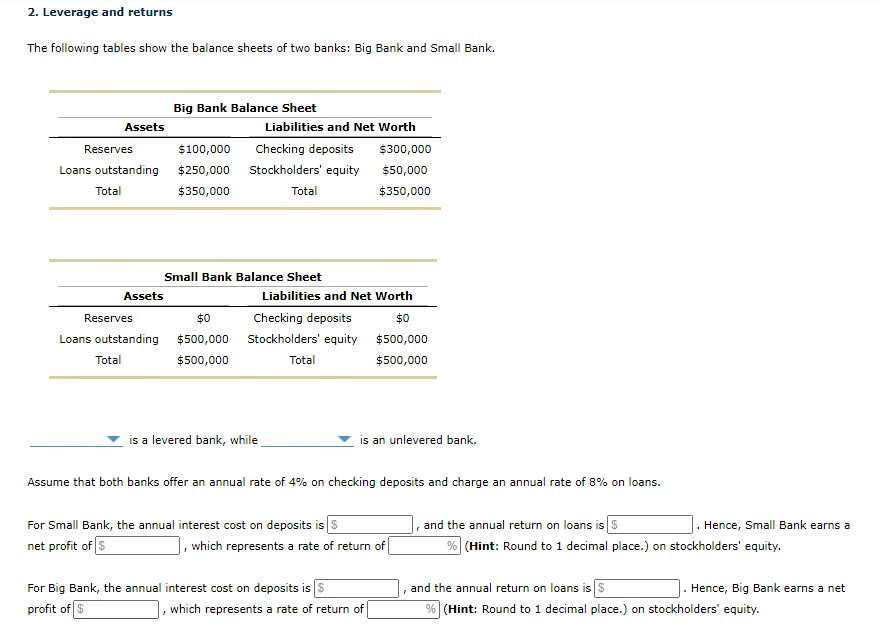
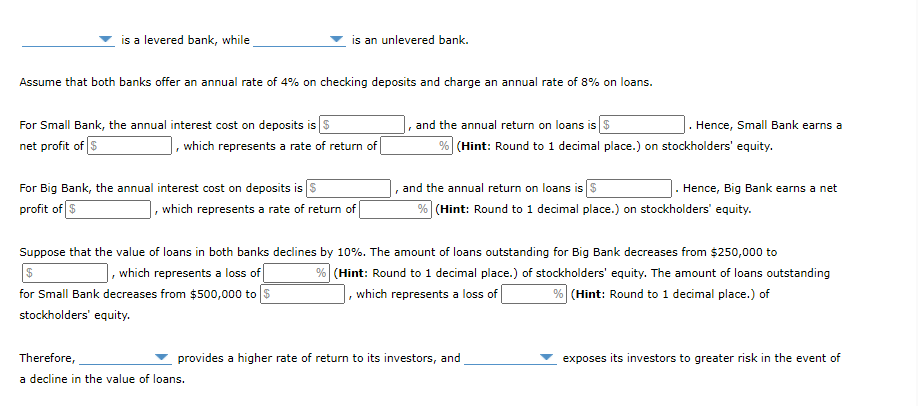
2. Leverage and returns The following tables show the balance sheets of two banks: Big Bank and Small Bank. Assets Reserves Loans outstanding Total Big Bank Balance Sheet Liabilities and Net Worth $100,000 Checking deposits $300,000 $250,000 Stockholders' equity $50,000 $350,000 Total $350,000 Small Bank Balance Sheet Assets Liabilities and Net Worth Reserves $0 Checking deposits $0 Loans outstanding $500,000 Stockholders' equity $500,000 Total $500,000 Total $500,000 is a levered bank, while is an unlevered bank. Assume that both banks offer an annual rate of 4% on checking deposits and charge an annual rate of 8% on loans. For Small Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is S net profit of $ which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ Hence, Small Bank earns a % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. For Big Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is S profit of $ which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ Hence, Big Bank earns a net % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. is a levered bank, while is an unlevered bank. Assume that both banks offer an annual rate of 4% on checking deposits and charge an annual rate of 8% on loans. For Small Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is $ net profit of $ , which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ . Hence, Small Bank earns a % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. For Big Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is 5 profit of $ which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ Hence, Big Bank earns a net % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. Suppose that the value of loans in both banks declines by 10%. The amount of loans outstanding for Big Bank decreases from $250,000 to $ which represents a loss of % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) of stockholders' equity. The amount of loans outstanding for Small Bank decreases from $500,000 to $ which represents a loss of| % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) of stockholders' equity. Therefore, provides a higher rate of return to its investors, and a decline in the value of loans. exposes its investors to greater risk in the event of 2. Leverage and returns The following tables show the balance sheets of two banks: Big Bank and Small Bank. Assets Reserves Loans outstanding Total Big Bank Balance Sheet Liabilities and Net Worth $100,000 Checking deposits $300,000 $250,000 Stockholders' equity $50,000 $350,000 Total $350,000 Small Bank Balance Sheet Assets Liabilities and Net Worth Reserves $0 Checking deposits $0 Loans outstanding $500,000 Stockholders' equity $500,000 Total $500,000 Total $500,000 is a levered bank, while is an unlevered bank. Assume that both banks offer an annual rate of 4% on checking deposits and charge an annual rate of 8% on loans. For Small Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is S net profit of $ which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ Hence, Small Bank earns a % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. For Big Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is S profit of $ which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ Hence, Big Bank earns a net % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. is a levered bank, while is an unlevered bank. Assume that both banks offer an annual rate of 4% on checking deposits and charge an annual rate of 8% on loans. For Small Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is $ net profit of $ , which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ . Hence, Small Bank earns a % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. For Big Bank, the annual interest cost on deposits is 5 profit of $ which represents a rate of return of and the annual return on loans is $ Hence, Big Bank earns a net % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) on stockholders' equity. Suppose that the value of loans in both banks declines by 10%. The amount of loans outstanding for Big Bank decreases from $250,000 to $ which represents a loss of % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) of stockholders' equity. The amount of loans outstanding for Small Bank decreases from $500,000 to $ which represents a loss of| % (Hint: Round to 1 decimal place.) of stockholders' equity. Therefore, provides a higher rate of return to its investors, and a decline in the value of loans. exposes its investors to greater risk in the event of








