Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
2. (a) A student has been asked to put some parcels on a shelf. The parcels all weigh different amounts, and the shelf has
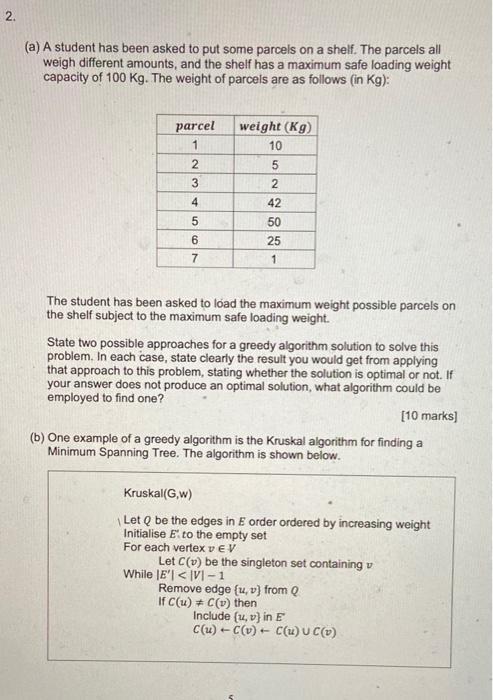
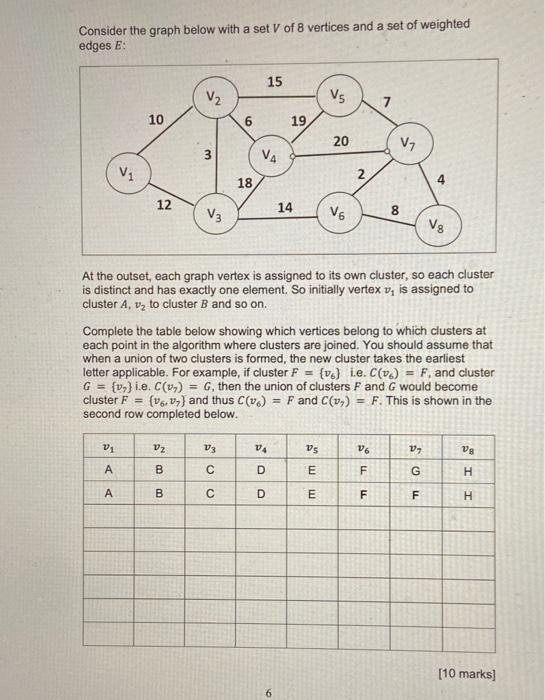

2. (a) A student has been asked to put some parcels on a shelf. The parcels all weigh different amounts, and the shelf has a maximum safe loading weight capacity of 100 Kg. The weight of parcels are as follows (in Kg): parcel 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 weight (Kg) 10 5 2 42 50 25 1 The student has been asked to load the maximum weight possible parcels on the shelf subject to the maximum safe loading weight. State two possible approaches for a greedy algorithm solution to solve this problem. In each case, state clearly the result you would get from applying that approach to this problem, stating whether the solution is optimal or not. If your answer does not produce an optimal solution, what algorithm could be employed to find one? [10 marks] (b) One example of a greedy algorithm is the Kruskal algorithm for finding a Minimum Spanning Tree. The algorithm is shown below. Kruskal(G,w) Let Q be the edges in E order ordered by increasing weight Initialise E to the empty set For each vertex v EV Let C(v) be the singleton set containing v While |E'| Consider the graph below with a set V of 8 vertices and a set of weighted edges E: V 10 V1 A A 12 V 3 Vz B B V3 6 18 V3 C C V4 15 SOO VA D D 19 14 6 V5 At the outset, each graph vertex is assigned to its own cluster, so each cluster is distinct and has exactly one element. So initially vertex V, is assigned to cluster A, to cluster B and so on. 20 Complete the table below showing which vertices belong to which clusters at each point in the algorithm where clusters are joined. You should assume that when a union of two clusters is formed, the new cluster takes the earliest letter applicable. For example, if cluster F = {v} ie. C(v) = F, and cluster G = (v) i.e. C(v) = G, then the union of clusters F and G would become cluster F= (v.7) and thus C (16) = F and C(v) = F. This is shown in the second row completed below. V5 E E V6 2 26 F 7 LL V7 F 8 4 V8 V7 G F I IS H [10 marks] (c) A message of length x symbols is made from a set of 8 symbols drawn from a vocabulary shown below, with each symbol being coded using 3 binary bits: 3-bit coding Symbol element (ii) A B C D E F G H 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 T(3) c when the size of A is 3 T(m) = T(m-3) + c otherwise Relative frequency So, the message BADGE (x = 5) would be coded as 001, 000, 011, 110,100. This message requires a constant 3 bits/symbol. Analysis shows that in general usage, the symbols appear with the relative frequency as shown also in the table. (1) 0.2 0.06 0.05 0.08 0.3 0.12 0.04 0.15 Construct a Huffman coding tree to determine the most efficient alternative coding for the symbols so as to minimise the number of bits/symbol to code a message. [10 marks] Determine the average number of bits/symbol required to code a message using this more efficient alternative coding. [5 marks] (d) A recursive algorithm is applied to some data A = (a,.....am) where m 2 3 and m is divisible by 3. The running time T is characterised using the following recurrence equations: Determine the running time complexity of this algorithm. Note that mis divisible by 3 and the problem size reduces by 3 for each recursion. [10 marks] (e) A student wishes to solve the Minimum Spanning Tree problem using a new algorithm they have devised. They decide to test their new algorithm against the well-known Kruskal and Prim algorithms. Discuss whether the new algorithm is guaranteed to produce an identical tree output as the Kruskal algorithm when provided with the same input graph. (5 marks]
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.39 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


