Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A discussion of the impact of different types of standards on motivations, and specifically the likely effect on motivation of adopting the labour standard recommended
A discussion of the impact of different types of standards on motivations, and specifically the likely effect on motivation of adopting the labour standard recommended for Harden Company by the engineering firm.
2. An evaluation of Harden Company's decision to employ dual standards in its standard cost system.
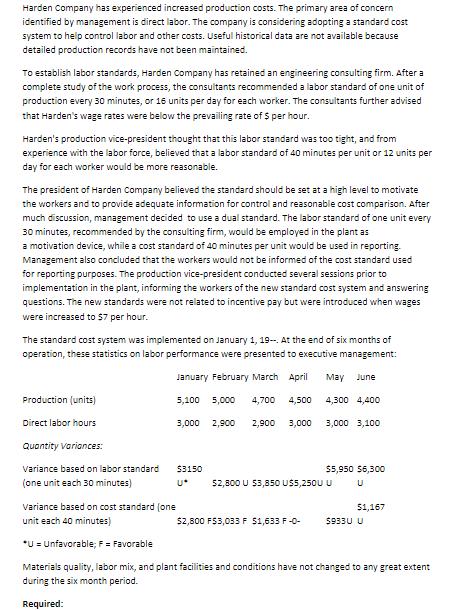
Harden Company has experienced increased production costs. The primary area of concern identified by management is direct labor. The company is considering adopting a standard cost system to help control labor and other costs. Useful historical data are not available because detailed production records have not been maintained. To establish labor standards, Harden Company has retained an engineering consulting firm. After a complete study of the work process, the consultants recommended a labor standard of one unit of production every 30 minutes, or 16 units per day for each worker. The consultants further advised that Harden's wage rates were below the prevailing rate of $ per hour. Harden's production vice-president thought that this labor standard was too tight, and from experience with the labor force, believed that a labor standard of 40 minutes per unit or 12 units per day for each worker would be more reasonable. The president of Harden Company believed the standard should be set at a high level to motivate the workers and to provide adequate information for control and reasonable cost comparison. After much discussion, management decided to use a dual standard. The labor standard of one unit every 30 minutes, recommended by the consulting firm, would be employed in the plant as a motivation device, while a cost standard of 40 minutes per unit would be used in reporting. Management also concluded that the workers would not be informed of the cost standard used for reporting purposes. The production vice-president conducted several sessions prior to implementation in the plant, informing the workers of the new standard cost system and answering questions. The new standards were not related to incentive pay but were introduced when wages were increased to 57 per hour. The standard cost system was implemented on January 1, 19--. At the end of six months of operation, these statistics on labor performance were presented to executive management: January February March April May June Production (units) 5,100 5,000 4,700 4,500 4,300 4,400 Direct labor hours 3,000 2,900 2,900 3,000 3,000 3,100 Quantity Variances: Variance based on labor standard $3150 $5,950 56,300 (one unit each 30 minutes) U* 52,800 U 53,850 US5,250U U Variance based on cost standard (one 51,167 unit each 40 minutes) $2,800 F53,033 F 51,633 F-0- 5933U U *U = Unfavorable, F = Favorable Materials quality, labor mix, and plant facilities and conditions have not changed to any great extent during the six month period. Required: Harden Company has experienced increased production costs. The primary area of concern identified by management is direct labor. The company is considering adopting a standard cost system to help control labor and other costs. Useful historical data are not available because detailed production records have not been maintained. To establish labor standards, Harden Company has retained an engineering consulting firm. After a complete study of the work process, the consultants recommended a labor standard of one unit of production every 30 minutes, or 16 units per day for each worker. The consultants further advised that Harden's wage rates were below the prevailing rate of $ per hour. Harden's production vice-president thought that this labor standard was too tight, and from experience with the labor force, believed that a labor standard of 40 minutes per unit or 12 units per day for each worker would be more reasonable. The president of Harden Company believed the standard should be set at a high level to motivate the workers and to provide adequate information for control and reasonable cost comparison. After much discussion, management decided to use a dual standard. The labor standard of one unit every 30 minutes, recommended by the consulting firm, would be employed in the plant as a motivation device, while a cost standard of 40 minutes per unit would be used in reporting. Management also concluded that the workers would not be informed of the cost standard used for reporting purposes. The production vice-president conducted several sessions prior to implementation in the plant, informing the workers of the new standard cost system and answering questions. The new standards were not related to incentive pay but were introduced when wages were increased to 57 per hour. The standard cost system was implemented on January 1, 19--. At the end of six months of operation, these statistics on labor performance were presented to executive management: January February March April May June Production (units) 5,100 5,000 4,700 4,500 4,300 4,400 Direct labor hours 3,000 2,900 2,900 3,000 3,000 3,100 Quantity Variances: Variance based on labor standard $3150 $5,950 56,300 (one unit each 30 minutes) U* 52,800 U 53,850 US5,250U U Variance based on cost standard (one 51,167 unit each 40 minutes) $2,800 F53,033 F 51,633 F-0- 5933U U *U = Unfavorable, F = Favorable Materials quality, labor mix, and plant facilities and conditions have not changed to any great extent during the six month period. Required: Harden Company has experienced increased production costs. The primary area of concern identified by management is direct labor. The company is considering adopting a standard cost system to help control labor and other costs. Useful historical data are not available because detailed production records have not been maintained. To establish labor standards, Harden Company has retained an engineering consulting firm. After a complete study of the work process, the consultants recommended a labor standard of one unit of production every 30 minutes, or 16 units per day for each worker. The consultants further advised that Harden's wage rates were below the prevailing rate of $ per hour. Harden's production vice-president thought that this labor standard was too tight, and from experience with the labor force, believed that a labor standard of 40 minutes per unit or 12 units per day for each worker would be more reasonable. The president of Harden Company believed the standard should be set at a high level to motivate the workers and to provide adequate information for control and reasonable cost comparison. After much discussion, management decided to use a dual standard. The labor standard of one unit every 30 minutes, recommended by the consulting firm, would be employed in the plant as a motivation device, while a cost standard of 40 minutes per unit would be used in reporting. Management also concluded that the workers would not be informed of the cost standard used for reporting purposes. The production vice-president conducted several sessions prior to implementation in the plant, informing the workers of the new standard cost system and answering questions. The new standards were not related to incentive pay but were introduced when wages were increased to 57 per hour. The standard cost system was implemented on January 1, 19--. At the end of six months of operation, these statistics on labor performance were presented to executive management: January February March April May June Production (units) 5,100 5,000 4,700 4,500 4,300 4,400 Direct labor hours 3,000 2,900 2,900 3,000 3,000 3,100 Quantity Variances: Variance based on labor standard $3150 $5,950 56,300 (one unit each 30 minutes) U* 52,800 U 53,850 US5,250U U Variance based on cost standard (one 51,167 unit each 40 minutes) $2,800 F53,033 F 51,633 F-0- 5933U U *U = Unfavorable, F = Favorable Materials quality, labor mix, and plant facilities and conditions have not changed to any great extent during the six month period. Required: Harden Company has experienced increased production costs. The primary area of concern identified by management is direct labor. The company is considering adopting a standard cost system to help control labor and other costs. Useful historical data are not available because detailed production records have not been maintained. To establish labor standards, Harden Company has retained an engineering consulting firm. After a complete study of the work process, the consultants recommended a labor standard of one unit of production every 30 minutes, or 16 units per day for each worker. The consultants further advised that Harden's wage rates were below the prevailing rate of $ per hour. Harden's production vice-president thought that this labor standard was too tight, and from experience with the labor force, believed that a labor standard of 40 minutes per unit or 12 units per day for each worker would be more reasonable. The president of Harden Company believed the standard should be set at a high level to motivate the workers and to provide adequate information for control and reasonable cost comparison. After much discussion, management decided to use a dual standard. The labor standard of one unit every 30 minutes, recommended by the consulting firm, would be employed in the plant as a motivation device, while a cost standard of 40 minutes per unit would be used in reporting. Management also concluded that the workers would not be informed of the cost standard used for reporting purposes. The production vice-president conducted several sessions prior to implementation in the plant, informing the workers of the new standard cost system and answering questions. The new standards were not related to incentive pay but were introduced when wages were increased to 57 per hour. The standard cost system was implemented on January 1, 19--. At the end of six months of operation, these statistics on labor performance were presented to executive management: January February March April May June Production (units) 5,100 5,000 4,700 4,500 4,300 4,400 Direct labor hours 3,000 2,900 2,900 3,000 3,000 3,100 Quantity Variances: Variance based on labor standard $3150 $5,950 56,300 (one unit each 30 minutes) U* 52,800 U 53,850 US5,250U U Variance based on cost standard (one 51,167 unit each 40 minutes) $2,800 F53,033 F 51,633 F-0- 5933U U *U = Unfavorable, F = Favorable Materials quality, labor mix, and plant facilities and conditions have not changed to any great extent during the six month period. Required:
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.32 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Different types of standards can have different effects on motivation For example if a company adopt...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


