Question
2. A moving 3.10 kg block collides with a horizontal spring whose spring constant is 415 N/m 2.1. The block compresses the spring a maximum
2. A moving 3.10 kg block collides with a horizontal spring whose spring constant is 415 N/m
2.1. The block compresses the spring a maximum distance of 4.00 cm from its rest position. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.490. What is the work done by the spring in bringing the block to rest?
2.2. How much mechanical energy is being dissipated by the force of friction while the block is being brought to rest by the spring?
2.3. What is the speed of the block when it hits the spring?
4. Calculate the change in potential energy of a 88.9 kg man when he takes an elevator from the first floor to 39th floor, if the distance between floors is 4.05 m
7. A 2.50 kg box slides down a rough incline plane from a height h of 1.99 m. The box had a speed of 3.21 m/s at the top and a speed of 2.78 m/s at the bottom. Calculate the mechanical energy lost due to friction (as heat, etc.).
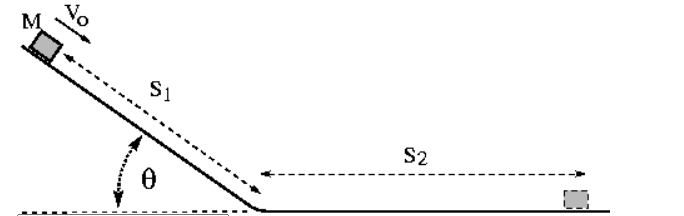
8. When mass M is at the position shown, it is sliding down the inclined part of a slide at a speed of 2.01 m/s. The mass stops a distance S2 = 1.9 m along the level part of the slide. The distance S1 = 1.07 m and the angle ? = 37.30. Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction for the mass on the surface.
9. A car (m = 680.0 kg) accelerates uniformly from rest up an inclined road which rises uniformly, to a height, h = 31.0 m. Find the average power the engine must deliver to reach a speed of 23.3 m/s at the top of the hill in 15.3 s(NEGLECT frictional losses: air and rolling, ...)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


