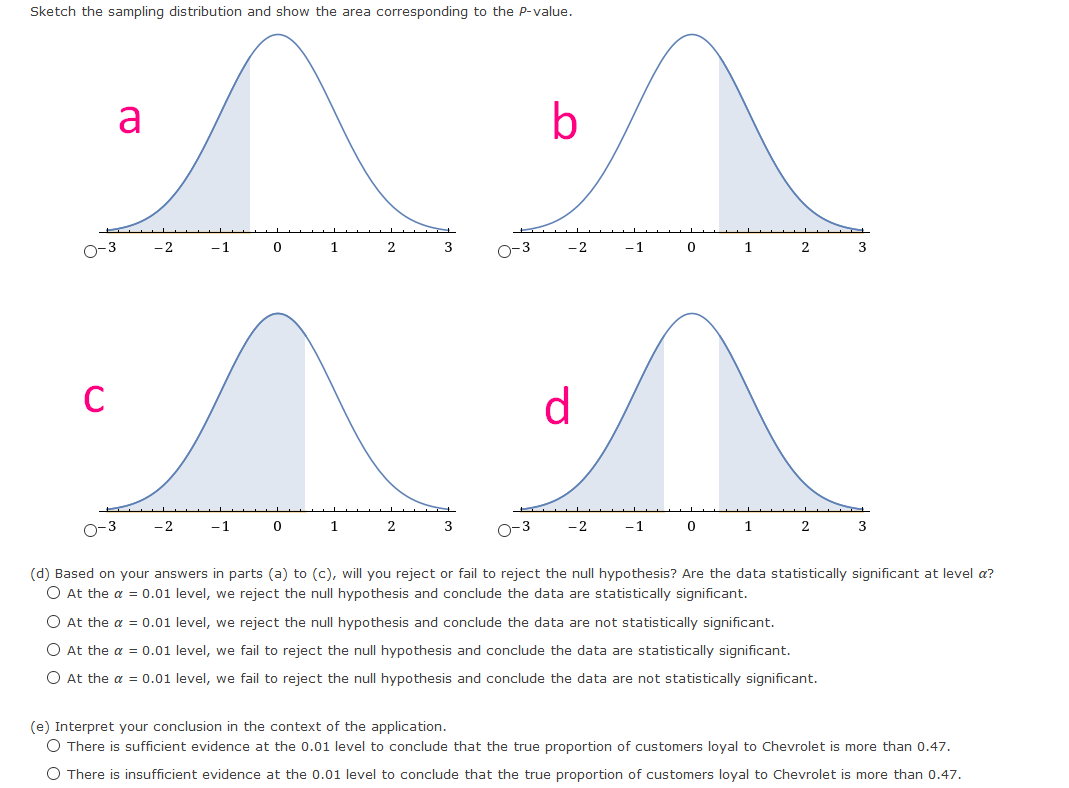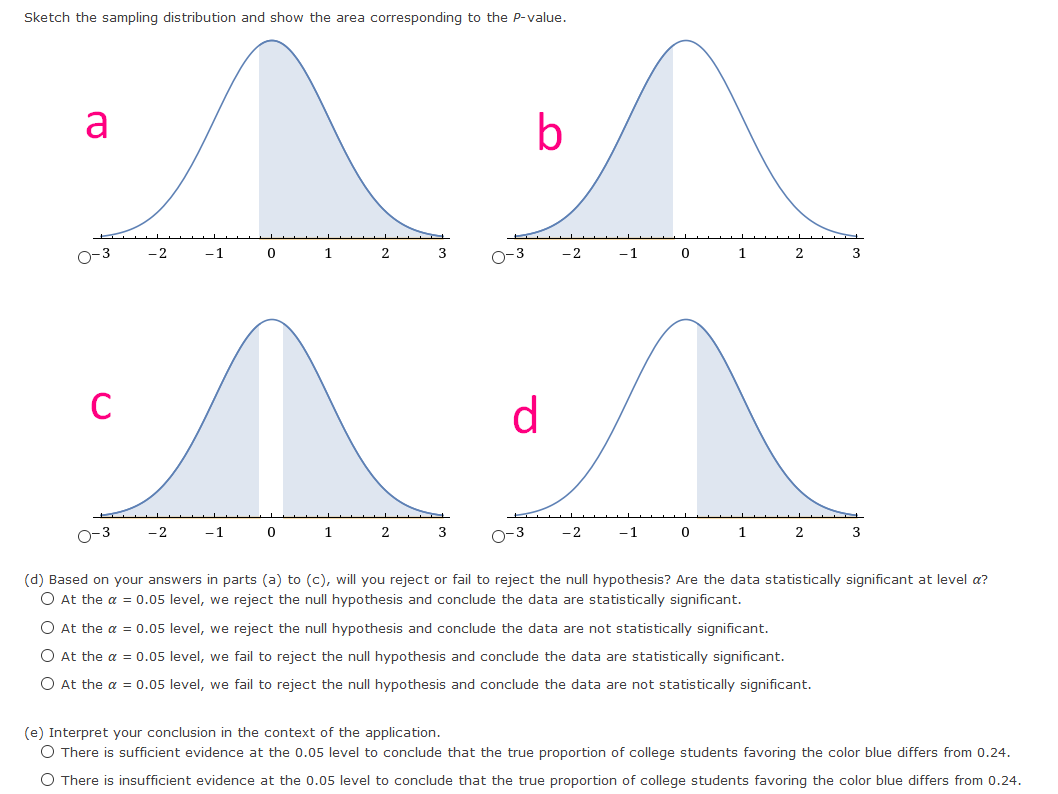
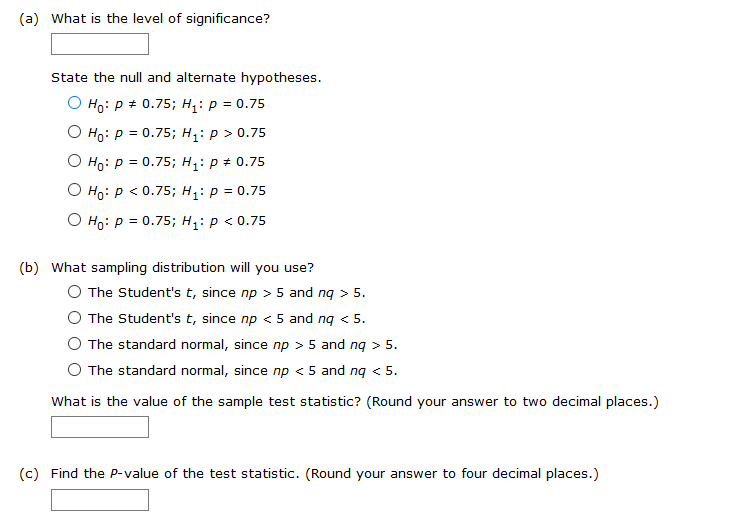
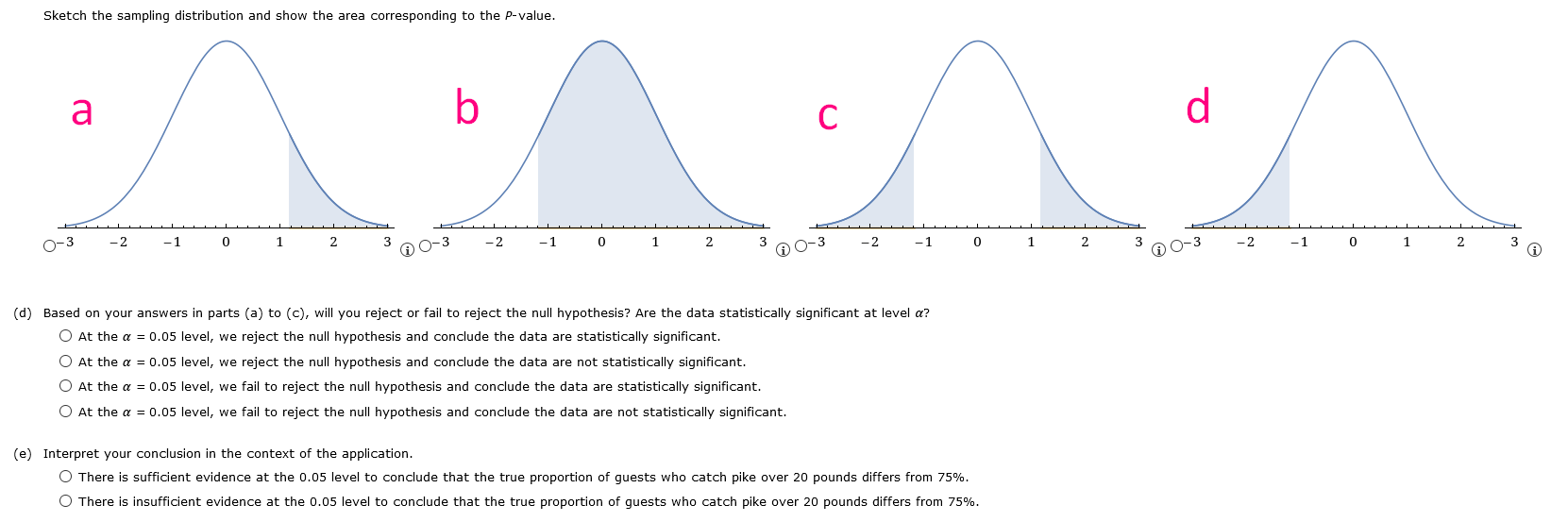


1.In general, if sample data are such that the null hypothesis is rejected at the ? = 1% level of significance based on a two-tailed test, is H0 also rejected at the ? = 1% level of significance for a corresponding one-tailed test? Explain your answer.
A. No. If the two-tailed P-value is smaller than ?, the one-tailed area is also smaller than ?.
B. Yes. If the two-tailed P-value is smaller than ?, the one-tailed area is also smaller than ?.
C. Yes. If the two-tailed P-value is smaller than ?, the one-tailed area will be larger than ?.
D. No. If the two-tailed P-value is smaller than ?, the one-tailed area will be larger than ?.
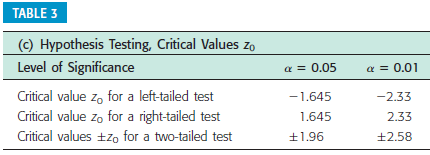
2.Is the national crime rate really going down? Some sociologists say yes! They say that the reason for the decline in crime rates in the 1980s and 1990s is demographics. It seems that the population is aging, and older people commit fewer crimes. According to the FBI and the Justice Department, 70% of all arrests are of males aged 15 to 34 years.? Suppose you are a sociologist in Rock Springs, Wyoming, and a random sample of police files showed that of 30 arrests last month, 25 were of males aged 15 to 34 years. Use a 1% level of significance to test the claim that the population proportion of such arrests is the city different from 70%. Solve the problem using both the traditional method and the P-value method. Since the sampling distribution of p? is the normal distribution, you can use critical values from the standard normal distribution as shown in the table of critical values of the z distribution. (Round the test statistic and the critical value to two decimal places. Round the P-value to four decimal places.)
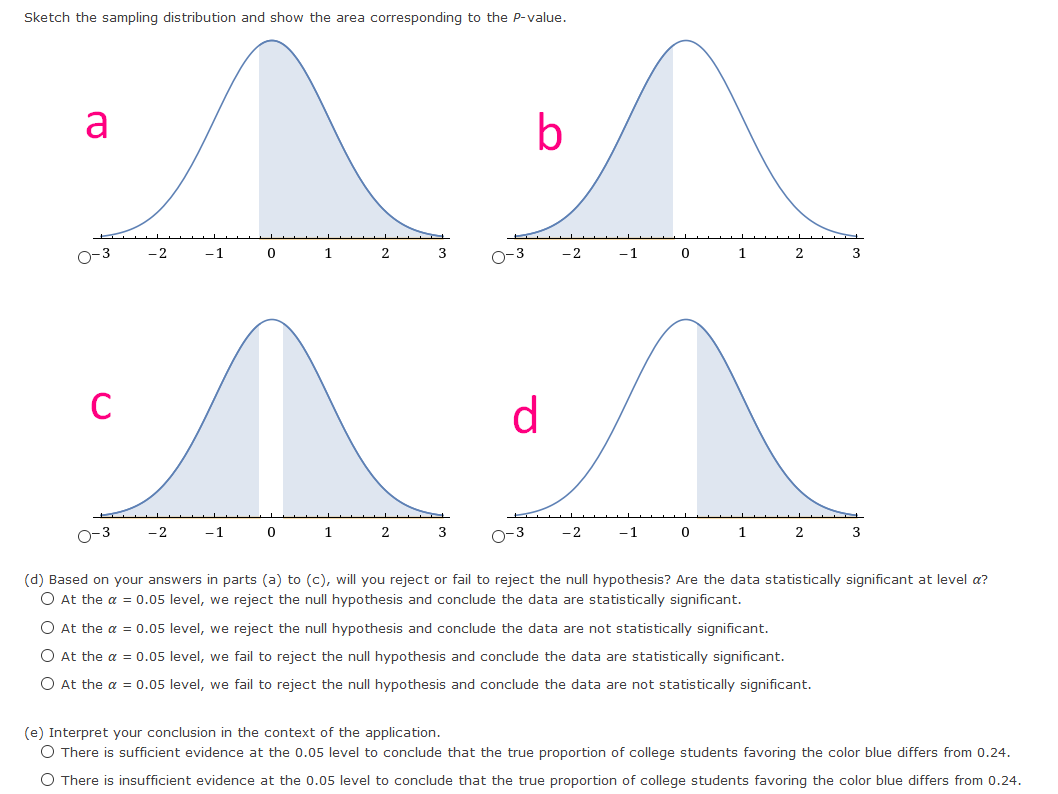
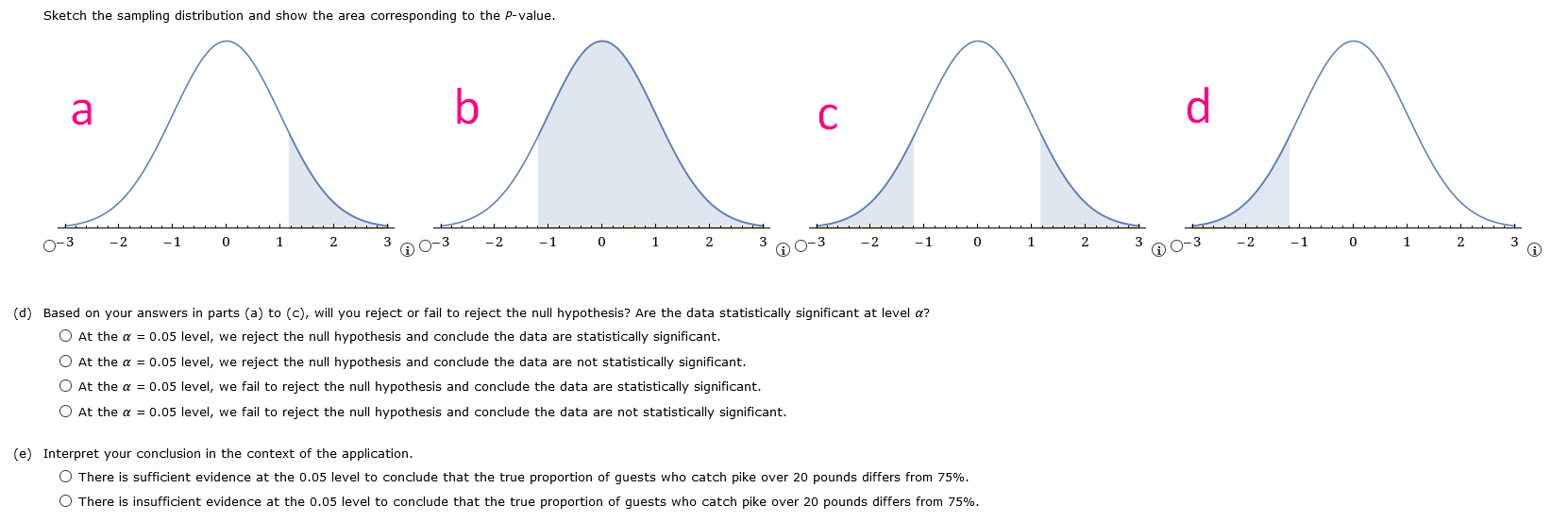
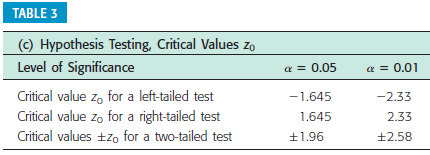
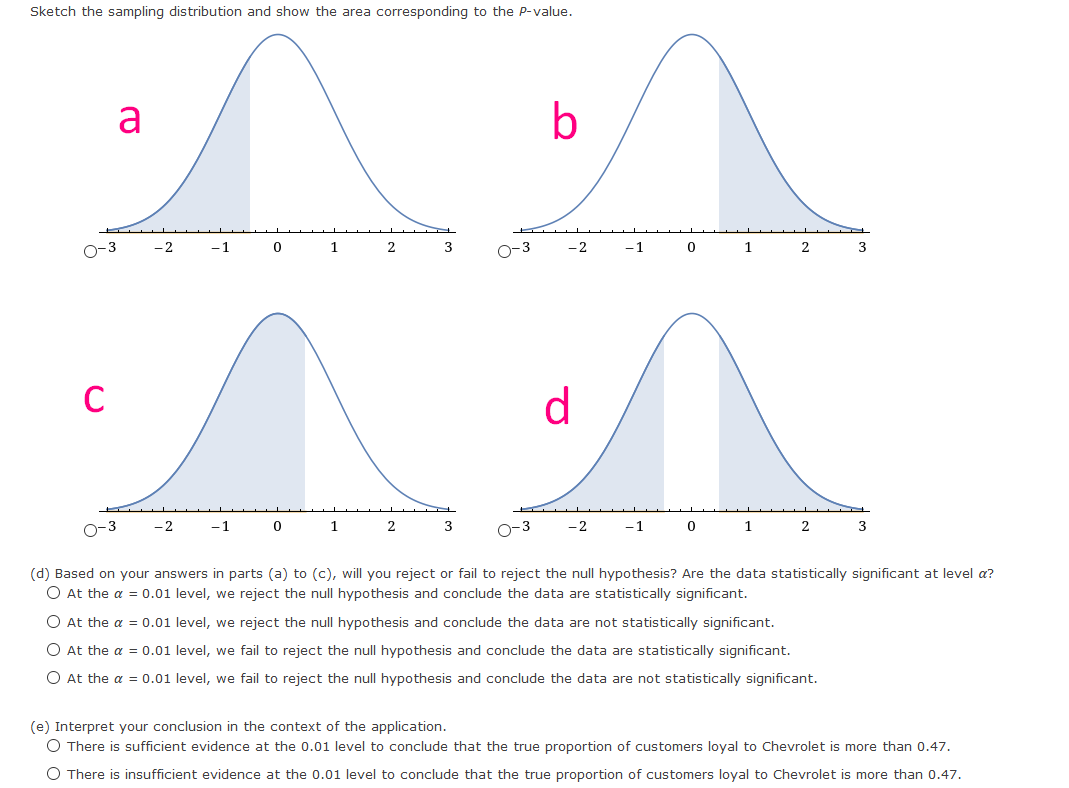
{a} What is the level of signicance? E State the null and alternate hypotheses. O HO: p = o.24; H1: p a: o.24 O HO: p = o.24; H1: p :: o.24 0 H0: .9 = o.24; H1: p : o.24 O HO: p 95 o.24; H1: p = o.24 {lo} What sampling distribution will you use? '3' The Student's t, since no c: 5 and no c: 5. D The standard normal, since no c: 5 and nor c: 5. O The Student's t, since op :- 5 and no :- 5. O The standard normal. since np :b 5 and no 3. 5. What is the value of the sample test statistic? {Round your answer to two decimal places.) E {c} Find the P-value of the test statistic. {Round your answer to four decimal places.) E Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value. a b O-3 -2 - 1 0 1 2 3 O-3 -2 - 1 0 1 2 3 C O-3 -2 -1 2 O-3 -2 -1 2 (d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level a? O At the a = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant. O At the a = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant. O At the a = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant. O At the a = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant. (e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application. O There is sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that the true proportion of college students favoring the color blue differs from 0.24. O There is insufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that the true proportion of college students favoring the color blue differs from 0.24.{a} What is the level of signicance? : State the null and alternate hypotheses. 0 H0: ,0 at on; H1: p = on 0 H0: ,0 = on; H1: p :=~ on 0 H0: ,0 = on; H1: p: on 0 H0: ,0 a: on; H1: p = on 0 Ha: {I = on: H1: p c on {lo} What sampling distribution will you use? 0 The Student's t, since op :: 5 and no a 5. C} The Student's t, since no a: 5 and nor =: 5. C} The standard normal, since np :b 5 and no :- 5. C} The standard normal, since np =: 5 and no =: 5. What is the value of the sample test statistic? {Round your answer to two decimal places.) : {c} Find the P-yalue of the test statistic. {Round your answer to four decimal places.) : Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value. a b C O-3 -2 0 A0-3 -2 2 A0-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 40-3 - 2 -1 0 1 2 3 A (d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level a? O At the a = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant. O At the a = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant. O At the a = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant. O At the a = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant. (e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application. O There is sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that the true proportion of guests who catch pike over 20 pounds differs from 75%. O There is insufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that the true proportion of guests who catch pike over 20 pounds differs from 75%.test statistic = critical value = + P- value = State your conclusion in the context of the application. There is sufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the true proportion of such arrests in the city differs from 70%. O There is insufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the true proportion of such arrests in the city differs from 70%. Compare your conclusion with the conclusion obtained by using the P-value method. Are they the same? O The conclusions obtained by using both methods are the same. O We reject the null hypothesis using the P-value method, but fail to reject using the traditional method. O We reject the null hypothesis using the traditional method, but fail to reject using the P-value method.TABLE 3 (c) Hypothesis Testing, Critical Values Zo Level of Significance ( = 0.05 a = 0.01 Critical value zo for a left-tailed test -1.645 -2.33 Critical value zo for a right-tailed test 1.645 2.33 Critical values +zo for a two-tailed test +1.96 12.58{a} What is the level of signicance? :l State the null and alternate hypotheses. O H0: .0 = 0.4?; H1: p : 0.4? (I) H0: .0 = 0.4?; H1: p a: 0.4? O H0: ,0 = 0.4?; H1: ,0 s 0.4? O HO: p := 0.4?; H1: p = 0.4? {lo} What sampling distriloution will you use? 0 The standard normal, since op <: and no the student t since np :="5" :- c op standard normal :5 what is value of sample test statistic your answer to two decimal places. :i find pvalue statistic. four sketch sampling distribution show area corresponding pvalue. based on answers in parts will you reject or fail null hypothesis are data statistically signicant at level a we conclude signicant. not interpret conclusion context application. sufcient evidence that true proportion customers loyal chevrolet more than insufcient>