3. The ABC Company has two manufacturing plants on opposite sides of India. Each of these plants produces the same two products and then
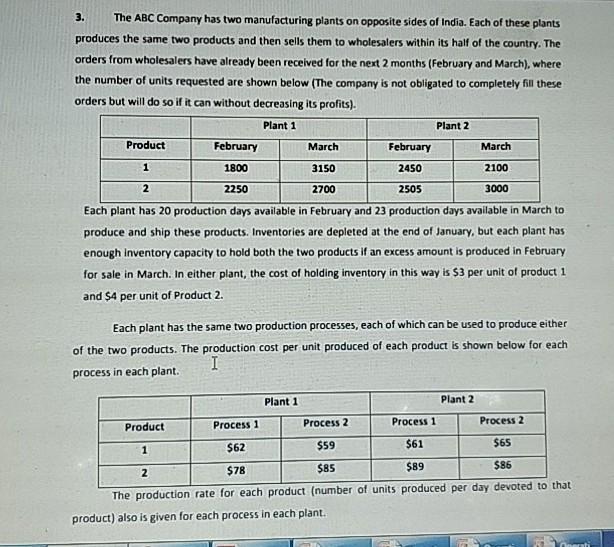
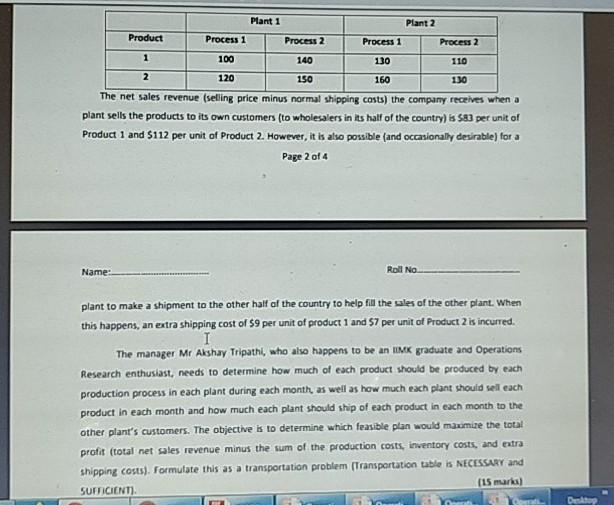
3. The ABC Company has two manufacturing plants on opposite sides of India. Each of these plants produces the same two products and then sells them to wholesalers within its half of the country. The orders from wholesalers have already been received for the next 2 months (February and March), where the number of units requested are shown below (The company is not obligated to completely fill these orders but will do so if it can without decreasing its profits). Plant 1 Plant 2 Product February March February March 1 1800 3150 2450 2100 2250 2700 2505 3000 Each plant has 20 production days available in February and 23 production days available in March to produce and ship these products. Inventories are depleted at the end of January, but each plant has enough inventory capacity to hold both the two products if an excess amount is produced in February for sale in March. In either plant, the cost of holding inventory in this way is $3 per unit of product 1 and $4 per unit of Product 2. Each plant has the same two production processes, each of which can be used to produce either of the two products. The production cost per unit produced of each product is shown below for each process in each plant. Plant 1 Plant 2 Product Process 1 Process 2 Process 1 Process 2 $62 $59 $61 $65 1 $78 $85 $89 $86 The production rate for each product (number of units produced per day devoted to that product) also is given for each process in each plant. Plant 1 Plant 2 Product Process 1 Process 2 Process 1 Process 2 100 140 130 110 2 120 150 160 130 The net sales revenue (selling price minus normal shipping costs) the company receives when a plant sells the products to its own customers (to wholesalers in its half of the country) is S83 per unit of Product 1 and $112 per unit of Product 2. However, it is also possible (and occasionally desirable) for a Page 2 of 4 Name: Roll No. plant to make a shipment to the other half af the country to help fil the sales of the other plant. When this happens, an extra shipping cost of $9 per unit of product 1 and $7 per unit of Product 2 is incurred. The manager Mr Akshay Tripathi, who also happens to be an IMK graduate and Operations Research enthusiast, needs to determine how much of each product should be produced by each production process in each plant during each month as well as how much each plant should sell each product in each month and how much each plant should ship of each product in each month to the other plant's customers. The objective is to determine which feasible plan would maximize the total profit (total net sales revenue minus the sum of the production costs, inventory costs, and extra shipping costs). Formulate this as a transportation problem (Transportation table is NECESSARY and (15 marks) SUFFICIENT). Dektop
Step by Step Solution
3.26 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


