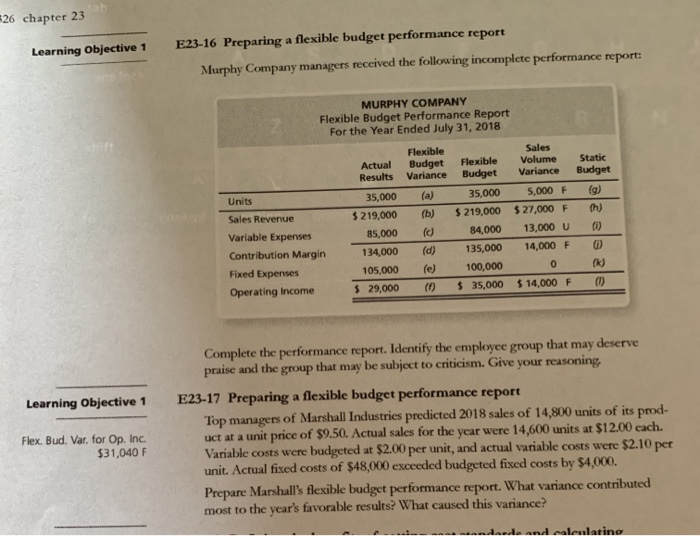
26 chapter 23 E23-16 Preparing a flexible budget performance report Learning Objective 1 Murphy Company managers received the following incomplete performance report MURPHY COMPANY Flexible Budget Performance Report For the Year Ended July 31, 2018 Flexible Actual Budget FlexibleVolume Static Results Variance Budget VarianceBudget 35,000 5,000 F (g) Units 35,000 (a) 219,000 (b) $219,000 $ 27,000 Fh) 85,000 () Sales Revenue 84,000 13,000 U Variable Expenses Contribution Margin 134,000 (d) 135,000 14,000F O 0 Fixed Expenses 105,000(e100,000 Operating Income 29,000(35,000 $14,000 F() Complete the performance report. Identify the employee group that may deserve praise and the group that may be subject to criticism. Give your reasoning E23-17 Preparing a flexible budget performance report Top managers of Marshall Industries predicted 2018 sales of 14,800 units of its prod- uct at a unit price of $9.50. Actual sales for the year were 14,600 units at $12.00 each. Variable costs were budgeted at $2.00 per unit, and actrual variable costs were $2.10 per unit. Actual fixed costs of $48,000 exceded budgeted fixed costs by $4,000. Learning Objective 1 Flex. Bud. Var. for Op. Inc $31,040 F Prepare Marshall's flexible budget performance report. What variance contributed most to the year's favorable results? What caused this variance? Flexible Budgets and Standard Cost Systems 13 Learning Objective 3 E23-19 Calculating materials and labor variances Matthews Fender, which uses a standard cost system, manufactured 20,000 boat fenders during 2018, using 143,000 square feet of extruded vinyl purchased at $1.30 DL Eff. Var. $2,400 F per square foot. Production required 400 direct labor hours that cost $16.00 per hour. The direct materials standard was seven square feet of vinyl per fender, at a standard cost of $1.35 per square foot. The labor standard was 0.028 direet labor hour per fender, at a standard cost of $15.00 per hour Compute the cost and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor. Does the pattern of variances suggest Matthews Fender's managers have been making trade- offs? Explain. Learning Objective 4 E23-21 Calculating overhead variances Mills, Inc. is a competitor of Murry, Inc. from Exercise E23-18. Mills also uses a standard cost system and provides the following information: 1. VOH Cost Var. $1,600 U Static budget variable overhead 1,200 1,600 Static budget fixed overhead 800 hours Static budget direct labor hours 400 units Static budget number of units 2 hours per unit Standard direct labor hours Mills allocates manufacturing overhead to production based on standard direct labor hours Mills reported the following actual results for 2018: actual number of units produced, 1,000; actual variable overhead, $4,000; actual fixed overhead, $3,100; actual direct labor hours, 1,600. Requirements 1. Compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances and fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Explain why the variances are favorable or unfavorable 2. E23-22 Preparing a standard cost income statement The May 2018 revenue and cost information for McDonald Outfitters, Inc. follows: Learning Objective 6 GP $270,700 Sales Revenue (at standard) $ 610,000 Cost of Goods Sold (at standard) 348,000 Direct Materials Cost Variance 1,500 F Direct Materials Efficiency Variance 6,600 F Direct Labor Cost Variance 4,200 U Direct Labor Efficiency Variance 2,700 F Variable Overhead Cost Variance 2,800 U Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance 1,100 U Fixed Overhead Cost Variance 2,300 U Fixed Overhead Volume Variance 8,300 F Prepare a standard cost income statement for management through gross profit. Report all standard cost variances for management's use Has management done a good or poor job of controlling costs? Explain