2. Shock intersection Consider a uniform flow of air at M = 3.0 that enters a channel defined by two sharp wedges with angles
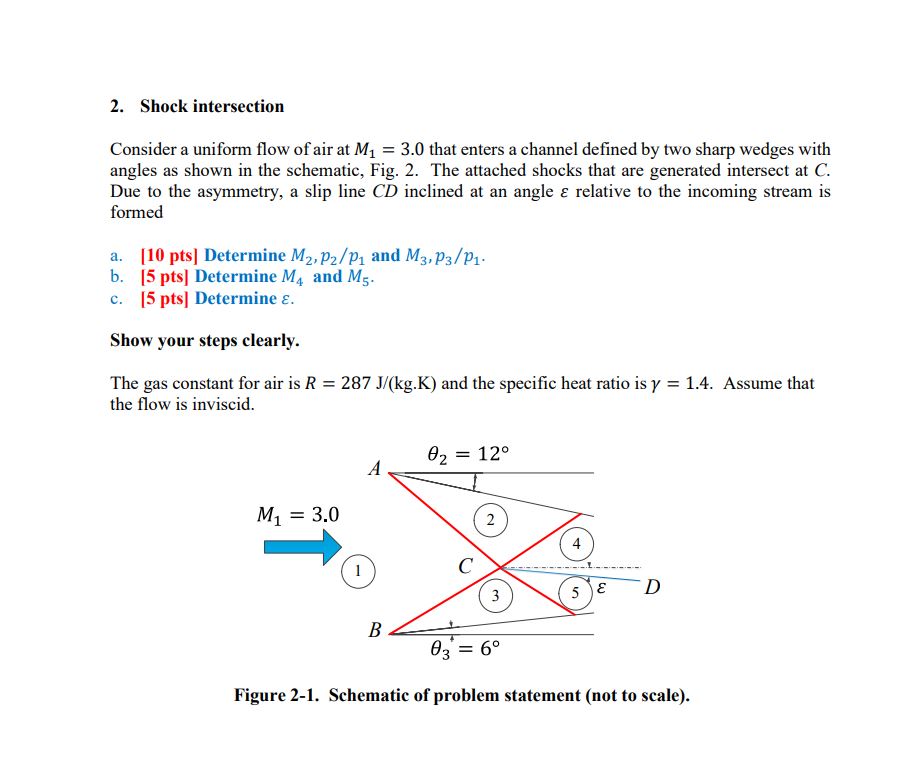
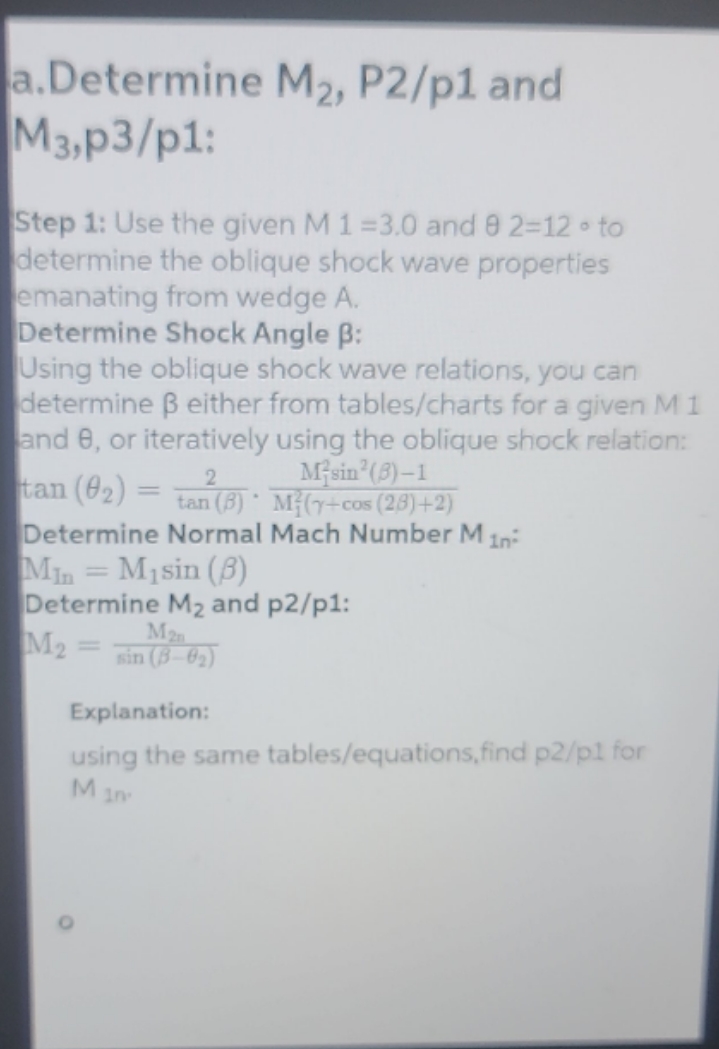






2. Shock intersection Consider a uniform flow of air at M = 3.0 that enters a channel defined by two sharp wedges with angles as shown in the schematic, Fig. 2. The attached shocks that are generated intersect at C. Due to the asymmetry, a slip line CD inclined at an angle & relative to the incoming stream is formed [10 pts] Determine M2, P2/p and M3, P3/P1 b. [5 pts] Determine M4 and M5. c. [5 pts] Determine . Show your steps clearly. The gas constant for air is R = 287 J/(kg.K) and the specific heat ratio is y = 1.4. Assume that the flow is inviscid. 02 = 12 A M1 = 3.0 2 B C 3 5 E D 03 - = 6 Figure 2-1. Schematic of problem statement (not to scale). a.Determine M2, P2/p1 and M3,p3/p1: 0 Step 1: Use the given M 1 =3.0 and 9 2=12 to determine the oblique shock wave properties emanating from wedge A. Determine Shock Angle : Using the oblique shock wave relations, you can determine either from tables/charts for a given M 1 and 8, or iteratively using the oblique shock relation: Misin (5)-1 tan (02) = 2 tan (8) M(y+cos (28)+2) Determine Normal Mach Number M 1n- Min Msin (B) = Determine M2 and p2/p1: M2 M2n = sin (8-02) Explanation: using the same tables/equations, find p2/pl for M10 Step 2: Repeat the process for wedge B using 8 3=6 'to find M 3 and p 1/p3 b. Determine M 4 and M 5: Step 1: Consider the flow properties behind the intersection point C. Use the Prandtl-Meyer expansion wave relation. Since both regions 2 and 3 experience expansion, calculate the Prandtl-Meyer function's increment: -1 tan (M-1 v2 = 1 tan 1/3= -1 tan ( M2-1 M M-1)-tan (3-1) Explanation: Use the changes in the Prandtl-Meyer function values to determine the Mach numbers M 4 and M5 c. Determine : Step 1: Calculate Mach angles for regions 2 and 3: H2= sin E M2 3 sin 1 M3 Step 2: Calculate the slip angle: = 3 - Explanation: Where is the Mach angle, defined asu=sin -1(1/M). 2. Shock intersection Consider a uniform flow of air at M = 3.0 that enters a channel defined by two sharp wedges with angles as shown in the schematic, Fig. 2. The attached shocks that are generated intersect at C. Due to the asymmetry, a slip line CD inclined at an angle & relative to the incoming stream is formed a. Determine M2, P2/P1 and M3, P3/P1 PLUG AND CHUG b. Determine M4 and M5. c. Determine . M = 3.0 1 02 = 12 2 B 03 = 6 5 D Problem 2 Parts b and c Solve by iteration on P4 and P5 Converged when P4= P5 First guess: = : 0 Second guess: ? P4 P5 3 M1 = 3.0 1 B 02 = 12 2 P4,1 3 5 E D P5,1 03 = 6 M = = 3.0 Problem 2 Parts b and c: Alternative Approach Using Pressure- Deflection Diagram 02 = 12 M3 = 2.701 Pressure ratio 16 15 14 1 B 03 = 6 E D 13 M = 2.406 12 M1 = 3 11 10 9 16 876543 UP -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 4,5 DOWN 10 20 30 40 Deflection, deg 50 50 Pressure ratio 4.0 35 3.5 3.0 M_3=2.701 2.5 2.0 1.5 4,5 M_2=2.406 M_1=3 1.0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Deflection, deg
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


