Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
3] Implement the iterative version of depth-first search. Here, for simplicity, we use visited as a list to store all visited vertices in order.
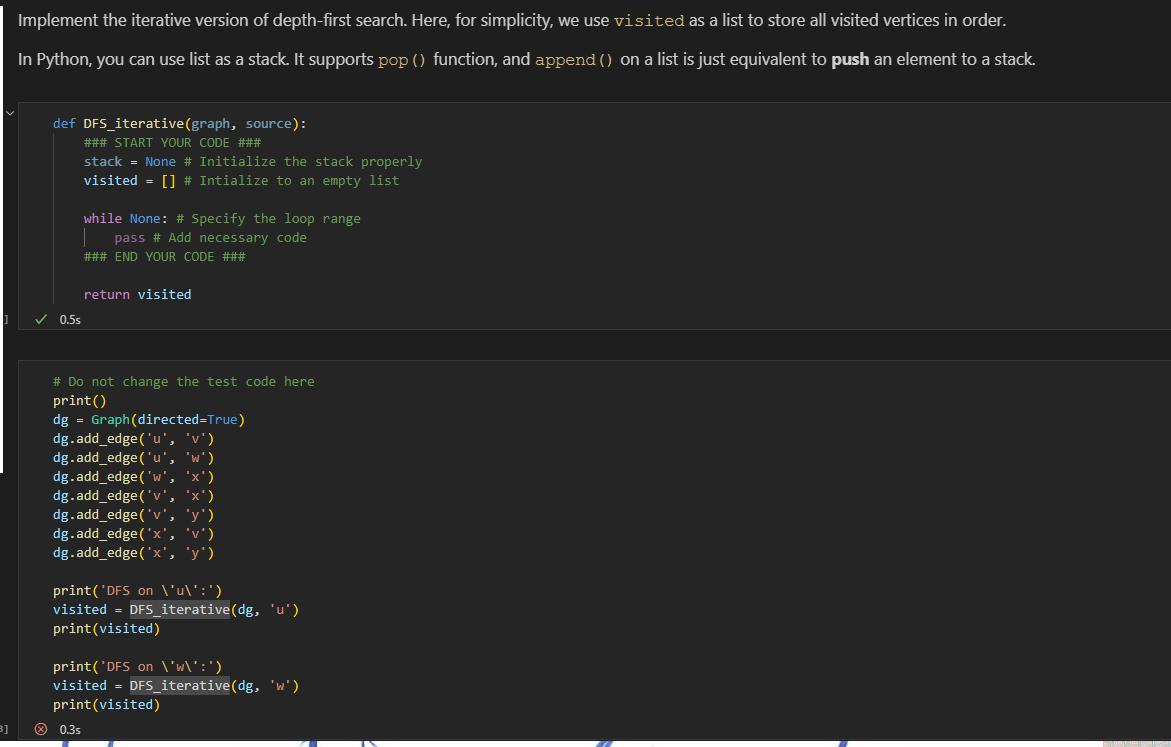
3] Implement the iterative version of depth-first search. Here, for simplicity, we use visited as a list to store all visited vertices in order. In Python, you can use list as a stack. It supports pop () function, and append () on a list is just equivalent to push an element to a stack. def DFS iterative (graph, source): ### START YOUR CODE ### 0.5s stack = None # Initialize the stack properly visited = [] # Intialize to an empty list while None: # Specify the loop range pass # Add necessary code ### END YOUR CODE ### return visited # Do not change the test code here print () dg = Graph (directed=True) 0.3s dg.add_edge('u', 'v') dg.add_edge('u', 'w') dg.add_edge('w', 'x') dg.add_edge('v', 'x'). dg.add_edge('v', 'y') dg.add_edge('x', 'v') dg.add_edge('x', 'y'). print('DFS on \'u\':') visited print (visited) DFS_iterative (dg, 'u') print('DFS on \'w\':') visited DFS_iterative (dg, 'w') print (visited)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.50 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Code class Graph def initself directedFalse selfgraph selfdirected directed def added...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


