
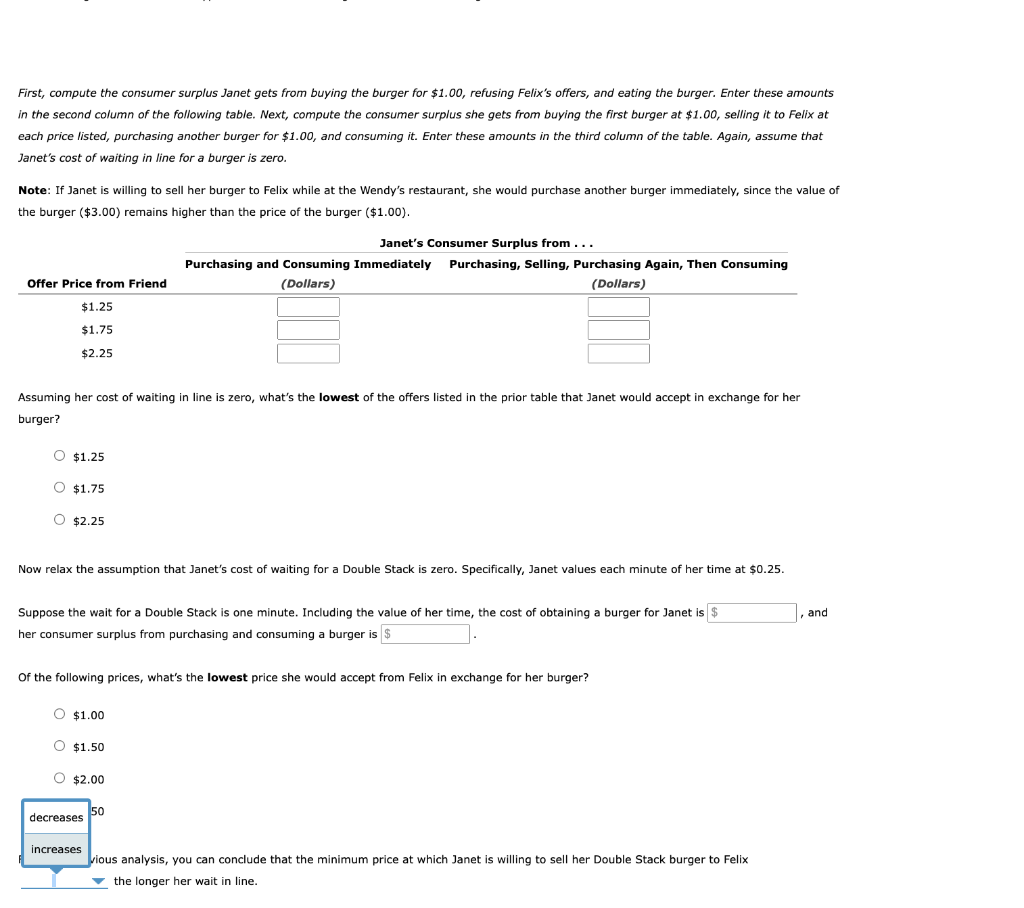
2. The effect of transaction costs on decision making This Wendy's commercial confuses the notions of appreciation and consumer surplus. Recall that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what he or she actually pays for it. According to standard economic theory, consumer surplus must always be Ec implify economic models by ignoring the role that transaction costs play in decision making. Purchasing a good often involves ex co costs, such as the cost of the gasoline used to get to the store, but there are also implicit transaction costs such as the opportunity ent shopping for and acquiring a product. The remaining questions will help you understand the importance of transaction costs. Suppuse saire vaides consuming her first Double Stack burger at $3.00, and she places no value on any additional burgers. Based on Janet's Double Stack burger. Using the green rectangle (triangle symbols), shade the area representing Janet's consumer surplus from purchasing a burger under these conditions on the following graph. Suppose Janet just sat down to enjoy the Double Stack burger that she purchased for $1.00. Her friend, Felix, would also like a Double Stack burger, but he strongly dislikes standing in line. Felix offers to buy Janet's Double Stack rather than wait in line himself and $1.00. The following table shows some hypothetical offers Felix might make for Janet's burger. First, compute the consumer surplus Janet gets from buying the burger for $1.00, refusing Felix's offers, and eating the burger. Enter these amounts each price listed, purchasing another burger for $1.00, and consuming it. Enter these amounts in the third column of the table. Again, assume that Janet's cost of waiting in line for a burger is zero. Note: If Janet is willing to sell her burger to Felix while at the Wendy's restaurant, she would purchase another burger immediately, since the value of the burger ($3.00) remains higher than the price of the burger ($1.00). Assuming her cost of waiting in line is zero, what's the lowest of the offers listed in the prior table that Janet would accept in exchange for her burger? $1.25 $1.75 $2.25 Now relax the assumption that Janet's cost of waiting for a Double Stack is zero. Specifically, Janet values each minute of her time at \$0.25. Suppose the wait for a Double Stack is one minute. Including the value of her time, the cost of obtaining a burger for , and her consumer surplus from purchasing and consuming a burger is Of the following prices, what's the lowest price she would accept from Felix in exchange for her burger? $1.00 $1.50 $2.00 50 vious analysis, you can conclude that the minimum price at which Janet is willing to sell her Double Stack burger to Felix the longer her wait in line. 2. The effect of transaction costs on decision making This Wendy's commercial confuses the notions of appreciation and consumer surplus. Recall that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what he or she actually pays for it. According to standard economic theory, consumer surplus must always be Ec implify economic models by ignoring the role that transaction costs play in decision making. Purchasing a good often involves ex co costs, such as the cost of the gasoline used to get to the store, but there are also implicit transaction costs such as the opportunity ent shopping for and acquiring a product. The remaining questions will help you understand the importance of transaction costs. Suppuse saire vaides consuming her first Double Stack burger at $3.00, and she places no value on any additional burgers. Based on Janet's Double Stack burger. Using the green rectangle (triangle symbols), shade the area representing Janet's consumer surplus from purchasing a burger under these conditions on the following graph. Suppose Janet just sat down to enjoy the Double Stack burger that she purchased for $1.00. Her friend, Felix, would also like a Double Stack burger, but he strongly dislikes standing in line. Felix offers to buy Janet's Double Stack rather than wait in line himself and $1.00. The following table shows some hypothetical offers Felix might make for Janet's burger. First, compute the consumer surplus Janet gets from buying the burger for $1.00, refusing Felix's offers, and eating the burger. Enter these amounts each price listed, purchasing another burger for $1.00, and consuming it. Enter these amounts in the third column of the table. Again, assume that Janet's cost of waiting in line for a burger is zero. Note: If Janet is willing to sell her burger to Felix while at the Wendy's restaurant, she would purchase another burger immediately, since the value of the burger ($3.00) remains higher than the price of the burger ($1.00). Assuming her cost of waiting in line is zero, what's the lowest of the offers listed in the prior table that Janet would accept in exchange for her burger? $1.25 $1.75 $2.25 Now relax the assumption that Janet's cost of waiting for a Double Stack is zero. Specifically, Janet values each minute of her time at \$0.25. Suppose the wait for a Double Stack is one minute. Including the value of her time, the cost of obtaining a burger for , and her consumer surplus from purchasing and consuming a burger is Of the following prices, what's the lowest price she would accept from Felix in exchange for her burger? $1.00 $1.50 $2.00 50 vious analysis, you can conclude that the minimum price at which Janet is willing to sell her Double Stack burger to Felix the longer her wait in line








