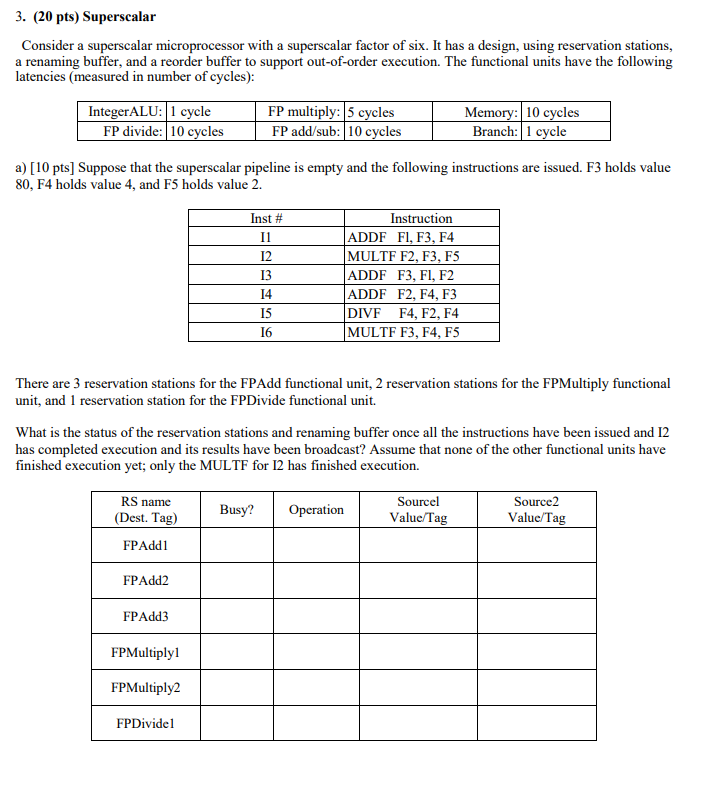
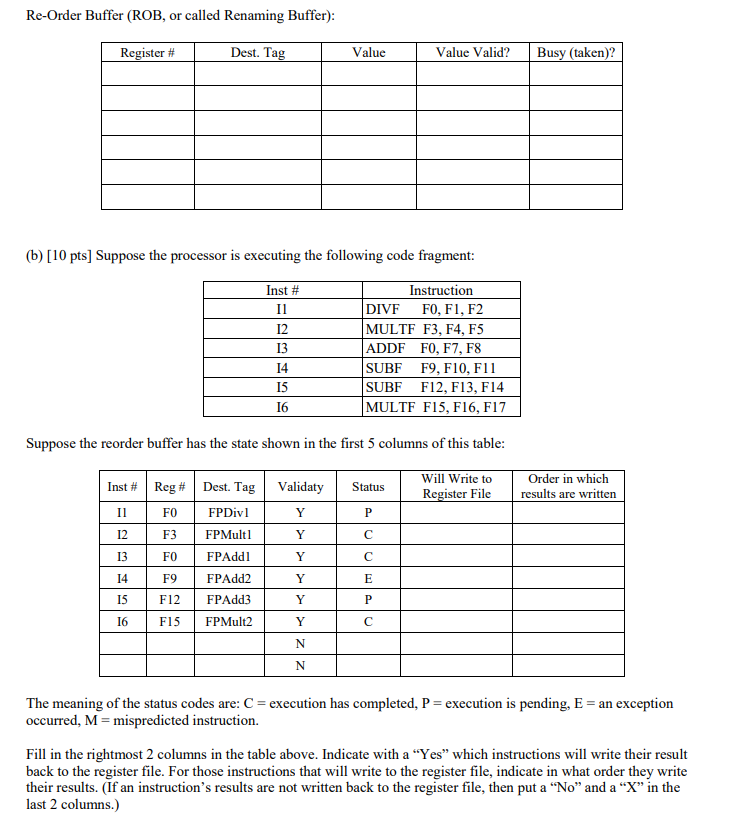
3. (20 pts) Superscalar Consider a superscalar microprocessor with a superscalar factor of six. It has a design, using reservation stations, a renaming buffer, and a reorder buffer to support out-of-order execution. The functional units have the following latencies (measured in number of cycles): Integer ALU: 1 cycle FP divide: 10 cycles FP multiply: 15 cycles FP add/sub: 10 cycles Memory: 10 cycles Branch: 1 cycle a) [10 pts] Suppose that the superscalar pipeline is empty and the following instructions are issued. F3 holds value 80, F4 holds value 4, and F5 holds value 2. Inst # Instruction ADDF FI, F3, F4 MULTF F2, F3, F5 ADDF F3, F1, F2 ADDF F2, F4, F3 DIVF F4, F2, F4 MULTF F3, F4, F5 There are 3 reservation stations for the FPAdd functional unit, 2 reservation stations for the FPMultiply functional unit, and 1 reservation station for the FPDivide functional unit. What is the status of the reservation stations and renaming buffer once all the instructions have been issued and 12 has completed execution and its results have been broadcast? Assume that none of the other functional units have finished execution yet; only the MULTF for 12 has finished execution. RS name (Dest. Tag) Busy? Operation Sourcel Value/Tag Source2 Value/Tag FPAddi FPAdd2 FPAdd3 FPMultiply FPMultiply FPDividel Re-Order Buffer (ROB, or called Renaming Buffer): Register # Dest. Tag Value Value Valid? Busy (taken)? (b) [10 pts) Suppose the processor is executing the following code fragment: Inst # 11 Instruction DIVF FO, F1, F2 MULTF F3, F4, F5 ADDF FO, F7, F8 SUBF F9, F10, F11 SUBF F12, F13, F14 MULTF F15, F16, F17 14 15 16 Suppose the reorder buffer has the state shown in the first 5 columns of this table: Inst # Reg# Status Will Write to Register File Order in which results are written Validaty Y FO F3 FO F9 F12 F15 Dest. Tag FPDivl FPMult1 FPAddl FPAdd2 FPAdd3 FPMult2 The meaning of the status codes are: C = execution has completed, P= execution is pending, E = an exception occurred, M=mispredicted instruction. Fill in the rightmost 2 columns in the table above. Indicate with a "Yes" which instructions will write their result back to the register file. For those instructions that will write to the register file, indicate in what order they write their results. (If an instruction's results are not written back to the register file, then put a "No" and a X in the last 2 columns.) 3. (20 pts) Superscalar Consider a superscalar microprocessor with a superscalar factor of six. It has a design, using reservation stations, a renaming buffer, and a reorder buffer to support out-of-order execution. The functional units have the following latencies (measured in number of cycles): Integer ALU: 1 cycle FP divide: 10 cycles FP multiply: 15 cycles FP add/sub: 10 cycles Memory: 10 cycles Branch: 1 cycle a) [10 pts] Suppose that the superscalar pipeline is empty and the following instructions are issued. F3 holds value 80, F4 holds value 4, and F5 holds value 2. Inst # Instruction ADDF FI, F3, F4 MULTF F2, F3, F5 ADDF F3, F1, F2 ADDF F2, F4, F3 DIVF F4, F2, F4 MULTF F3, F4, F5 There are 3 reservation stations for the FPAdd functional unit, 2 reservation stations for the FPMultiply functional unit, and 1 reservation station for the FPDivide functional unit. What is the status of the reservation stations and renaming buffer once all the instructions have been issued and 12 has completed execution and its results have been broadcast? Assume that none of the other functional units have finished execution yet; only the MULTF for 12 has finished execution. RS name (Dest. Tag) Busy? Operation Sourcel Value/Tag Source2 Value/Tag FPAddi FPAdd2 FPAdd3 FPMultiply FPMultiply FPDividel Re-Order Buffer (ROB, or called Renaming Buffer): Register # Dest. Tag Value Value Valid? Busy (taken)? (b) [10 pts) Suppose the processor is executing the following code fragment: Inst # 11 Instruction DIVF FO, F1, F2 MULTF F3, F4, F5 ADDF FO, F7, F8 SUBF F9, F10, F11 SUBF F12, F13, F14 MULTF F15, F16, F17 14 15 16 Suppose the reorder buffer has the state shown in the first 5 columns of this table: Inst # Reg# Status Will Write to Register File Order in which results are written Validaty Y FO F3 FO F9 F12 F15 Dest. Tag FPDivl FPMult1 FPAddl FPAdd2 FPAdd3 FPMult2 The meaning of the status codes are: C = execution has completed, P= execution is pending, E = an exception occurred, M=mispredicted instruction. Fill in the rightmost 2 columns in the table above. Indicate with a "Yes" which instructions will write their result back to the register file. For those instructions that will write to the register file, indicate in what order they write their results. (If an instruction's results are not written back to the register file, then put a "No" and a X in the last 2 columns.)








