Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
19B.11 Oxidation of silicon.5 A slab of silicon is exposed to gaseous oxygen (species A) at pressure p, producing a layer of silicon dioxide
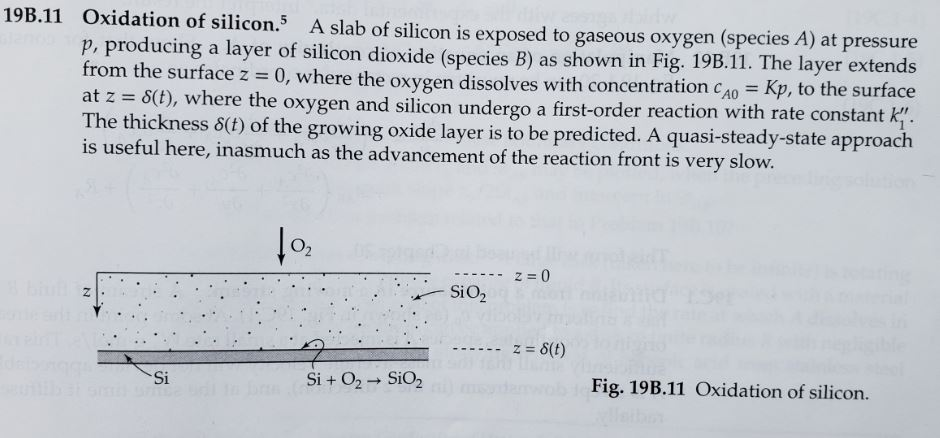
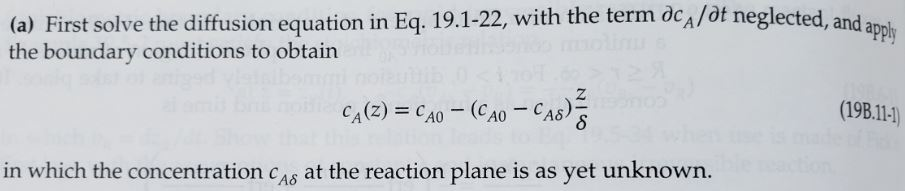
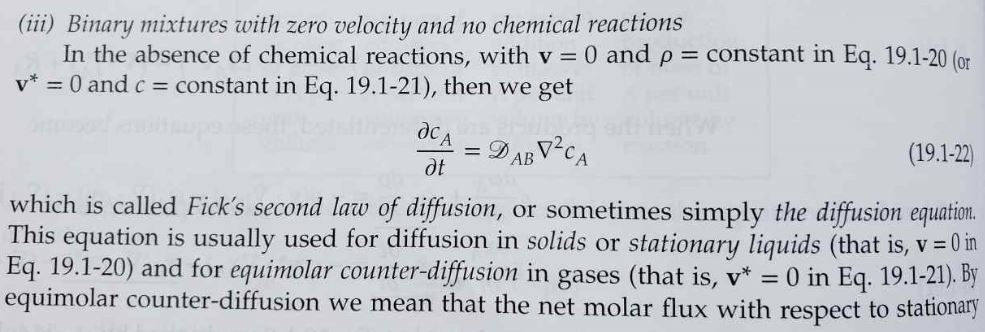
19B.11 Oxidation of silicon.5 A slab of silicon is exposed to gaseous oxygen (species A) at pressure p, producing a layer of silicon dioxide (species B) as shown in Fig. 19B.11. The layer extends from the surface z = 0, where the oxygen dissolves with concentration CA0 = Kp, to the surface at z = 8(t), where the oxygen and silicon undergo a first-order reaction with rate constant k The thickness 8(t) of the growing oxide layer is to be predicted. A quasi-steady-state approach is useful here, inasmuch as the advancement of the reaction front is very slow. squilib st sm uzu Si 10 S Si + O SiO SiO z = 0 --- z = 8(t) Fig. 19B.11 Oxidation of silicon. apply (a) First solve the diffusion equation in Eq. 19.1-22, with the term dc/ot neglected, and a the boundary conditions to obtain CA(Z) = CAO (CAO CAO) 8 in which the concentration CAS at the reaction plane is as yet unknown.e reaction. (19B.11-1) (iii) Binary mixtures with zero velocity and no chemical reactions In the absence of chemical reactions, with v = 0 and p = constant in Eq. 19.1-20 (or v* = 0 and c = constant in Eq. 19.1-21), then we get dt = DAB VCA (19.1-22) which is called Fick's second law of diffusion, or sometimes simply the diffusion equation. This equation is usually used for diffusion in solids or stationary liquids (that is, v = 0 in Eq. 19.1-20) and for equimolar counter-diffusion in gases (that is, v* = 0 in Eq. 19.1-21). By equimolar counter-diffusion we mean that the net molar flux with respect to stationary
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.43 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Solution Above ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


