Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
2. Findings: 2.1. Evaluation of Fair Value Measurement and Disclosures # 1 Criteria Completeness 2 Faithfulness 3 Qualitative Characteristics A complete depiction includes all
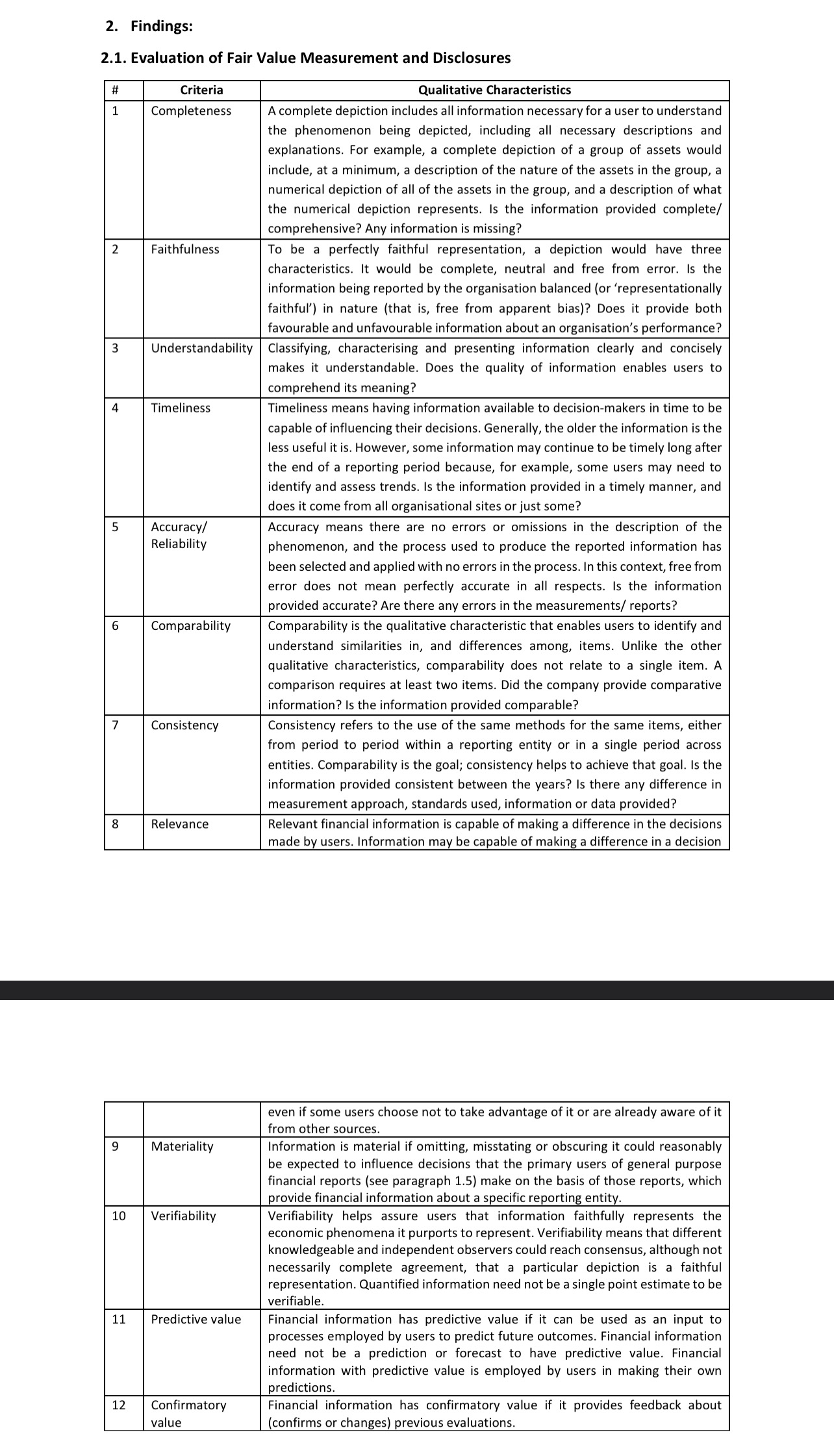
2. Findings: 2.1. Evaluation of Fair Value Measurement and Disclosures # 1 Criteria Completeness 2 Faithfulness 3 Qualitative Characteristics A complete depiction includes all information necessary for a user to understand the phenomenon being depicted, including all necessary descriptions and explanations. For example, a complete depiction of a group of assets would include, at a minimum, a description of the nature of the assets in the group, a numerical depiction of all of the assets in the group, and a description of what the numerical depiction represents. Is the information provided complete/ comprehensive? Any information is missing? To be a perfectly faithful representation, a depiction would have three characteristics. It would be complete, neutral and free from error. Is the information being reported by the organisation balanced (or 'representationally faithful') in nature (that is, free from apparent bias)? Does it provide both favourable and unfavourable information about an organisation's performance? Understandability Classifying, characterising and presenting information clearly and concisely makes it understandable. Does the quality of information enables users to comprehend its meaning? 4 Timeliness 5 Accuracy/ Reliability 6 Comparability 7 Consistency 8 Relevance Timeliness means having information available to decision-makers in time to be capable of influencing their decisions. Generally, the older the information is the less useful it is. However, some information may continue to be timely long after the end of a reporting period because, for example, some users may need to identify and assess trends. Is the information provided in a timely manner, and does it come from all organisational sites or just some? Accuracy means there are no errors or omissions in the description of the phenomenon, and the process used to produce the reported information has been selected and applied with no errors in the process. In this context, free from error does not mean perfectly accurate in all respects. Is the information provided accurate? Are there any errors in the measurements/ reports? Comparability is the qualitative characteristic that enables users to identify and understand similarities in, and differences among, items. Unlike the other qualitative characteristics, comparability does not relate to a single item. A comparison requires at least two items. Did the company provide comparative information? Is the information provided comparable? Consistency refers to the use of the same methods for the same items, either from period to period within a reporting entity or in a single period across entities. Comparability is the goal; consistency helps to achieve that goal. Is the information provided consistent between the years? Is there any difference in measurement approach, standards used, information or data provided? Relevant financial information is capable of making a difference in the decisions made by users. Information may be capable of making a difference in a decision 9 Materiality 10 11 Verifiability Predictive value Confirmatory 12 value even if some users choose not to take advantage of it or are already aware of it from other sources. Information is material if omitting, misstating or obscuring it could reasonably be expected to influence decisions that the primary users of general purpose financial reports (see paragraph 1.5) make on the basis of those reports, which provide financial information about a specific reporting entity. Verifiability helps assure users that information faithfully represents the economic phenomena it purports to represent. Verifiability means that different knowledgeable and independent observers could reach consensus, although not necessarily complete agreement, that a particular depiction is a faithful representation. Quantified information need not be a single point estimate to be verifiable. Financial information has predictive value if it can be used as an input to processes employed by users to predict future outcomes. Financial information need not be a prediction or forecast to have predictive value. Financial information with predictive value is employed by users in making their own predictions. Financial information has confirmatory value if it provides feedback about (confirms or changes) previous evaluations.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


