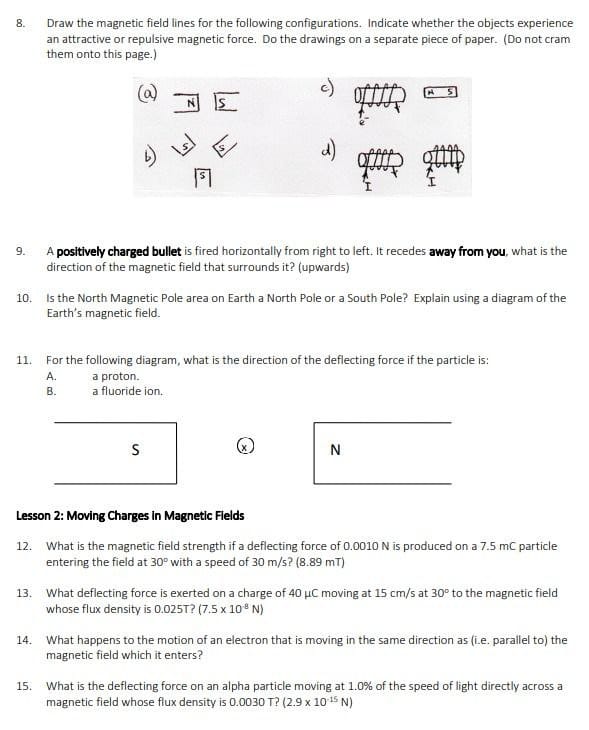
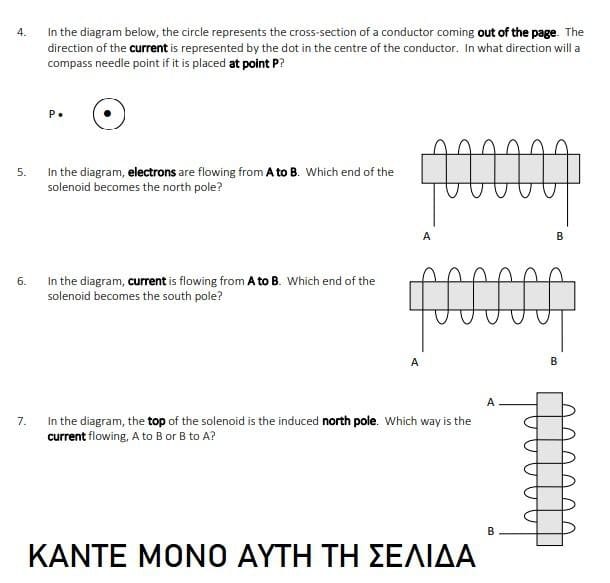
16. An electron and a proton, each with a speed of 1.2 x 107 m/s enter a magnetic field of 0.0020 T at 90 to the field as shown below. Calculate the force on each particle. (3.84 x 10 20 N) N A. B. Calculate the acceleration experienced by each particle. (4.2 x 1010 m/s' out of page, O-> 2.3 x 10' m/s' into page) 5 17. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on an alpha particle moving south at a speed of 7.40 x 10* m/s through a vertically upward magnetic field of 5.50 mT. (1.30x 10-16 N west) 18. Current is flowing from A to B. Predict the direction of movement of the conductor. A S N 19. Current through the conductor results in a force to the right. Which way is conventional current flowing? N F S 20. In the diagram below, a 10 cm wire carries a current of 20 A through a magnetic field of 2.0 T. What is the deflecting force on the conductor? (4.0 N into page) S N21. A 40 cm conductor cuts through a magnetic field of 0.50 T at an angle of 60 to the field. If the wire carries a current of 20 A, what is the deflecting force on the conductor? (3.5 N) 22. A single conductor in a power transmission line is 40 m long and carries a current of 80 A from east to west. It lies perpendicularly across the Earth's magnetic field somewhere in Canada. If the Earth's magnetic flux density is 2.0 x 10"T, what is the magnitude and direction of the deflecting force on the transmission line? (6.4 x 10* N down) 23 A conductor which is 30 cm long with a mass of 20 g is suspended horizontally in a magnetic field whose magnetic flux density is 0.12 T. What current is required in order that the magnetic force balances the gravitational force? (5.5 A) 24. If a 45 mg conductor that is 15 cm long is accelerating upward (against gravity) at 4.19 m/s in a 5.0 mT field, how much current must be flowing in the conductor? (0.84 A) 25. Trace out the path of the positive particle in the indicated D (into paper) magnetic field. 26. Three particles move through a constant magnetic field and follow the paths shown in the drawing. Determine whether each particle is 12 positive, negative, or neutral. Give reasons for your answers. 27. Three particles have identical charges and masses. They enter a constant magnetic field and follow the paths shown in the picture. Which particle is moving fastest, which is moving slowest? Justify your answer.28. A magnesium ion (Me *) traveling at 60 000 m/s enters a mass spectrometer with a magnetic field of 0.0800 T at an angle of 90" to the field. What is the radius of the curve followed by the magnesium ion? (9.39 x 10 m) 29. The solar wind is a thin hot gas given off by the sun in all directions. Some of the charged particles enter the magnetic field of the Earth and can experience a magnetic force. Suppose some charged particles traveling at 9.0 x 10# m/s encounter the Earth's magnetic field at an angle of 90" where the magnitude of the field is 1.2 x 10" T. Find the radius of the circular path on which the particle would move it were (a) an electron and (b) a proton. (4.3 x 103 m, 7.8 x 105 m) 30. An alpha particle with a speed of 4.4 x 10m/s moves perpendicular to a 0.75 T magnetic field in a circular path with a radius of 0.012 m. What is the magnitude of the charge on the helium nucleus? (3.2 x 10 9 () 31. An ion source in a particular mass spectrometer produces deuterons (a deuteron has twice the mass of a proton, but the same charge). Each deuteron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 2000 V after which it enters a 0.600 T magnetic field. Find the radius of the circular path. (0.0152 m) 32. A mass spectrometer uses a potential difference of 2.00 kV to accelerate a singly charged ion to the proper speed. A 0.400 T magnetic field bends the ion into a circular path of radius 0.226 m millimeter. What is the mass of the ion? (3.27 x 10 25 kg) 33. (omitted) Lesson 3: Induced Magnetic Fields 34. For each situation to the right, a) determine the polarity of the induced magnetic field and the direction of induced electron flow for each of the following cases. Indicate which end of bj the "generator" wire becomes a negative terminal in each case. (A) 35. An aluminum airplane is flying west, parallel to the ground, at 350 m/s. The Earth's magnetic field produces a downward component of 8.0 x 10ST. For this question, treat the wing as a conducting rod, Which wing tip would be negatively charged, the wing on the north side or the south side of the plane? Support your answer with a diagram. (the north side)36. A positively charged sphere is suspended between two large metal plates as shown in the diagram. A wire is placed between the poles of a horseshoe magnet and connected to the metal plates. When the wire is drawn horizontally to the right the charged ball is observed to swing toward the right-hand metal plate. a) Determine the direction of the induced electron flow in the wire in the horseshoe magnet. Explain. b) Is the top pole of the magnet a north pole or a south pole? Explain. A wire is pulled to the right. Flat metal platesDraw the magnetic field lines for the following configurations. Indicate whether the objects experience an attractive or repulsive magnetic force. Do the drawings on a separate piece of paper. (Do not cram them onto this page.) (a) N Is c ) offfe S d ) offff 9. A positively charged bullet is fired horizontally from right to left. It recedes away from you, what is the direction of the magnetic field that surrounds it? (upwards) 10. Is the North Magnetic Pole area on Earth a North Pole or a South Pole? Explain using a diagram of the Earth's magnetic field. 11. For the following diagram, what is the direction of the deflecting force if the particle is: A. a proton. a fluoride ion. S (x) N Lesson 2: Moving Charges In Magnetic Fields 12. What is the magnetic field strength if a deflecting force of 0.0010 N is produced on a 7.5 mC particle entering the field at 30" with a speed of 30 m/s? (8.89 mT) 13. What deflecting force is exerted on a charge of 40 pC moving at 15 cm/s at 30 to the magnetic field whose flux density is 0.025T? (7.5 x 10# N) 14. What happens to the motion of an electron that is moving in the same direction as (Le. parallel to) the magnetic field which it enters? 15. What is the deflecting force on an alpha particle moving at 1.0% of the speed of light directly across a magnetic field whose flux density is 0.0030 T? (2.9 x 10 15 N)4. In the diagram below, the circle represents the cross-section of a conductor coming out of the page. The direction of the current is represented by the dot in the centre of the conductor. In what direction will a compass needle point if it is placed at point P? P 5. In the diagram, electrons are flowing from A to B. Which end of the solenoid becomes the north pole? In the diagram, current is flowing from A to B. Which end of the solenoid becomes the south pole? A B A 7. In the diagram, the top of the solenoid is the induced north pole. Which way is the current flowing, A to B or B to A? B KANTE MONO AYTH TH EEAIAA
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


