Question: 3:02AM Sat Mar 9 eoe ;e 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf @) IS SR8 B AN 1.1 a. Put in two words: A train moves



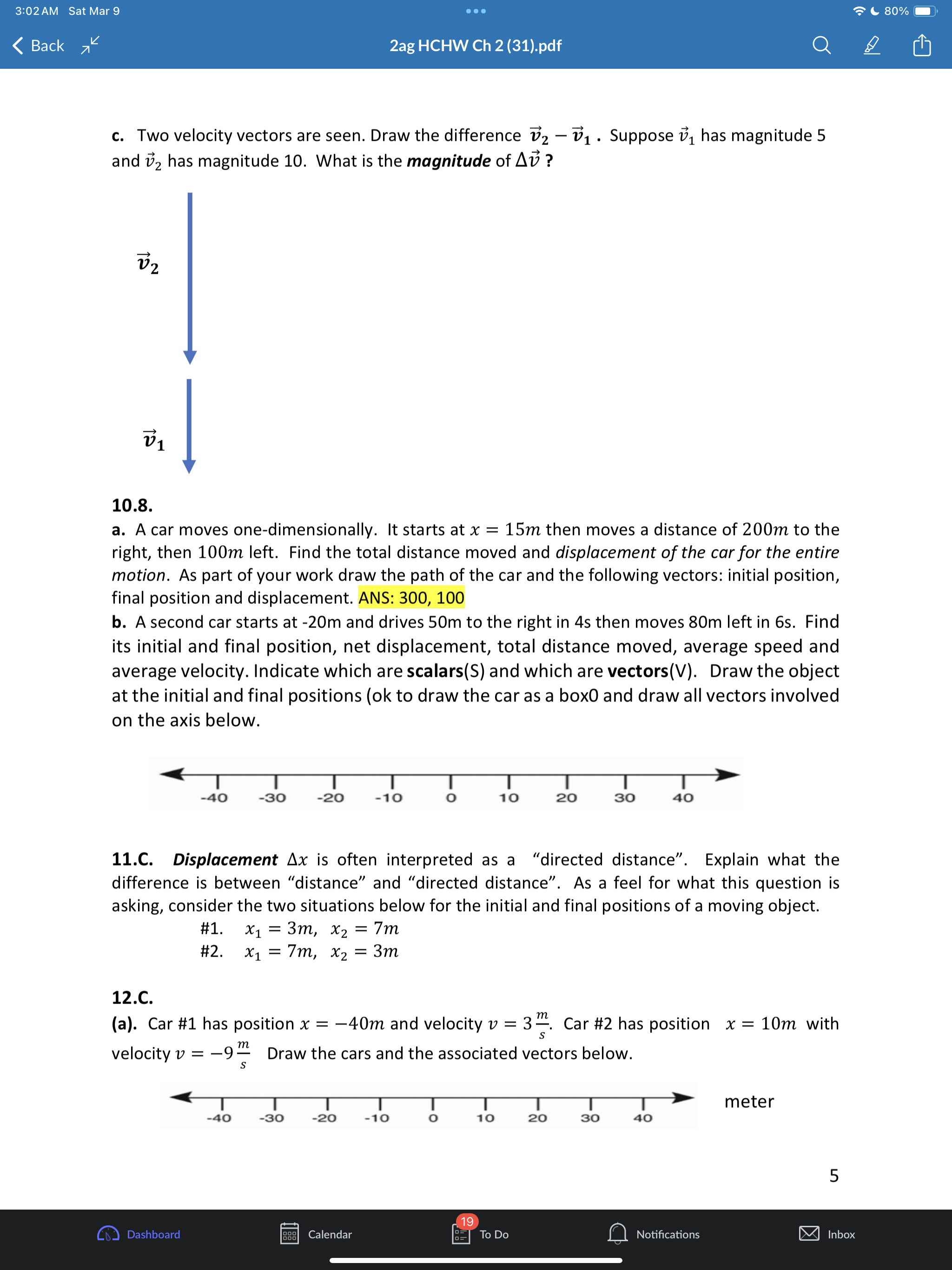

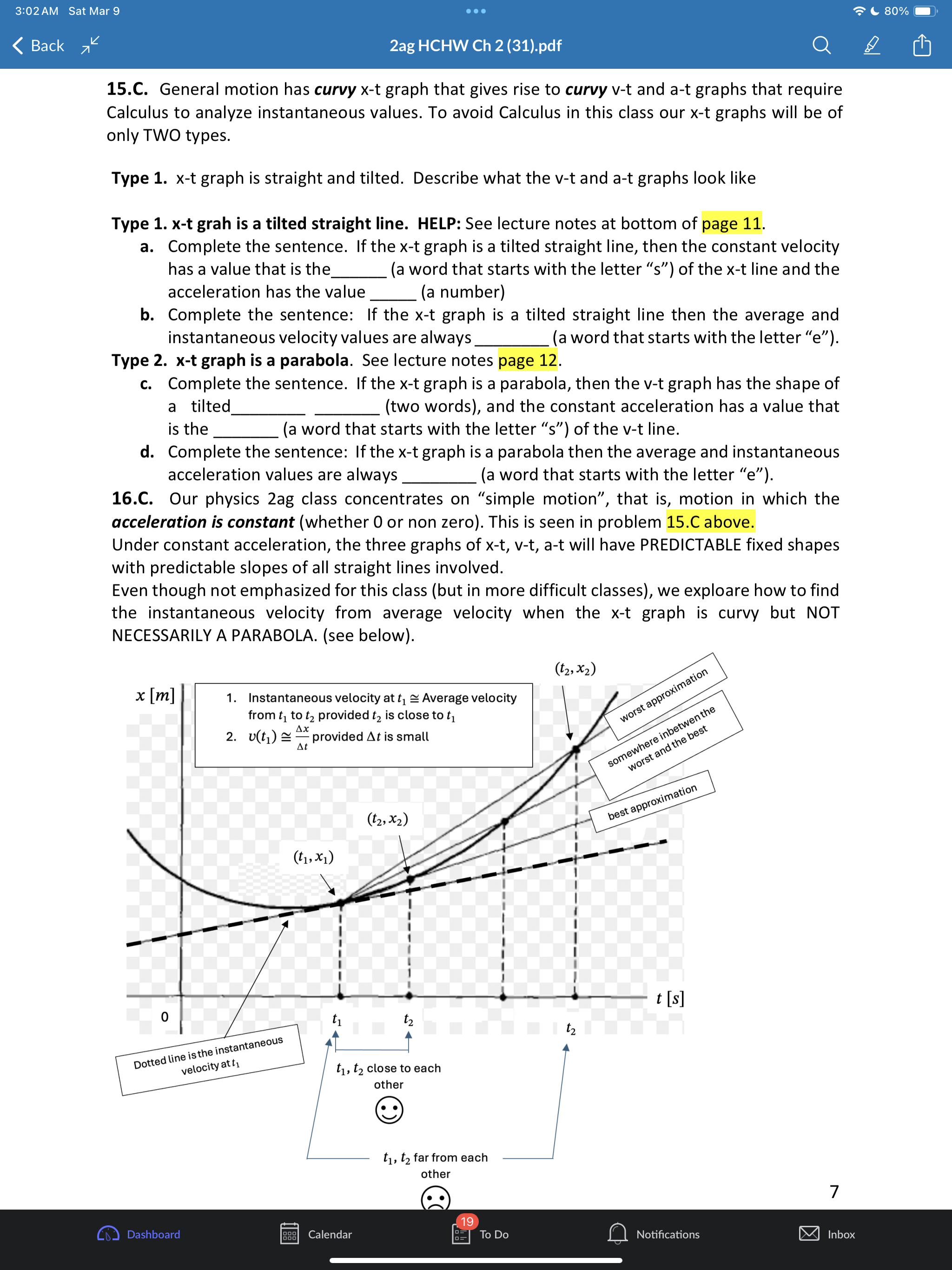
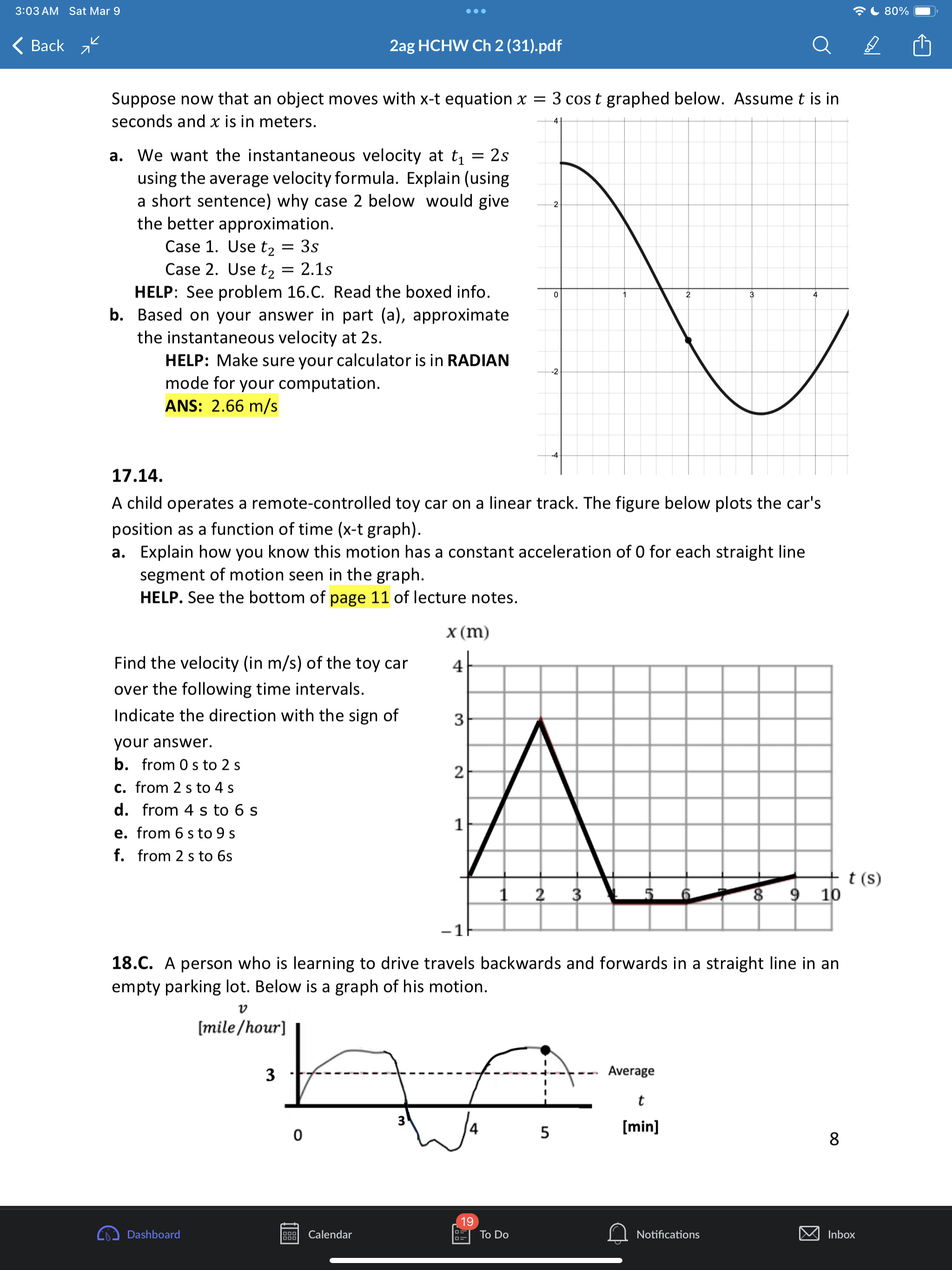
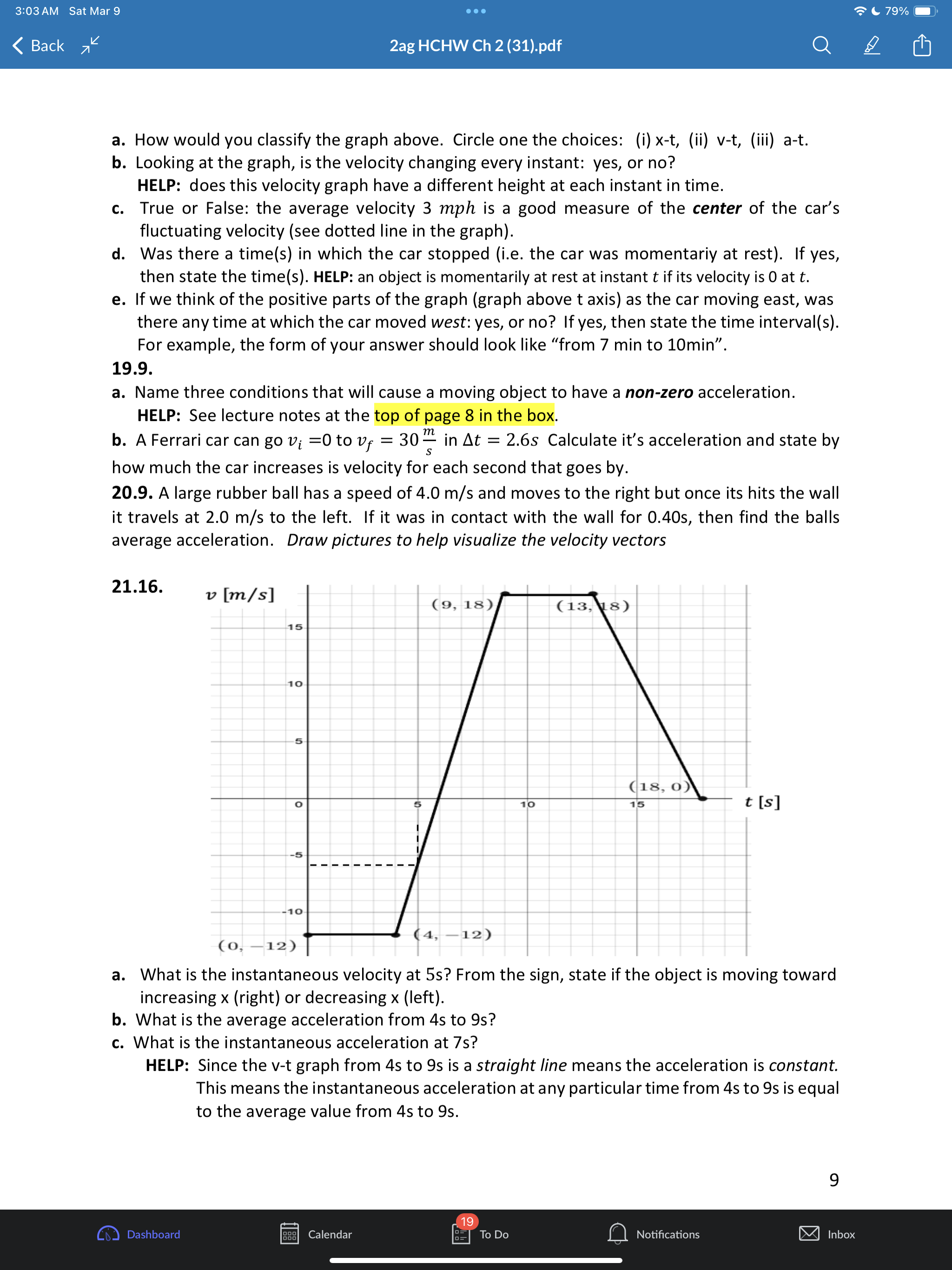







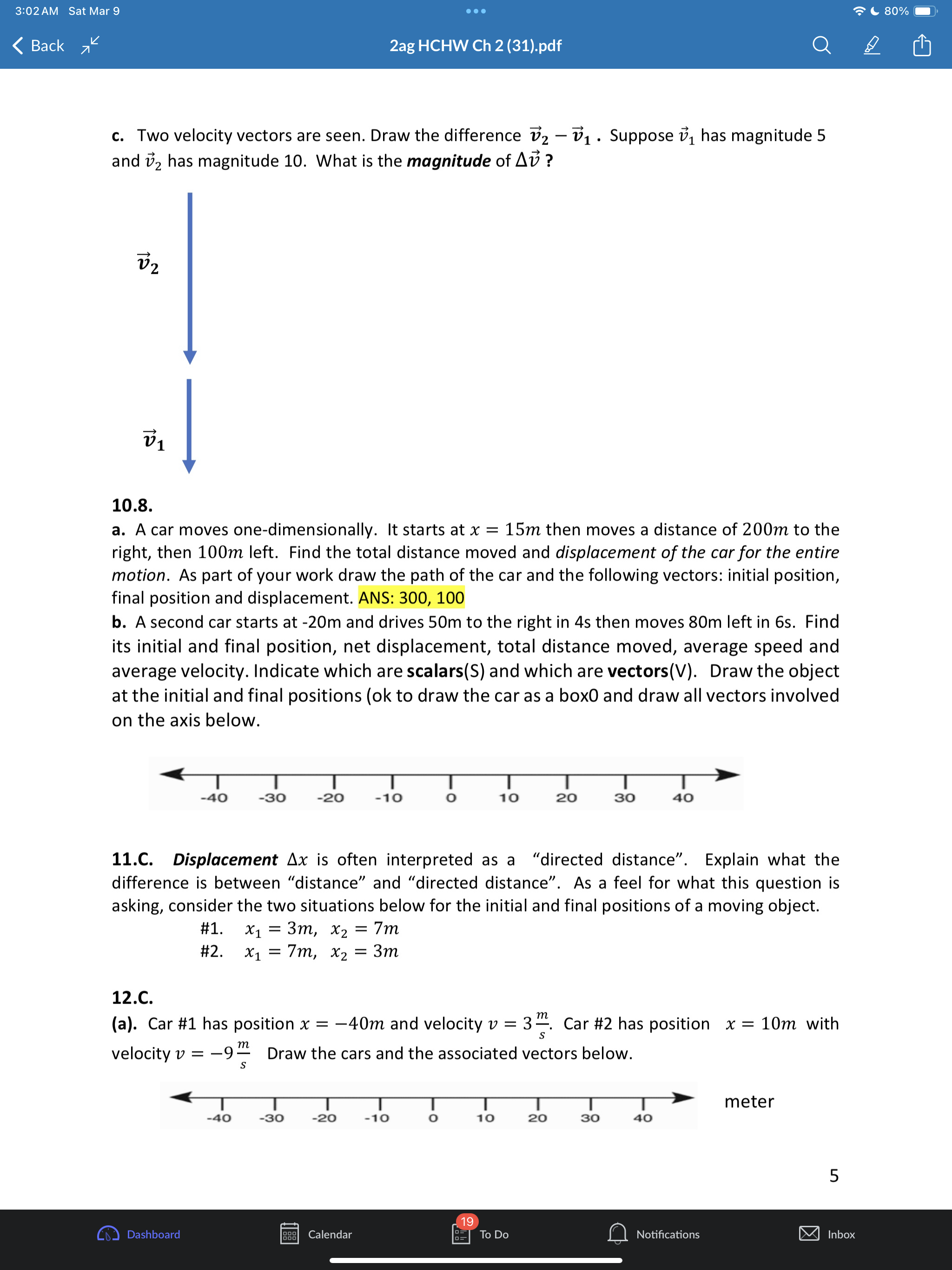

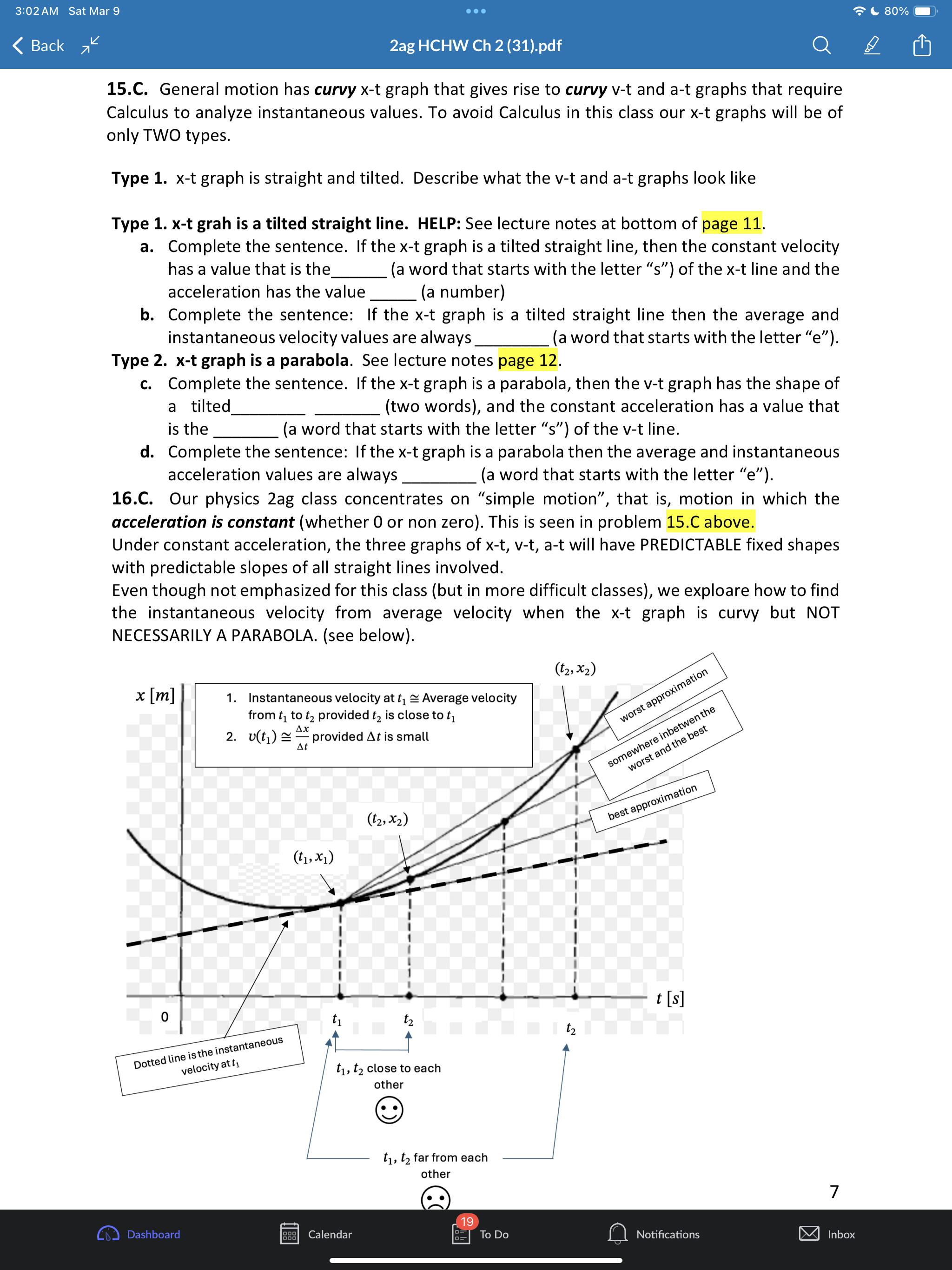
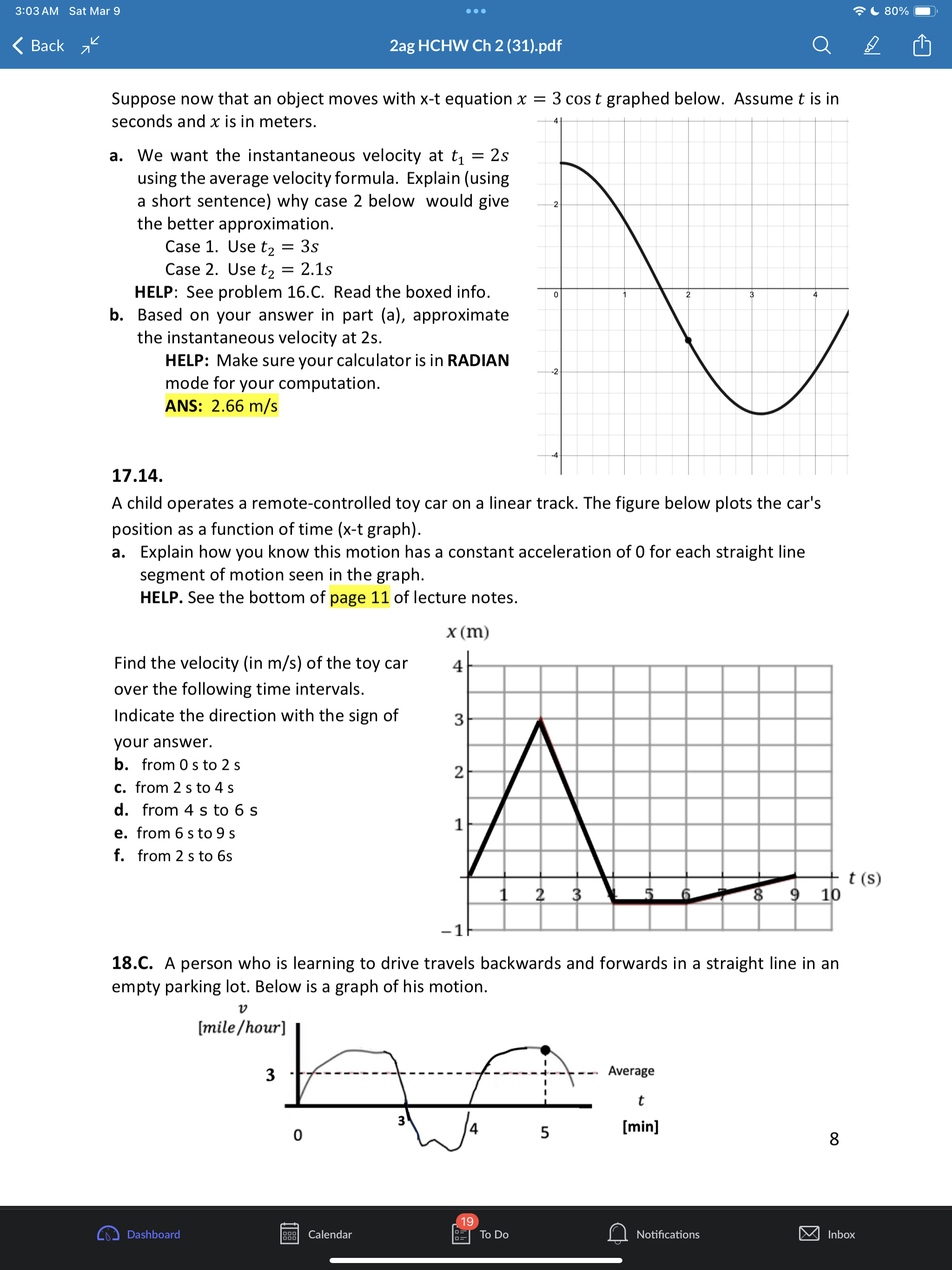
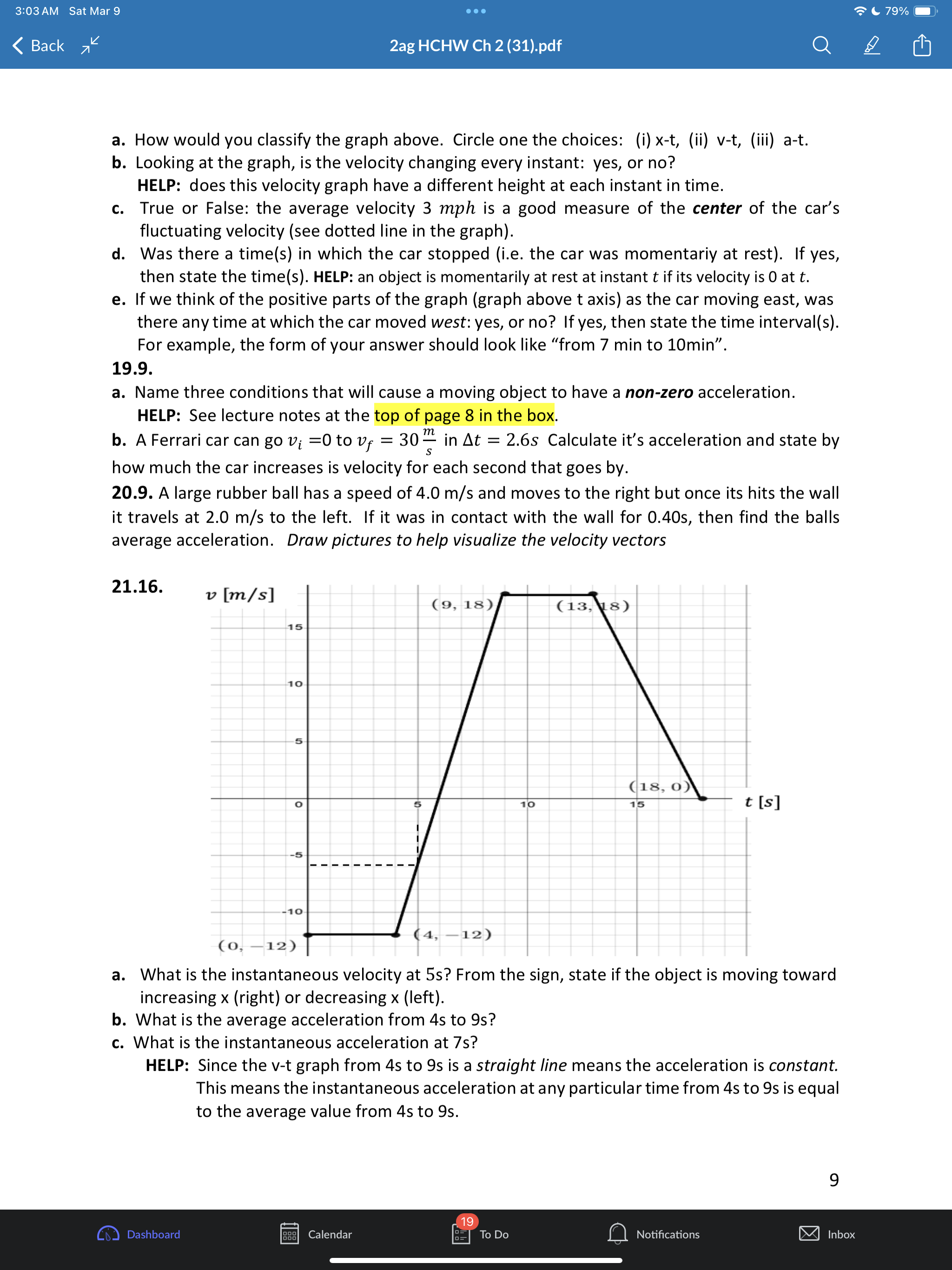




3:02AM Sat Mar 9 eoe ;e 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf @) IS SR8 B AN 1.1 a. Put in two words: A train moves with one-dimesional motion. This means along the x-axis below the train can either move or b. Draw the postion and velocity vector for each train above. c. How you draw the size of the velocity vector of each train is unrelated to the size of each position vector. Explain why. Give a short sentence as your answer. ANS: the position vectors have units of distance like meters but the velocity vectors have units of distance over time like meters per second. 2.2. a. A dogis running. If its velocity vector component is v = 0.4% then which picture of the dog is correct if using the standard orientation of the axis (seen below) where postive is to the right. T 1T T T T 71 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 #1 H#2 b. Ifits velocity vector componentis v = 0.4? then which picture is correct if using the non- standard axis seen below where postive is now to the left. 3 2 1 o -1 -2 -3 c. If a physics student says a cat's speed is |[v| = 0.4 % Explainin a short sentence why you don't know if the cat is moving left or right. d. A dog moves with initial position x; = 2m with net displacement Ax = 5m. Draw the initial and final position vectors (arrows) of the dog below. HELP: recall that postion vectors are drawn with their tail at the origin and tip at the location of the object. The dog must have final postion x, = =7m -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Q Notifications 3:02AM Sat Mar 9 Goo = 80% W) & 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf Oy N e. Suppose a dog moved so that its initial postion was x = +1m and the magnitude of its displacement vector was |[Ax| = 5m. Explainin a short setence why you don't know if the dog's final position is - 4m or + 6m. 3.3. a. The dog seen below moves with velocity v = 1.5 % Put a number in the first blank and a word in the second: It's speed is m/s and its direction is . Assume the standard orientation of the axis where postive is the right. b. Suppose also that a cat moves with velocity v = 3.0 % Draw the velocity vector on each animal below and comment on the drawing scale: i.e., how much longer is the cat's velocity vector compared to the dogs? S \"-\\ 3 - 3 = W 4.4, A quick way to see if a variable n represents a vector component or a scalar is to add the phrase \"in the direction east\" and see if that sentence makes sense. Do that to each below and state if the variable represents a scalar or vector a. A force of F = 10 lbs was applied to the brick b. Juan drank V = 2 Liters of Pepsi. 5.C. B > _ feet -10 o 10 20 30 40 S50 The jogger moves from point A to point B. Assume distance units of feet [ft] a. Onan axes with no numbers you will often see a + and/or symbol at the end of the axis like > What purpose does the + sign serve? Explain in a short sentence. HELP: See problem 2.2a,b. b. In the diagram above, what is the jogger's initial position? c. What is the jogger's final position? d. What is his displacement? e. What distance did he move? f. Draw both position vectors and the displacement vector in the picture above. HELP: the displacement vector has its tail at the initial position and tip at the final position. 6.C. a. Some quantities in physics are not just numbers but are considered a geometric arrow (having both a size and direction). These quantities are called Q Notifications 3:02AM Sat Mar 9 (XY} & 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf @] G I3 PN b. Physics quantities that are not arrows (i.e., don't have a direction) are called c. Classify each as a scalar (S) or vector (V) (i) position (ii) displacement (iii) time (iv) distance (v) velocity (vi) speed (vii) acceleration 7.C. a. When you add two vectors you get another vector: yes or no? b. When you subtract two vectors you get another vector: yes or no? c. Given the coordinate system below where increasing numbers are to the right and decreasing numbers are to the left, any vector component that has a negative value must point left or right? - + 8 B8 -7 -6 - 5 6 7 8 9 10 - 5 4 3 2 14 0 1 2 3 4 10 d. Ifavector has a positive component, then which way does it point for the axis above? e. The magnitude of a vector means its size. Size is always a positive number. The magnitude of any one-dimensional vector can be found by taking its absolute value: yes, or no? ANS: yes. f. What is the quick name given to \"the magnitude of the velocity vector\". HELP: it starts with the letters. 8.6. a. Draw the addition of the two force vectors on a separate sheet: this is called the net force or total force fnet = f')l + f')z. HELP: Use the tail-to-tip drawing rule - = F, F _ b. Suppose l has size 6 and z has size 2. What is the size of Fnet? HELP: recall that the size of a vector is called its magnitude and is always a positive quantity. c. Two momentum vectors are seen below. Draw net = 171 + }72 on a separate sheet d. Suppose p; has size 8 and p, has size 4. What is the size (positive) of Ppe;? 9.6. a. Two position vectors are seen. Draw the displacement , , on a separate sheet. HELP: Use the tip-to-tip drawing rule X A Xy b. Suppose ; has magnitude 6 and X, has magnitude 2. What is the magnitude of AX = X, , 19 Calendar Q Notifications 3:02AM Sat Mar 9 LX) ISR G B & 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf Oy N c. Two velocity vectors are seen. Draw the difference , , . Suppose #; has magnitude 5 and , has magnitude 10. What is the magnitude of AU ? V1 10.8. a. A car moves one-dimensionally. It starts at x = 15m then moves a distance of 200m to the right, then 100m left. Find the total distance moved and displacement of the car for the entire motion. As part of your work draw the path of the car and the following vectors: initial position, final position and displacement. ANS: 300, 100 b. Asecond car starts at -20m and drives 50m to the right in 4s then moves 80m left in 6s. Find its initial and final position, net displacement, total distance moved, average speed and average velocity. Indicate which are scalars(S) and which are vectors(V). Draw the object at the initial and final positions (ok to draw the car as a box0 and draw all vectors involved on the axis below. -40 -30 -20 -10 o 10 20 30 40 11.C. Displacement Ax is often interpreted as a \"directed distance\". Explain what the difference is between \"distance\" and \"directed distance\". As a feel for what this question is asking, consider the two situations below for the initial and final positions of a moving object. #1. x,=3m, x, =7m #2. x1 =7m, x5, =3m 12.C. (a). Car #1 has position x = 40m and velocity v = 3%. Car #2 has position x = 10m with velocity v = 9% Draw the cars and the associated vectors below. meter -40 -30 -20 -10 o 10 20 30 40 k) Calendar U To Do Q Notifications @ 11194 3:02AM Sat Mar 9 LX) ISR G B & 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf Oy N (b). How much longer should car #2's velocity be drawn compared to car #1? (c). Explain why you can't compare a position vector's size to a velocity vector's size. 13.C. Suppose remote-control toy car can move backward/forwards according to the equation x = 2t3 5t% where position is in [m] and time in [s] a. True or false: the t variable in this equation is an \"instant\" of time and can be any real number like 0, 0.3s, 2s, 3.86s, or 11.774s. b. Compute the car's average velocity from Os to 3s Ax HELP: Uavg = E 14.E. Average velocity is always computed between two instants in time (called a time interval) whereas instantaneous velocity is always computed at one instant in time. We explore how these two (average versus instantaneous) are related below. Instantaneous velocity v: how is it different than average velocity v,,,, 1. Average velocity V4 is always computed between two times ty, t; 2. Instantaneous velocity v is the velocity at one instant in time t; and is approximately equal to the average velocity if the time interval At = t, t; is small. v(t1) = Vgpg When t; is close to t; approximately equal to In a physics experiment a toy car moves with position function x(t) = 0.15 a l_'_l function notation Fill out the two tables below (the first row is done for you already) m | mtonuos | assms 18 75 ' Vgapg from 1sto 2s Vgang from 1sto 1.5s Vang from 1sto 1.1s Vapg from 1s to 1.01s What is the best approximation to the car's instantaneous velocity at 1s? ANS: 0.45 Q Notifications 3:02AM Sat Mar 9 eoe ;e 2ag HCHW Ch 2 (31).pdf @] Gl O Z8 B AN 15.C. General motion has curvy x-t graph that gives rise to curvy v-t and a-t graphs that require Calculus to analyze instantaneous values. To avoid Calculus in this class our x-t graphs will be of only TWO types. Type 1. x-t graph is straight and tilted. Describe what the v-t and a-t graphs look like Type 1. x-t grah is a tilted straight line. HELP: See lecture notes at bottom of page 11. a. Complete the sentence. If the x-t graph is a tilted straight line, then the constant velocity has a value that is the (a word that starts with the letter \"s\") of the x-t line and the acceleration has the value (a number) b. Complete the sentence: If the x-t graph is a tilted straight line then the average and instantaneous velocity values are always (a word that starts with the letter \"e\"). Type 2. x-t graph is a parabola. See lecture notes page 12. c. Complete the sentence. If the x-t graph is a parabola, then the v-t graph has the shape of a tilted (two words), and the constant acceleration has a value that is the (a word that starts with the letter \"s\") of the v-t line. d. Complete the sentence: If the x-t graph is a parabola then the average and instantaneous acceleration values are always (a word that starts with the letter \"e\"). 16.C. Our physics 2ag class concentrates on \"simple motion\3:03 AM Sat Mar 9 . . . 80%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


