Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
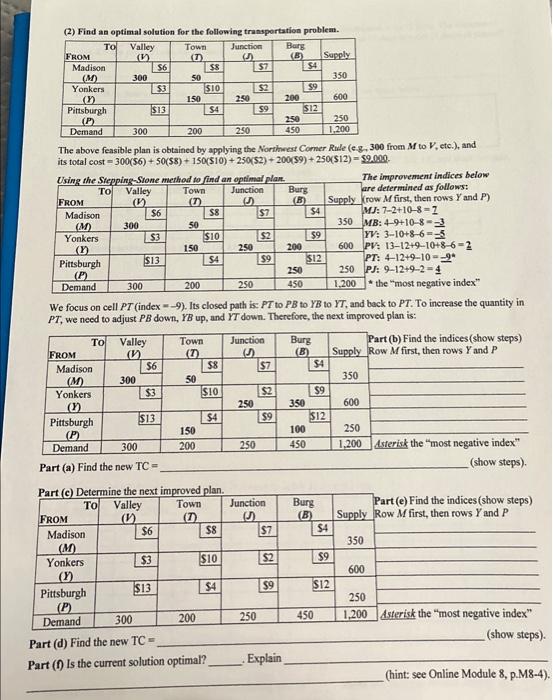
(2) Find an optimal solution for the following transportation problem. To Town (1) FROM Madison (M) Yonkers (Y) Pittsburgh (P) Demand FROM Madison (M) Yonkers
(2) Find an optimal solution for the following transportation problem. To Town (1) FROM Madison (M) Yonkers (Y) Pittsburgh (P) Demand FROM Madison (M) Yonkers (Y) Pittsburgh (P) Demand FROM Madison (M) Yonkers (Y) Valley (1) 300 FROM To Valley (1) To Madison (M) Yonkers (Y) Pittsburgh (P) Demand 300 300 Using the Stepping-Stone method to find an optimal plan. Town Junction (7) (1) Valley (1) 300 $13 $6 $3 $13 $6 $3 300 200 250 The above feasible plan is obtained by applying the Northwest Corner Rule (e.g., 300 from M to V, etc.), and its total cost = 300($6) +50($8) + 150($10) +250($2) +200($9) + 250($12) = $9,000. Pittsburgh (P) Demand 300 Part (a) Find the new TC = $6 $3 $13 $6 $3 $13 50 150 50 150 Town (7) 50 150 200 $8 $10 Town (7) $4 200 Part (c) Determine the next improved plan. To Valley (1) $8 $10 300 Part (d) Find the new TC = Part (f) Is the current solution optimal? $4 $8 $10 $4 Junction (J) $8 $10 250 $4 200 We focus on cell PT (index = -9). Its closed path is: PT to PB to YB to YT, and back to PT. To increase the quantity in PT, we need to adjust PB down, YB up, and YT down. Therefore, the next improved plan is: 250 250 $7 $2 250 $9 250 250 $7 $2 Junction () $9 $7 $2 $9 Junction () $7 $2 Burg (B) Supply $4 200 $9 Explain 250 450 200 $12 Burg (B) 250 450 $9 350 $4 100 450 $9 $12 Burg (B) $4 $9 $12 450 Burg (B) 250 1,200 350 600 The improvement indices below are determined as follows: Supply (row M first, then rows Y and P) MJ: 7-2+10-8=1 $4 $9 $12 350 600 250 1,200 MB: 4-9+10-8=-3 YV: 3-10+8-6=-5 PV: 13-12+9-10+8-6=2 350 Part (b) Find the indices (show steps) Supply Row M first, then rows Y and P 600 PT: 4-12+9-10=-9* PJ: 9-12+9-2=4 *the "most negative index" 250 1,200 Asterisk the "most negative index" (show steps). Part (e) Find the indices (show steps) Supply Row M first, then rows Y and P 350 600 250 1,200 Asterisk the "most negative index" (show steps). (hint: see Online Module 8, p.M8-4).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


