Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The composite shaft shown in the figure is fixed at both ends. It consists of two solid shafts of different diameter and material. Shafts
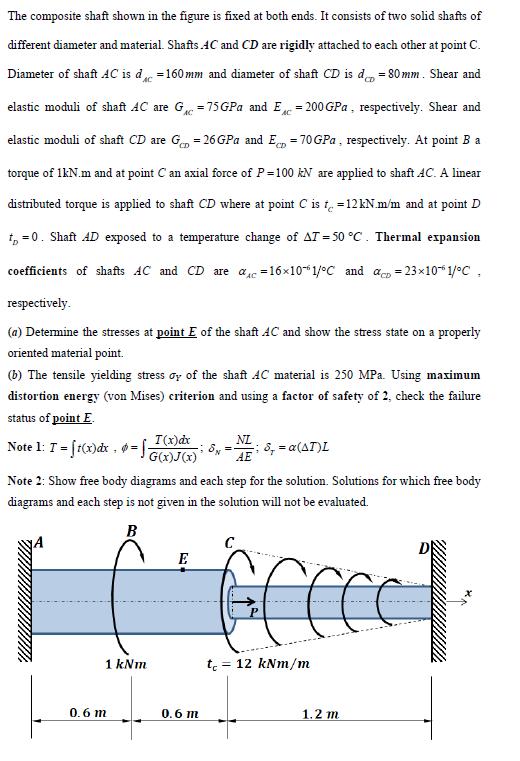
The composite shaft shown in the figure is fixed at both ends. It consists of two solid shafts of different diameter and material. Shafts AC and CD are rigidly attached to each other at point C. Diameter of shaft AC is d =160 mm and diameter of shaft CD is d, = 80 mm. Shear and elastic moduli of shaft AC are G = 75 GPa and E = 200 GPa, respectively. Shear and AC elastic moduli of shaft CD are G = 26 GPa and E, = 70 GPa , respectively. At point B a torque of 1kN.m and at point C an axial force of P=100 kN are applied to shaft AC. A linear distrbuted torque is applied to shaft CD where at point C is t. =12 kN.m/m and at point D t, =0. Shaft AD exposed to a temperature change of AT = 50 C. Thermal expansion coefficients of shafts AC and CD are ac =16x101/C and a, = 23x10* 1/C , respectively. (a) Determine the stresses at point E of the shaft AC and show the stress state on a properly oriented material point. (b) The tensile yielding stress oy of the shaft AC material is 250 MPa. Using maximum distortion energy (von Mises) criterion and using a factor of safety of 2, check the failure status of point E. Note 1: T = ft(x)dx . *- G(x)J(x) T(x)dx NL ;8, = a(AT)L %3D AE Note 2: Show free body diagrams and each step for the solution. Solutions for which free body diagrams and each step is not given in the solution will not be evaluated. B C E 1 kNm t = 12 kNm/m 0.6 m 0.6 1.2 m
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.42 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


