Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
(20 pts) Consider a finned heat sink used to cool a computer processor. The lid of the processor package is a uniform temperature square
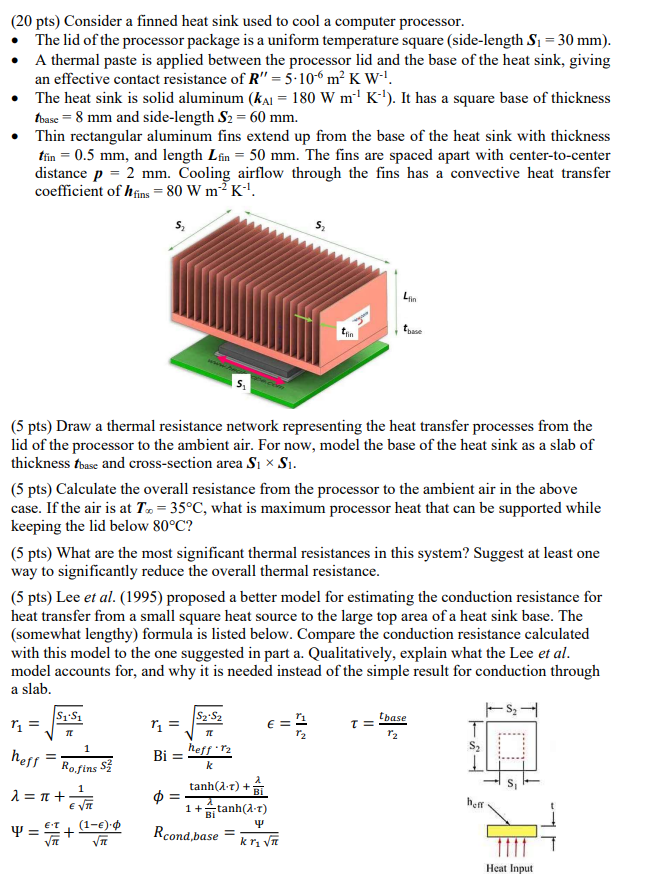
(20 pts) Consider a finned heat sink used to cool a computer processor. The lid of the processor package is a uniform temperature square (side-length S = 30 mm). A thermal paste is applied between the processor lid and the base of the heat sink, giving an effective contact resistance of R"-5-106 m K W-'. The heat sink is solid aluminum (KA = 180 W m K). It has a square base of thickness tbase 8 mm and side-length S2 = 60 mm. Thin rectangular aluminum fins extend up from the base of the heat sink with thickness tfin = 0.5 mm, and length Lfin = 50 mm. The fins are spaced apart with center-to-center distance p = 2 mm. Cooling airflow through the fins has a convective heat transfer coefficient of hfins = 80 W m K-. S 5 Lim tbase (5 pts) Draw a thermal resistance network representing the heat transfer processes from the lid of the processor to the ambient air. For now, model the base of the heat sink as a slab of thickness tbase and cross-section area S S. (5 pts) Calculate the overall resistance from the processor to the ambient air in the above case. If the air is at T = 35C, what is maximum processor heat that can be supported while keeping the lid below 80C? (5 pts) What are the most significant thermal resistances in this system? Suggest at least one way to significantly reduce the overall thermal resistance. (5 pts) Lee et al. (1995) proposed a better model for estimating the conduction resistance for heat transfer from a small square heat source to the large top area of a heat sink base. The (somewhat lengthy) formula is listed below. Compare the conduction resistance calculated with this model to the one suggested in part a. Qualitatively, explain what the Lee et al. model accounts for, and why it is needed instead of the simple result for conduction through a slab. 1 = heff = 1 = 1 heff.12 Bi = Ro.fins S k 1 + = 1 + (1-). tanh(1-1)+ 1+ Bi tanh(27) Rcond,base= Y 52 tbase T= heff Heat Input
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


