Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
[25 points] The figure below shows a PRA model for a fire-induced scenario at a nuclear power plant. The initiating event (denoted as FIRE)
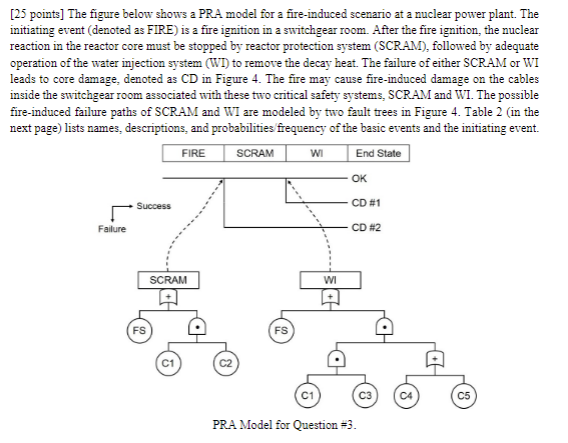
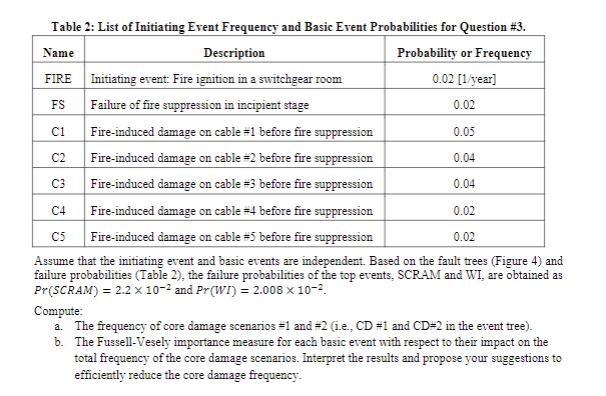
[25 points] The figure below shows a PRA model for a fire-induced scenario at a nuclear power plant. The initiating event (denoted as FIRE) is a fire ignition in a switchgear room. After the fire ignition, the nuclear reaction in the reactor core must be stopped by reactor protection system (SCRAM), followed by adequate operation of the water injection system (WI) to remove the decay heat. The failure of either SCRAM or WI leads to core damage, denoted as CD in Figure 4. The fire may cause fire-induced damage on the cables inside the switchgear room associated with these two critical safety systems, SCRAM and WI. The possible fire-induced failure paths of SCRAM and WI are modeled by two fault trees in Figure 4. Table 2 (in the next page) lists names, descriptions, and probabilities frequency of the basic events and the initiating event. FIRE SCRAM Success Failure FS SCRAM C1 FS WI End State OK CD #1 WI CD #2 PRA Model for Question #3. C3 C4 C5 Table 2: List of Initiating Event Frequency and Basic Event Probabilities for Question #3. Name Description FIRE Initiating event: Fire ignition in a switchgear room Probability or Frequency 0.02 [1/year] FS Failure of fire suppression in incipient stage 0.02 C1 Fire-induced damage on cable #1 before fire suppression 0.05 C2 Fire-induced damage on cable #2 before fire suppression 0.04 C3 Fire-induced damage on cable #3 before fire suppression 0.04 33 0.02 C4 Fire-induced damage on cable #4 before fire suppression C5 Fire-induced damage on cable #5 before fire suppression 0.02 Assume that the initiating event and basic events are independent. Based on the fault trees (Figure 4) and failure probabilities (Table 2), the failure probabilities of the top events, SCRAM and WI, are obtained as Pr(SCRAM) = 2.2 x 10-2 and Pr(WI) = 2.008 10-. Compute: a. The frequency of core damage scenarios #1 and #2 (ie., CD #1 and CD#2 in the event tree). b. The Fussell-Vesely importance measure for each basic event with respect to their impact on the total frequency of the core damage scenarios. Interpret the results and propose your suggestions to efficiently reduce the core damage frequency.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


