Question
1.A box is supported by a 5.4 N vertical force and carried 2.5 m horizontally across a room at constant speed. Then, the same box
1.A box is supported by a 5.4 N vertical force and carried 2.5 m horizontally across a room at constant speed. Then, the same box is pushed 2.5 m horizontally across a smooth table (smooth enough to ignore friction) by a 5.4 N horizontal force. In which case was more work done on the box by the 5.4 N force?
- More work was done when the box was carried across the room.
- More work was done when the box was pushed across the table.
- The work was the same in each case, since the force and distance were of equal magnitudes in both situations.
2.A satellite in orbit decreases in speed but maintains the same angular momentum. How must the radius of the orbit change?
The radius of the orbit must increase.
The radius of the orbit must decrease.
The radius of the orbit will remain unchanged; angular momentum does not depend on speed.
3.A loaded gun is dropped on a frozen lake. The gun fires, with the bullet going horizontally in one direction and the gun sliding on the ice in the other direction. The bullet's mass is 0.03 kg, and its speed is 290 m/s. If the gun's mass is 2.1 kg, what is its speed (in m/s)? .............m/s
4.A 26 kg child uses a pogo stick to bounce up and down. The spring constant, k, of the toy equals 8,600 N/m.(a)By how much would the spring be compressed by the child if she simply balanced herself vertically on the pedals of the stick? (Give your answer in cm.)
..............cm
(b)How much energy (in J) is stored in the spring under this circumstance? ............J
5.A 3,500-kg truck runs into the rear of a 1,000-kg car that was stationary. The truck and car are locked together after the collision and move with speed 3 m/s. Compute how much kinetic energy was "lost" in this inelastic collision........... J
6.For what type of interaction between bodies is the law of conservation of linear momentum most useful?
gravity
collisions
friction
diffusion
7.When you throw a ball, the work you do to accelerate it equals the kinetic energy the ball gains. If you dotwiceas much work when throwing the ball, does it gotwice as fast? Explain.
- Yes. Twice as much work will give the ball four times as much kinetic energy. Since KE is proportional to the speed squared, the speed will be the square root of 4, or twice as fast.
- Yes. Twice as much work will give the ball twice as much kinetic energy. Since KE is proportional to the speed, the speed will double as well.
- No. Twice as much work will give the ball four times as much kinetic energy. Since KE is proportional to the speed, the speed will be four times larger.
- No. Twice as much work will give the ball twice as much kinetic energy. But since KE is proportional to the speed squared, the speed will be 2 times larger.
8.A spring is stretched by an initial amount from its relaxed state. If the spring is then stretched by five times that amount from its relaxed state, by what factor does the amount of mechanical energy stored in the spring change?
PEfinal/PEinitial=..........................
9.A sprinter with a mass of 66 kg reaches a speed of 7 m/s during a race. Find the sprinter's linear momentum (in kg m/s). (Enter the magnitude.) ............kg m/s
10.Which has the larger linear momentum: a 2,400-kg houseboat going 9 m/s or a 960-kg speedboat going 25 m/s?
houseboat
speedboat
11,Using the alternate form of Newton's second law, compute the force (in N) needed to accelerate a 1,020 kg car from 0 to 29 m/s in 20 s. The change in momentum is the car's momentum when traveling 29 m/s minus its momentum when going 0 m/s. (Enter the magnitude.) .............N
12.A runner with a mass of 63 kg accelerates from 0 to 8 m/s in 4 s. Find the net force on the runner using the alternate form of Newton's second law. ..............N
13.A pitcher throws a 0.80 kg ball of clay at a 4.0 kg block of wood. The clay sticks to the wood on impact, and their joint velocity afterward is 1.7 m/s. What was the original speed of the clay (in m/s)? ..........m/s
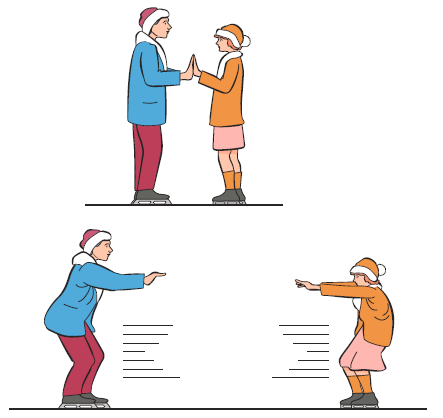
14.Two persons on ice skates stand face to face and then push each other away (see figure below). Their masses are 85 and 95 kg.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


