
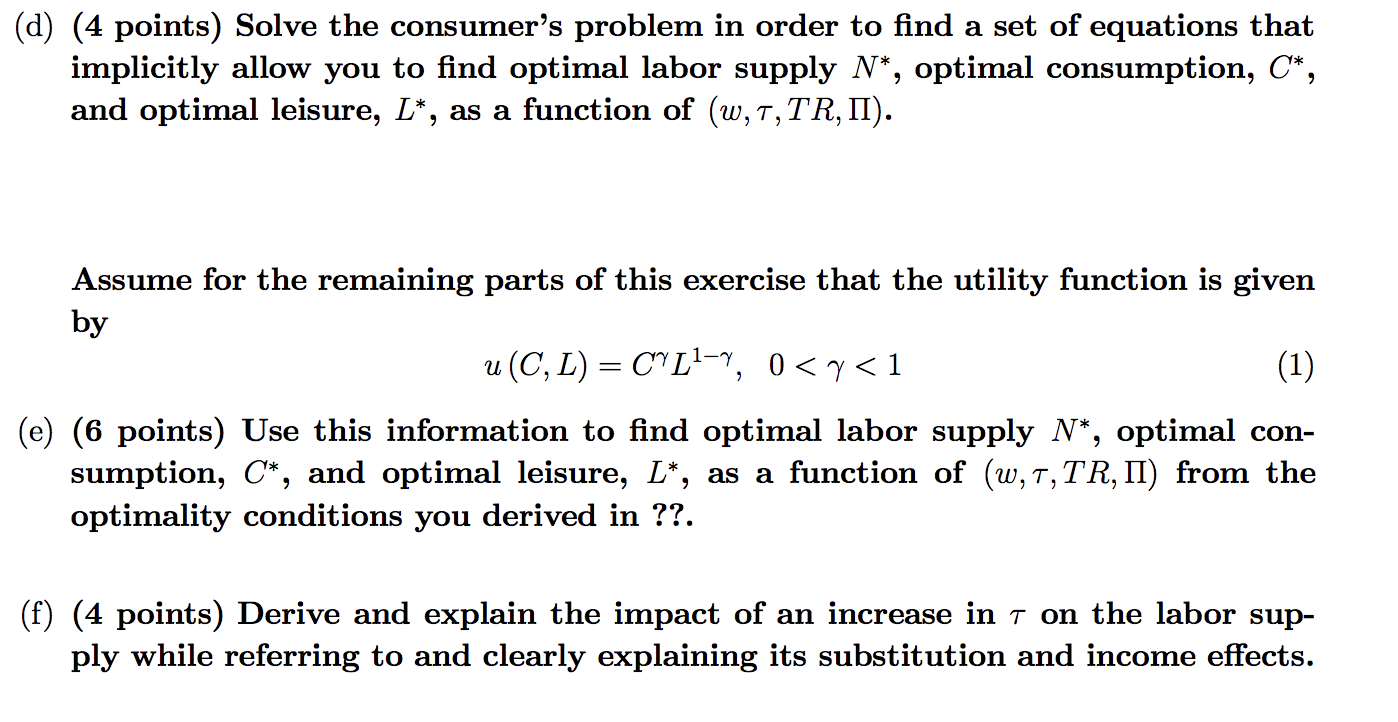

(24 + 4 points) Tax on labor income Consider an economy where the representative consumer has a utility function u (C, L) over consumption C and leisure L. Assume preferences satisfy the standard proper- ties we assumed in class. The consumer has an endowment of H units of time, faces a wage rate w and receives profits II from the representative firm. The representative firm has a production technology given by Y zf (K, N) where K is the fixed capital input and N is labor input. Suppose that the government levies a proportional tax, t, where TE (0,1) on labor income. So the taxes paid by the representative consumer are twN. The revenues from the taxes collected by the government from all consumers are rebated lump- sum to consumers. Let TR denote the lump sum transfer that the representative consumer receives. As usual, assume that the representative consumer takes w, II, T, and TR as given. (a) (3 points) Write and explain the budget constraint for the representative con- sumer in this economy. (b) (3 points) Derive the relative price of leisure in terms of consumption. (c) (2 points) Set up the consumer's problem. (d) (4 points) Solve the consumer's problem in order to find a set of equations that implicitly allow you to find optimal labor supply N*, optimal consumption, C*, and optimal leisure, L*, as a function of (w, T,TR, II). Assume for the remaining parts of this exercise that the utility function is given by u(C, L) = C^L1-9, 0
0 (g) (2 points) Derive and explain the impact of an increase in t on consumption while referring to its substitution and income effects (assume that TR+II > 0). (h) (4 extra points) Derive and explain the impact of an increase in t on the la- bor supply when we take into account that in equilibrium consumers receive in lump-sum transfers the amount received as a subsidy to consumption, TR= TWN (assume that II > 0). Do you think the response of the labor supply in this case is stronger or weaker than what you saw in 3f. (24 + 4 points) Tax on labor income Consider an economy where the representative consumer has a utility function u (C, L) over consumption C and leisure L. Assume preferences satisfy the standard proper- ties we assumed in class. The consumer has an endowment of H units of time, faces a wage rate w and receives profits II from the representative firm. The representative firm has a production technology given by Y zf (K, N) where K is the fixed capital input and N is labor input. Suppose that the government levies a proportional tax, t, where TE (0,1) on labor income. So the taxes paid by the representative consumer are twN. The revenues from the taxes collected by the government from all consumers are rebated lump- sum to consumers. Let TR denote the lump sum transfer that the representative consumer receives. As usual, assume that the representative consumer takes w, II, T, and TR as given. (a) (3 points) Write and explain the budget constraint for the representative con- sumer in this economy. (b) (3 points) Derive the relative price of leisure in terms of consumption. (c) (2 points) Set up the consumer's problem. (d) (4 points) Solve the consumer's problem in order to find a set of equations that implicitly allow you to find optimal labor supply N*, optimal consumption, C*, and optimal leisure, L*, as a function of (w, T,TR, II). Assume for the remaining parts of this exercise that the utility function is given by u(C, L) = C^L1-9, 0 0 (g) (2 points) Derive and explain the impact of an increase in t on consumption while referring to its substitution and income effects (assume that TR+II > 0). (h) (4 extra points) Derive and explain the impact of an increase in t on the la- bor supply when we take into account that in equilibrium consumers receive in lump-sum transfers the amount received as a subsidy to consumption, TR= TWN (assume that II > 0). Do you think the response of the labor supply in this case is stronger or weaker than what you saw in 3f









