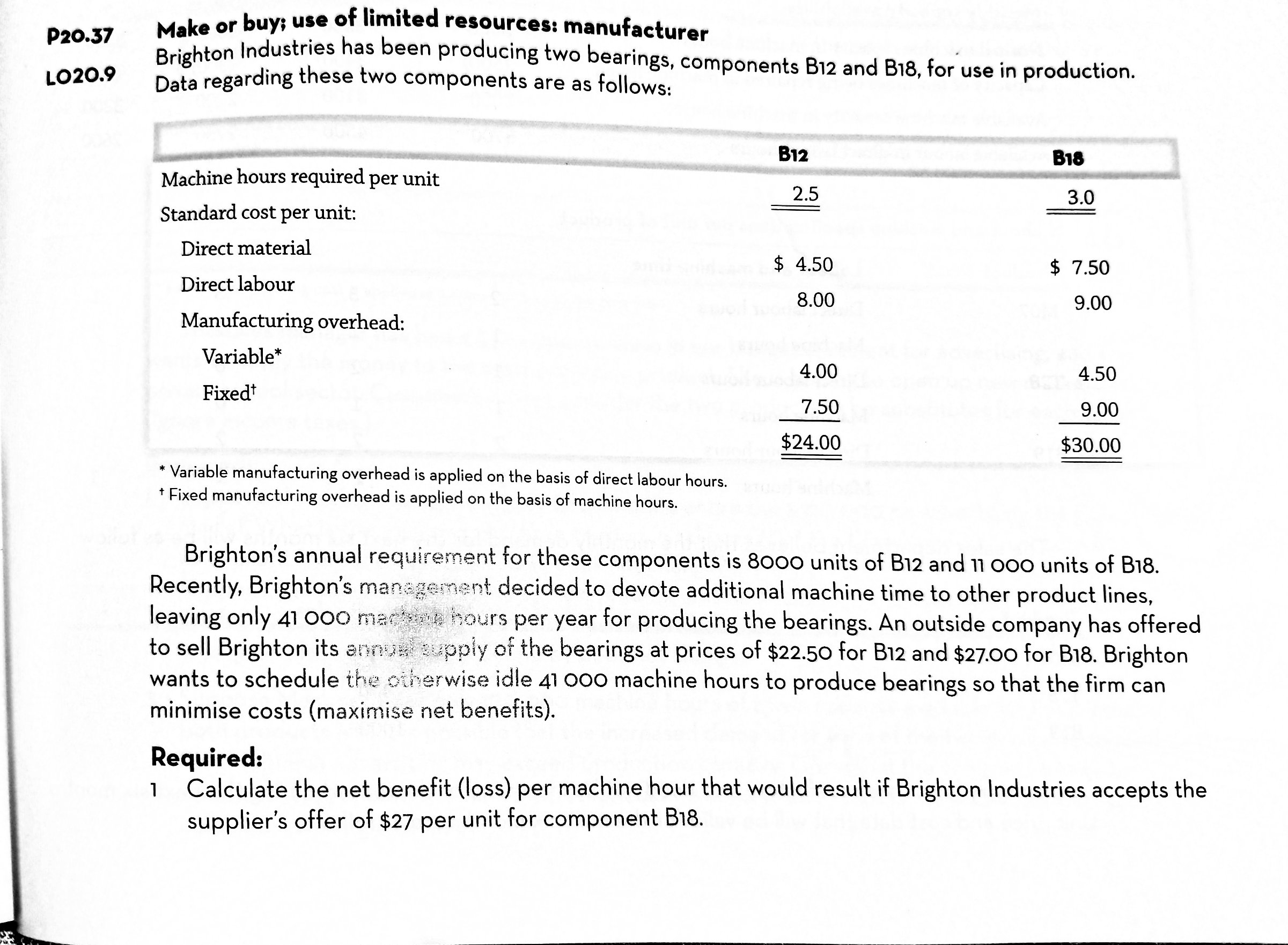
20.17 Explain why different costs and revenues may be relevant when making s'nort-term product mix decisions compared with making long-term product mix decisions. LO 20.9 20.29 L020.9 Product mix; limited resources: manufacturer ArchoChem Ltd manufactures two chemicals, Wes'n a ,. .. We 5.\" I Unit sales price $ 1 3 '7' f Less: Direct material 7 .0 CF Direct labour 1 . 00 Variable warhead 1.25 Variable selling and administrative costs 0.75 Unit contribution margin $ 3.00 nd Westz. Corv'\" . my: margin data follow: West: $31.00 5.00 6.00 7.50 0.50 $12.00 \\ E20030 LO2OJO ArchoChem production process uses highly skilled labour, which is in short supply. The same employees work on both products and earn the same wage rate of $21 per hour. Required: Which of ArchoChem's products is the more profitable? Explain. (appendix) Linear programming; formulate and solve graphically: manufacturer The Jersey Chemical Company manufactures two industrial chemical products, callecl Zanide and Kreolite. Two machines are used in the process, and each machine has 24 hours of capacity per day. The following data are available: Zanide , , Kreolite Selling price per drum $36 1 $42 > ' Variable cost per drum $28 $28 Hours required per drum on machine I 2 hours 2 hours Hours required per drum on machine II 1 hour 3 hours The company can produce and sell partially full drums of each chemical. For example. a half drum of Zanide sells for $18. Required: 1 Formulate the product mix problem as a linear program. 2 Solve the problem graphically. 3 What is the value of the objective function at the optimal solution? P20.37 LO20.9 Make or buy: use of limited resources: manufacturer Brighton Industries has been producing two bearings, components 312 and B18, tor'use in production. Data regarding these two components are as follows: WMWW r - , . , i 7 _ V Bu 318 Machine hours required per unit 25 i l \"A . 3.0 Standard cost per unit: Direct material $ 4 50 $ 7.50 Direct labour 8.00 9.00 Manufacturing overhead: Variable" 4 oo 4.50 Fixed'r 7 50 9.00 $24.00 $30.00 * Variable manufacturing overhead is applied on the basis of direct labour hours. * Fixed manufacturing overhead is applied on the basis of machine hours. Brighton's annual requirement for these components is 8000 units of B12 and 11 000 units of B18. Recently, Brighton's man ant decided to devote additional machine time to other product lines, leaving only 41 000 m: urs per year for producing the bearings. An outside company has offered to sell Brighton its at t the bearings at prices of $22.50 for B12 and $27.00 for 818. Brighton piy o: wants to schedule the {'51: zerwise idle 41 000 machine hours to produce bearings so that the firm can minimise costs (maximise net benefits). Required: 1 Calculate the net benefit (loss) per machine hour that would result it Brighton industries accepts the supplier's offer of $27 per unit for component B18. PART FOUR INFORMATION FOR CREATING VALUE V . .-\\ 2 Choose the correct answer. Brighton Industries will maximise its net benefits by: (a) Purchasing 4800 units of B12 and manufacturing the remainlng bearings. (b) Purchasing 8000 units of B12 and manufacturing 11 000 units of B18. (c) Purchasing 11 000 units of B18 and manufacturing 8000 units of B12. (d) Purchasing 4000 units of 818 and manufacturing the remaining bearings. (e) Purchasing and manufacturing some amounts other than those given above. 3 Suppose that management have decided to drop product B12. Independently of requirements 1 and 2, assume that Brighton lndustries' idle capacity of 41 000 machine hours has a traceable, avoidable annual fixed cost of $88 000, which will be incurred only if some of the spare capacity is used. Calculate the maximum price Brighton Industries should pay a supplier for component B18