Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
19. The demand for a necessity whose cost is a small portion of one's total income is: A. perfectly price inelastic. B. perfectly price

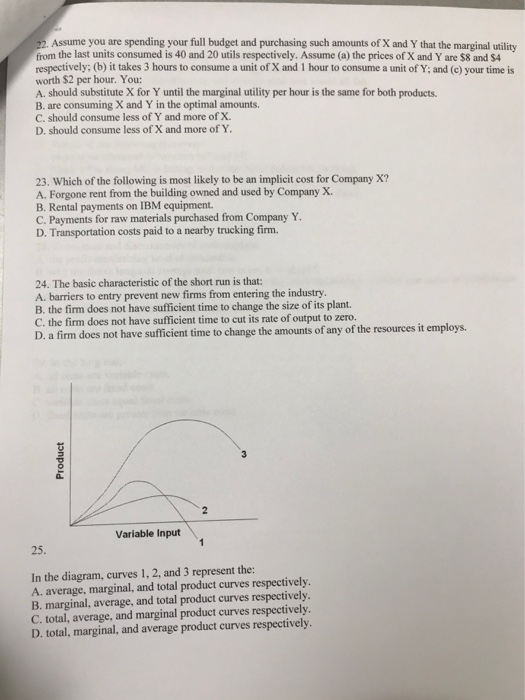

19. The demand for a necessity whose cost is a small portion of one's total income is: A. perfectly price inelastic. B. perfectly price elastic. C. relatively price inelastic. D. relatively price elastic. 20. Answer the question on the basis of the following two schedules, which show the amounts of additional satisfaction (marginal utility) that a consumer would get from successive quantities of products J and K. Units of J 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 MU 56 8982222 23 4 5 6 7 48 32 24 20 16 12 Units of J MU 1 56 48 32 24 20 16 12 Units of K MU. 1 2 3 4 5 7 Refer to the data. What level of total utility is realized from the equilibrium combination of J and K, if the consumer has a money income of $52 and the prices of J and K are $8 and $4 respectively? A. 156 utils B. 124 utils C. 276 utils D. 36 utils = 2840208 6 10 21. Answer the question on the basis of the following two schedules, which show the amounts of additional satisfaction (marginal utility) that a consumer would get from successive quantities of products J and K. 32 Units of K 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 MU. 32 28 24 20 12 10 8 Refer to the data. If the consumer's money income were cut from $52 to $28, and the prices of J and K remain $8 and $4 respectively, she would maximize her satisfaction by purchasing: A. 3 units of J and 3 units of K. B. 1 unit of J and 3 units of K. C. 4 units of J and 1 unit of K. D. 2 units of J and 3 units of K. 22. Assume you are spending your full budget and purchasing such amounts of X and Y that the marginal utility from the last units consumed is 40 and 20 utils respectively. Assume (a) the prices of X and Y are $8 and $4 respectively; (b) it takes 3 hours to consume a unit of X and 1 hour to consume a unit of Y; and (c) your time is worth $2 per hour. You: A. should substitute X for Y until the marginal utility per hour is the same for both products. B. are consuming X and Y in the optimal amounts. C. should consume less of Y and more of X. D. should consume less of X and more of Y. 23. Which of the following is most likely to be an implicit cost for Company X? A. Forgone rent from the building owned and used by Company X. B. Rental payments on IBM equipment. C. Payments for raw materials purchased from Company Y. D. Transportation costs paid to a nearby trucking firm. 24. The basic characteristic of the short run is that: A. barriers to entry prevent new firms from entering the industry. B. the firm does not have sufficient time to change the size of its plant. C. the firm does not have sufficient time to cut its rate of output to zero. D. a firm does not have sufficient time to change the amounts of any of the resources it employs. 25. Product Variable Input 2 1 In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A. average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B. marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C. total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D. total, marginal, and average product curves respectively. 26. Other things equal, if the prices of a firm's variable inputs were to fall: A. one could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected. B. marginal cost, average variable cost, and average fixed cost would all fall. C. marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost would all fall. D. average variable cost would fall, but marginal cost would be unchanged. 27. Which of the following is correct? A. There is no relationship between MP and MC. B. When AP is rising MC is falling, and when AP is falling MC is rising. C. When MP is rising MC is rising, and when MP is falling MC is falling. D. When MP is rising MC is falling, and when MP is falling MC is rising. 28. Economies and diseconomies of scale explain: A. the profit-maximizing level of production. B. why the firm's long-run average total cost curve is U-shaped. C. why the firm's short-run marginal cost curve cuts the short-run average variable cost curve at its minimum. point. D. the distinction between fixed and variable costs. 29. In the long run: A. all costs are variable costs. B. all costs are fixed costs. C. variable costs equal fixed costs. D. fixed costs are greater than variable costs.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.40 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed answer for the above question is provided below 19 Answer C relatively price inelastic Explanation relatively inelastic has the demand to ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


